Learning how to train teams on new SOPs is one of the most crucial steps for ensuring efficient and effective processes.
Understand with us the steps you must follow to train employees for SOP, the critical factors of success and how to measure effectiveness of the training.
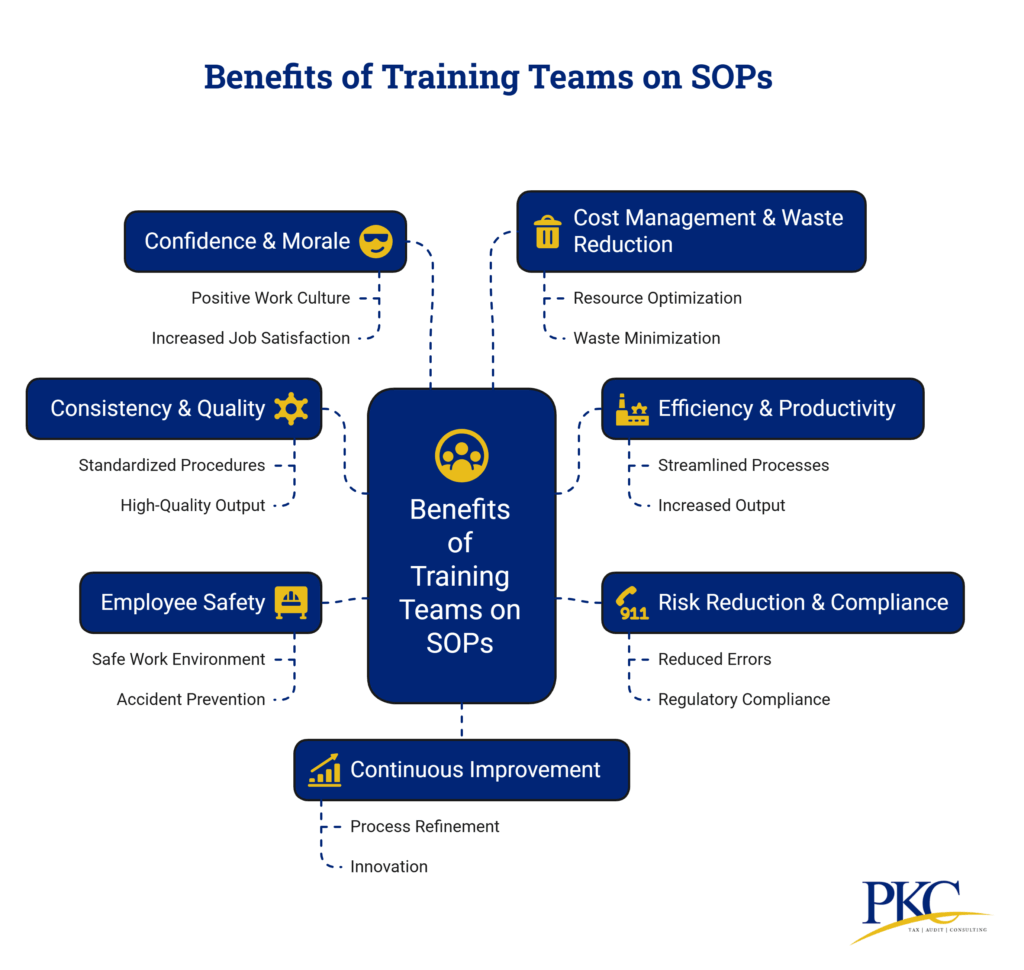
Why Training Teams on New SOPs Matters
Training teams on new SOPs is an important investment. Here’s why training your team on new SOPs is essential:
1. Ensures Consistency & Quality: Training standardizes processes, minimizing errors and ensuring high-quality outputs.
In sectors like healthcare and manufacturing, any deviation from SOPs can lead to product defects or safety hazards.
Example: In manufacturing, untrained staff on safety checks can result in defective products, damaging safety and brand reputation.
2. Boosts Efficiency & Productivity: Proper training helps employees perform tasks more quickly and accurately, reducing delays and bottlenecks.
Everyone knowing their role speeds up workflows.
Example: Trained retail teams can restock shelves 30% faster, reducing labor costs.
3. Reduces Risk & Ensures Compliance: Sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing have strict regulations.
SOP training ensures compliance, reducing the risk of legal violations and penalties.
Example: Untrained staff in healthcare on HIPAA procedures could result in data breaches and costly fines.
4. Improves Employee Safety: Training on updated safety SOPs reduces workplace accidents.
Employees become aware of protocols like proper PPE use, preventing safety issues.
Example: Failing to train staff on PPE protocols in chemical handling can result in hazardous exposure.
5. Enhances Employee Confidence & Morale: Clear understanding of roles and procedures boosts employee confidence, reduces mistakes, and improves job satisfaction.
Result: A well-trained team requires less supervision, fostering a positive work environment.
6. Supports Cost Management & Reduces Waste: Training minimizes costly errors, waste, and inefficiencies. Employees who follow SOPs reduce the need for rework and save resources.
Example: In customer service, training staff on complaint resolution improves retention and reduces follow-ups.
7. Supports Continuous Improvement: Training creates a feedback loop, allowing employees to suggest process improvements, helping the organization evolve.
Example: An employee’s idea to improve a process during training can streamline workflows for everyone.
Training Teams on SOPs: Step By Step Guide
Training teams on new Standard Operating Procedures can be complex, but with proper plan and execution, it can help enhance efficiency, compliance, and team engagement.
Here are the key phases and often overlooked tactics you must adopt:
Phase 1: Pre-Training Foundation
Step 1: Audit Your Current SOPs
Often, organizations train on SOPs that haven’t been tested leading to confusion and errors.
So, before diving into training, assess existing SOPs to ensure they are ready for instruction.
- Mapping: map SOPs to current workflows, and adjust as needed. Create 1-page visual summaries with color-coded key steps.
- Review Readability: Make sure language is clear and simple enough for employees to understand.
- Test Completeness: Walk through each SOP yourself to check missing steps, unclear instructions, or assumptions.
- Check Relevance: Make sure that all references are up-to-date and that outdated procedures are removed.
- Validate Accuracy: Confirm that every step leads to the intended outcome.
Step 2: Identify Learning Styles and Skill Gaps
Not all employees learn the same way, so it’s critical to assess their learning preferences and proficiency levels.
- Skills Assessment: Identify knowledge gaps and current competencies.
- Survey Preferred Learning Methods: Ask your team whether they prefer visual, hands-on, or reading-based learning.
- Map Competencies: Align team skill levels with the required SOP proficiency.
Phase 2: Design the Training Program
Step 3: Create Multi-Modal Training Materials
Don’t rely solely on written SOPs. Diversify your training approach to cater to various learning styles.
- Visual Aids: Use flowcharts, screenshots, or process maps to simplify complex procedures.
- Video Demonstrations: Record step-by-step videos of complex procedures.
- Quick Reference Cards: Provide laminated cheat sheets for on-the-job use.
- Interactive Elements: Incorporate quizzes, decision trees, and scenarios for deeper engagement.
Step 4: Structure Progressive Learning
Training everything at once overwhelms employees and dilutes the learning process.
Break down your training into manageable phases.
- Foundational Concepts First: Start with an overview before diving into the details.
- Crawl, Walk, Run: Begin with basic execution, progress to variations, and finish with troubleshooting.
- Create Prerequisite Maps: Ensure that employees master foundational SOPs before tackling more advanced ones.
Phase 3: Delivery and Practice
Step 5: Use the “I Do, We Do, You Do” Method
This approach allows employees to learn progressively:
- I Do: Trainer demonstrates the procedure while explaining the rationale.
- We Do: Trainee executes the task with real-time coaching.
- You Do: Trainee independently completes the procedure while the trainer observes.
- Solo Execution: Finally, trainee performs the SOP without supervision.
Step 6: Implement Scenario-Based Training
Focusing only on the ideal situations leaves employees unprepared for common real-world complications.
Prepare employees for real-world challenges by simulating error-prone situations.
- Error Scenarios: In hands-on drills, intentionally insert common errors. Let teams find/fix them.
- Edge Cases: Train employees on handling out-of-the-ordinary situations, such as unusual customer requests.
- Integration Points: Demonstrate how the SOP interacts with other processes.
- Escalation Triggers: Teach when to escalate issues to a supervisor.
Step 7: Establish Peer Learning Systems
Leverage your experienced employees to enhance the training process.
- Buddy Assignments: Pair new hires with seasoned team members for hands-on guidance.
- Rotating Teaching: Allow team members to teach SOPs to one another, promoting ownership and deeper understanding.
- Cross-Training Circles: Create small groups where employees can master various SOPs and teach others.
Phase 4: Validation and Certification
Step 8: Create Competency Assessments
Test employees in real-world scenarios to ensure they can apply SOPs effectively.
- Practical Demonstrations: Employees must complete tasks while demonstrating SOP adherence.
- Situational Judgment: Present scenarios that require applying SOPs to make decisions.
- Quality Checks: Assess the quality of the work produced, not just completion.
- Time Benchmarks: Measure how efficiently employees can complete tasks.
Step 9: Implement Graduated Certification
Simply using a pass/fail model ignores the varying levels of mastery employees may achieve.
Recognize different levels of competency through staged certification.
- Basic Certification: Employee can execute procedures with supervision.
- Independent Certification: Employee can execute without supervision.
- Advanced Certification: Employee can troubleshoot and train others.
- Expert Certification: Employee can improve and modify procedures.
Phase 5: Reinforcement and Maintenance
Step 10: Schedule Regular Refresher Training
To ensure SOPs remain ingrained in the workforce, periodic reinforcement is key.
- Quarterly Reviews: Conduct brief refresher sessions on critical procedures.
- Annual Deep Dives: Review all SOPs in depth at least once a year.
- Incident-Triggered Training: Provide additional training after mistakes or near-misses.
- Update Training: Train staff immediately when SOPs change.
Step 11: Create Feedback Loops
Treating training as a one-time event, rather than an ongoing process, leads to lost knowledge and increased errors over time.
Continuous feedback is essential for improvement.
- Employee Input: Conduct surveys to gather feedback on SOP clarity and effectiveness.
- Performance Data: Track error rates, task completion times, and quality metrics.
- Supervisor Observations: Provide structured observation and feedback to improve adherence.
- Customer Feedback: Use external feedback to identify process gaps.
- Track “Red Flag Ratio”: Monitor the ratio of questions/errors to SOP executions. A rising ratio signals needed revisions.
Critical Points Often Missed When Training Teams on SOPs
Let’s take a look at some of the most important points oorganisations often miss.
Document Everything:
Keep written records of all training sessions, questions asked, answers given, and feedback from employees.
Example: Create a training log that shows who attended, what they asked about, and any confusion that came up.
Address the “Why” Not Just the “How”: Don’t just tell people what to do, explain why it matters for safety, quality, or business success.
Example: Instead of just saying “wash hands for 30 seconds,” explain “washing hands for 30 seconds removes 99% of germs that could contaminate our food products.”
Plan for Resistance
Expect that some experienced workers will push back against new procedures and have a plan to handle it.
Example: A 20-year employee might say “We’ve always done it this way and it works fine.” Be ready with data showing why the new way is better.
Create Accountability Systems
Set up ways to check if people are actually following the SOPs after training, not just during it.
Example: Random spot checks, monthly reviews, or buddy systems where employees check each other’s work.
Make SOPs Easily Accessible
Put procedures where people can find them quickly when they need them during work.
Example: QR codes on equipment that link to digital SOPs, or laminated cards that fit in tool boxes.
Lead Time Between SOP Approval and Training
Give yourself enough time to prepare good training materials and schedule sessions properly.
Example: Don’t approve an SOP on Monday and expect to train everyone by Friday. Allow 2-4 weeks for preparation.
Hierarchy-Driven Hesitation
Some employees won’t follow SOPs if their boss tells them to do something different.
Example: A supervisor says “just skip step 3 to save time” but the SOP requires it for safety. Train managers first to prevent this.
Schedule Follow-Up Training
Plan refresher sessions because people forget things over time. Example: Schedule 30-minute refresher sessions every 6 months, or whenever accident rates start going up.
Show How Departments Work Together
Explain how one department’s SOP affects other teams’ work.
Example: Show warehouse staff how their packing SOP affects shipping times, and how shipping delays impact customer service.
Give People Ways to Report Problems
Create easy ways for employees to tell you when SOPs aren’t working or need improvement.
Example: A suggestion box, monthly team meetings, or a simple online form where people can report SOP issues.
Test Understanding Before Going Live
Check that people actually understand the SOPs before they start working alone.
Example: A short quiz, practical demonstration, or having them walk through the procedure with a trainer watching.
How to Measure Effectiveness of SOP Training?
To ensure that the SOP training has been impactful, it is essential to measure its effectiveness through a range of quantitative and qualitative metrics.
Many organizations use the Kirkpatrick Four-Level Model to evaluate the effectiveness of training programs:
- Reaction: How did employees respond to the training? Did they find it engaging and valuable?
- Learning: What knowledge or skills did employees gain from the training?
- Behavior: Are employees applying the knowledge on the job? Are they following the SOP consistently?
- Results: What tangible impact has the training had on business outcomes, such as productivity, quality, or customer satisfaction?
Based on this framework and other important considerations here are some important metrics you can use:
1. Knowledge Retention and Assessment
- Use quizzes, practical demonstrations, and Q&A sessions to assess employees’ understanding.
- Compare pre-training vs post-training assessments to measure how much knowledge employees have retained.
- Track employees’ ability to explain and apply the SOPs accurately in real-world tasks.
2. Observation and On-the-Job Performance
- Directly observe employees performing tasks to verify if SOPs are being followed.
- Look for mistakes, skipped steps, or misunderstandings in real-time.
- Use supervisors or peer reviews to identify areas where employees need additional support.
3. Compliance and Adherence Monitoring
- Use checklists, audits, and compliance tracking tools to monitor SOP adherence.
- Regular spot checks help ensure employees consistently follow the SOP across teams.
- High compliance rates indicate that employees are internalizing and applying the SOP properly.
4. Error Rates, Efficiency, and KPIs
- Measure error reduction (e.g., fewer defects) and improved efficiency (e.g., reduced task completion time).
- Track KPIs such as resource waste reduction, or task accuracy before and after training.
- Improvements suggest that SOP training is enhancing operational performance.
5. Employee Feedback and Satisfaction
- Collect feedback through surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gauge employee satisfaction with the training.
- Ask about clarity, relevance, and confidence in following the SOP
- Employee insights help refine training methods and identify areas for improvement.
6. Customer or Client Impact
- Measure changes in customer satisfaction scores, service response times, or complaint rates if the SOP impacts customer-facing processes.
- Positive shifts in these metrics typically indicate that the SOP training has led to better customer service and outcomes.
7. Behavioral and Cultural Shifts
- Track reductions in unsafe practices or shortcuts that bypass SOPs.
- Measure peer coaching rates to see how often employees help each other follow SOPs.
- Regular surveys on psychological safety (e.g., employees’ comfort in reporting deviations) can highlight cultural changes toward SOP adherence.
8. Long-Term Retention, Follow-ups, and Cost-Effectiveness
- Conduct refresher training and periodic knowledge checks to ensure long-term retention and SOP application.
- Measure the employee ramp-up time for new hires to determine how quickly they adapt to SOPs.
- Evaluate ROI by comparing training costs with improvements in productivity, error reduction, and overall operational efficiency.
FAQs on How to Train Teams on New SOPs
1. How often should SOP training be done?
SOP training should be conducted whenever new procedures are introduced or updated. Regular refreshers every 6–12 months help keep teams aligned.
2. What’s the best format for SOP training?
A blended approach works best, combining workshops, online training, and hands-on practice. This keeps employees engaged and ensures better retention.
3. Who should lead SOP training sessions?
Ideally, supervisors, managers, or SOP champions should lead the training. They provide real-world context and can answer team-specific questions.
4. How to know if SOP training was successful?
You’ll know SOP training worked if employees can perform tasks correctly, consistently, and without confusion. Quizzes, audits, and observation help confirm this.
5. Can SOP training be done online?
Yes, SOP training can be delivered online using e-learning platforms, videos, and digital checklists. However, hands-on practice is still essential for certain tasks.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

