If you’re a non-resident Indian earning rent from property in India, you need to know the essentials of tax on rental income in India for NRI.
This guide breaks down the rules, compliance requirements, and deductions available, ensuring NRIs stay tax-compliant while optimizing their tax liability.
Understanding Rental Income Tax Rules for NRIs
If you’re an NRI earning rental income from property located in India, you must understand what income tax rules apply to you.
Whether you receive your rent in India or abroad, the Indian Income Tax Department considers this income taxable in India, owing to the property’s location.
Here’s are some few key rules before we delve into the details:
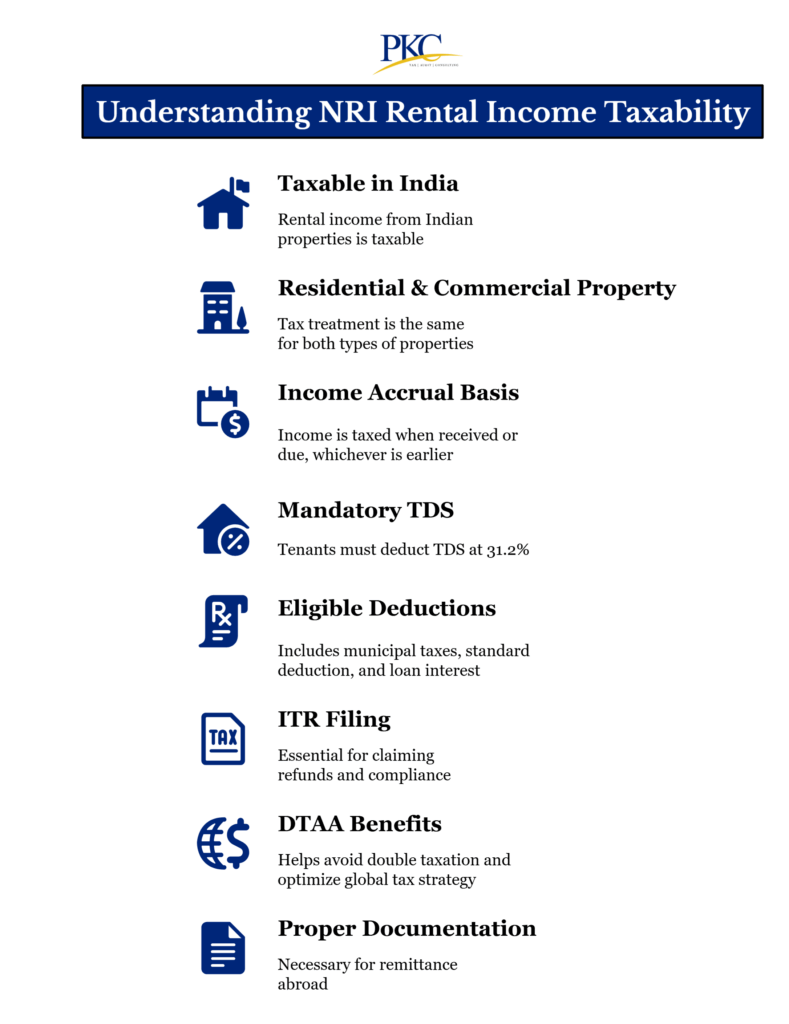
How is Rental Income Taxed for NRIs in India: Taxes & Tax Rates Applicable
Here’s a look at how NRI rental income taxation works, and what taxes are to be paid:
Income Tax
Rental income from any residential or commercial property located in India is taxable under the “Income from House Property” head of the Indian Income Tax Act.
This applies even if:
- You receive the rent in your foreign bank account.
- You are permanently residing outside India.
- The tenant is also an NRI.
Applicable Income Tax Rates for NRIs
NRIs are taxed as per regular slab rates under the old or new regime (you can choose).
Here are the old regime slabs most NRIs use to claim deductions:
| Income Slab | Tax Rate |
| Up to ₹2.5 lakh | Nil |
| ₹2.5 lakh – ₹5 lakh | 5% |
| ₹5 lakh – ₹10 lakh | 20% |
| Above ₹10 lakh | 30% |
To this add:
- Surcharge: 10%–37% depending on income level (applies above ₹50 lakh).
- Health & Education Cess: 4% on total tax (including surcharge).
TDS on Rental Income : Mandatory for NRIs (Section 195)
Unlike resident landlords, TDS is always mandatory for NRIs, under Section 195.
The tenant must deduct TDS at 31.2% (30% basic tax + 4% health & education cess) on the entire rent, regardless of the amount.
This applies from ₹1 rent onward — unlike resident landlords where TDS applies only if rent > ₹50,000/month.
Tenant’s Compliance Responsibilities
- Deduct TDS every month
- Must obtain a TAN (Tax Deduction Account Number).
- File Form 15CA (online declaration of remittance) for each rent payment.
- If annual rent exceeds ₹5 lakh, obtain Form 15CB from a CA before submitting Form 15CA.
- Deposit the TDS with the government by the 7th of the following month.
- Provide the NRI landlord with Form 16A (TDS certificate) every quarter.
Tip: Ensure your PAN is shared with the tenant; otherwise, TDS may be deducted at a higher rate under Section 206AA.
TDS Rate Applicable to NRIs on Property:
- 31.2% (30% tax + 4% cess), deducted before rent is paid to you.
- This is a flat rate, applied regardless of the rent amount.
This high TDS is just a withholding tax. Your actual tax may be lower after deductions — you can claim a refund by filing your return.
Lower or Nil TDS Certificate (Section 197)
If your actual tax liability is lower than 31.2%, you can apply to the Income Tax Department for a Lower or Nil TDS Certificate using Form 13.
Once approved, this certificate is provided to your tenant, who can then deduct TDS at the lower specified rate..
Special Cases & Considerations
Joint Ownership
- If a property is jointly owned, rental income must be split as per the ownership share in the sale deed.
- TDS applies only on the NRI’s share, not the resident co-owner’s portion.
Unrealized Rent / Arrears (Section 25B)
- If you receive rent arrears from prior years, it’s taxable in the year of receipt.
- 30% standard deduction can be claimed.
- File Form 10E to claim tax relief for income spread over multiple years.
Rental Income Paid to NRE Account
- Normally, rental income must be credited to an NRO account.
- It may be credited to an NRE account only if the tenant is an NRI and remits funds from another NRE account.
How Taxable Rental Income is Calculated for NRIs
To compute the taxable amount, follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine Gross Annual Value (GAV)
This is the higher of:
- Actual rent received or receivable in a year.
- Municipal valuation or fair market rent (in certain cases).
If the property is vacant for part of the year, GAV is calculated only for the rented period.
Step 2: Deduct Municipal Taxes
Property or municipal taxes paid during the year are fully deductible from GAV.
Only taxes actually paid during the year can be deducted.
Step 3: Apply Standard Deduction (Section 24(a))
A flat 30% deduction on Net Annual Value (NAV = GAV – municipal taxes) is allowed for repairs, maintenance, and depreciation.
No bills or documentation are needed.
Step 4: Deduct Home Loan Interest (Section 24(b))
- If you have a loan on the property, interest paid is fully deductible.
- For a let-out property, there’s no limit on the deduction amount (unlike self-occupied property).
- Pre-construction interest can be claimed in 5 equal installments starting the year the construction is completed.
Final Taxable Rental Income = GAV – Municipal Taxes – 30% Standard Deduction – Home Loan Interest
Sample Calculation Example: NRI Renting a Flat in India
Let’s say:
- Monthly rent = ₹50,000
- Annual rent = ₹6,00,000
- Municipal taxes paid = ₹20,000
- Interest on home loan = ₹1,00,000
Step-by-step:
- GAV = ₹6,00,000
- Less Municipal Taxes = ₹20,000
- NAV = ₹5,80,000
- Less Standard Deduction (30%) = ₹1,74,000
- Less Interest on Loan = ₹1,00,000
- Taxable Rental Income = ₹3,06,000
Now apply slab rates to ₹3,06,000 (if this is your only Indian income).
TDS deducted by tenant = 31.2% of ₹6,00,000 = ₹1,87,200
You file ITR and claim a refund for excess TDS.
Step-by-Step Process for Paying Taxes on Rental Income in India (For NRIs)
Here’s the full process, of paying taxes including TDS, ITR filing, DTAA, and more:
Step 1: Receive Rent in an Appropriate NRI Bank Account
- Rent should ideally be credited to your NRO account.
- If the tenant is an NRI paying from an NRE account, rent can go to your NRE account.
Step 2: TDS Deduction by Tenant (Section 195)
Tenant must deduct 31.2% TDS (30% basic + 4% cess) on gross rent every month.
TDS applies even if rent is less than ₹50,000/month for NRIs.
Step 3: Maintain All Documentation
- Rent Agreement mentioning your NRI status
- Property Tax Receipts
- Home Loan Interest Certificate (if applicable)
- Form 16A (TDS proof)
- Form 15CA/CB copies
- Passport, PAN, and address proof for KYC
Step 4: Calculate Your Taxable Rental Income
This has been shown above. Once you know the taxable income, apply the correct income tax slab rates.
Remember, when income is below the threshold of income tax applicability, there is no income tax, but TDS of 31.2% is still deducted.
Step 5: File Your Income Tax Return (ITR-2)
As an NRI, you must file an ITR in India if:
- Your total income in India exceeds the threshold – ₹2.5 lakh (old regime) or ₹3 lakh (new)
- You want to claim a refund of excess TDS.
- You want to report losses or claim deductions like home loan interest (Section 24).
File ITR-2 online via https://incometax.gov.in
Attach the following documents:
- Form 16A
- Interest certificate
- Municipal tax proof
Deadline of submission is July 31 of the assessment year
Step 6: Claim DTAA Benefits (If Applicable)
If you’re in a country with a Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) with India:
- Claim tax credit in your country for tax paid in India
- Submit:
- Tax Residency Certificate (TRC)
- Form 10F
- Self-declaration
DTAA countries include USA, UK, UAE, Canada, Australia, Singapore, etc.
Step 7: Pay Balance Tax (If Any)
If TDS deducted is less than your actual tax liability, pay balance tax via Challan 280 on the income tax portal.
If TDS is more than tax due claim refund in your ITR.
Step 8: Apply for Lower/Nil TDS Certificate (Optional)
If your actual tax is much lower than 31.2%:
- Apply for Section 197 Certificate
- Submit to the tenant
- Tenant can deduct lower or zero TDS
Apply online through the TRACES portal.
Repatriating Rental Income Abroad (NRO to Overseas)
For NRIs earning rental income in India, repatriating the funds involves following RBI and tax regulations. Here’s how:
- Rental Income in NRO Account: As per RBI rules, rental income must be credited to a NRO account. Only after the income is in the NRO account can it be repatriated abroad.
- Tax Compliance: Ensure tax obligations are fulfilled before repatriation. The tenant must deduct 30% TDS and provide a Form 16A certificate as proof of payment.
- RBI Repatriation Limit: A maximum of USD 1 million per financial year is allowed to be repatriated from your NRO account, covering rental income, dividends, interest, etc. If you wish to exceed this limit, RBI approval is required, usually for special purposes like medical or educational expenses.
- Required Documentation:
- Form 15CA: Online declaration confirming tax payment.
- Form 15CB: A certificate from a Chartered Accountant verifying tax compliance.
- TDS Proof: Form 16A or TDS challan.
- Property Documents: Rental agreement and proof of property ownership.
- KYC: Passport, PAN, OCI/PIO card.
- Steps of Repatriation Process:
- Tenant pays rent into your NRO account (after deducting TDS).
- You file your income tax return in India, if required.
- Get Form 15CB from a Chartered Accountant.
- Upload Form 15CA on the income tax portal.
- Submit both forms and supporting documents to your bank.
- Bank processes the remittance and sends funds to your overseas account.
If the rent is paid from an NRE account by another NRI, it can be repatriated freely without restrictions or taxes.
Tax Deductions & Exemptions for NRIs on Rental Income
The Income Tax Act offers key deductions and reliefs for NRIs that can substantially lower their taxable income.
Let’s take a look at how to save taxes on rental income for NRIs:
1. Municipal/Property Taxes Paid
NRIs can deduct property taxes paid to local authorities, only when paid from the Gross Annual Value (GAV).
This reduces the total rental income and thus the tax liability..
2. Standard Deduction (Section 24a – 30%)
Flat 30% deduction on NAV is available for NRIs for maintenance and repairs. It is allowed on every let-out property, regardless of actual expenses.
This again reduces the taxable income
3. Interest on Housing Loan (Section 24b)
NRIs can claim deduction for interest paid on home loans taken for buying, constructing, or renovating property.
There’s no upper limit for rented properties. The required document is an interest certificate from the lender (bank/NBFC).
4. Pre-Construction Interest Deduction
NRIs can claim deduction on interest paid before property construction is completed, spread over 5 equal installments, starting from the year construction is finished.
You will need an interest certificate from the lender + proof of construction completion year.
5. Joint Ownership Advantage
If NRIs jointly own a rented property, rental income is split as per ownership share, and each co-owner can claim deductions separately under Sections 24(b) and 80C.
This helps in reducing taxable income and staying in lower tax slabs.
Even a 50–50 split with a spouse can lead to significant tax savings.
6. Lower or Nil TDS Certificate (Section 197)
By default, 31.2% TDS is deducted on gross rent paid to NRIs.
If your actual tax liability is lower, you can apply for a Lower or Nil TDS Certificate from the Income Tax Department under Section 197 to reduce or avoid excess TDS.
Helps improve cash flow and avoid refunds later.
How:
- File Form 13 on TRACES portal
- Submit to tenant once approved
- Tenant deducts TDS at approved lower rate (e.g., 10% or 0%)
This is add Subject to income Tax Approval
7. Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)
If you’re a tax resident of a DTAA country (e.g., US, UK, UAE, Canada, Australia, etc.), you can claim tax credit in your resident country for taxes paid in India.
8. Unrealized Rent or Vacancy Adjustment
If the tenant didn’t pay rent or the property was vacant, you can:
- Deduct unrealized rent from Gross Annual Value (GAV) if you made efforts to recover it.
- If the property was genuinely vacant, reduce the rental income for those months
Use reasonable expected rent as the basis, not just the actual rent received.
Deductions NRIs CANNOT Claim:
| Not Allowed | Reason |
| Self-Occupied Property “Nil” Income | NRIs can’t claim self-occupied status in India. Even vacant homes are taxed. |
| Deduction for Principal (Section 80C) via rent | Section 80C applies only if you have other taxable income in India. |
| Deduction for Insurance, Utilities, or Repairs | Not allowed unless part of NAV deduction. |
| Notional Rent on More Than One Property (for NRIs) | NRIs must report notional rent for every property not self-occupied |
FAQs – Tax on Rental Income in India for NRIs
1. Do NRIs have to pay tax on rental income in India?
Yes. If the property is located in India, the rental income is taxable in India for NRIs, regardless of where they live or where the rent is credited.
2. What is the TDS rate for rent if landlord is NRI?
Tenants must deduct 30% TDS (plus surcharge and cess, if applicable) under Section 195 before paying rent to an NRI landlord.
3. Which tax rate is applicable unless NRI landlord has a certificate stating that his total income from India is below the exemption limit?
A flat 30% TDS rate applies unless the NRI obtains a lower or nil deduction certificate from the Income Tax Department based on their total Indian income.
4. How to avoid tax on rental income in India for NRI?
You cannot completely avoid tax, but you can reduce it by claiming deductions under Section 24 (30% standard deduction, municipal taxes, and housing loan interest) and using DTAA to avoid double taxation.
5. How to calculate rental income tax for NRI?
Taxable rental income = Gross Annual Value – Municipal Taxes Paid – 30% Standard Deduction – Home Loan Interest (if any), taxed as per income tax slabs, with TDS deducted at 30% by the tenant.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

