A procurement to payment process audit empowers you to make informed purchases, manage payments efficiently, and stay compliant with tax regulations.
Here’s your complete guide to P2P process internal audit, how it’s done and a checklist to help you get started.
What is Procurement to Payment (P2P) Process & Why It Needs Auditing?
The Procurement to Payment (P2P) process is the complete, end-to-end lifecycle governing how your company buys goods or services and ultimately pays for them.
It’s the operational backbone connecting procurement, finance, and operations. Here’s a simplified flow:
⬇️A department identifies the need for goods or services
⬇️A purchase request is created and approved based on budget and policy
⬇️A vendor is selected, and a Purchase Order (PO) is issued.
⬇️The goods or services are delivered and verified against the PO using a Goods Receipt Note or Service Entry Sheet.
⬇️The supplier submits an invoice, which is matched with the PO and receipt (3-way match).
⬇️If matched, the invoice is approved; any discrepancies are resolved with the supplier.
⬇️Approved invoices are paid according to agreed terms (e.g., Net 30).
⬇️All related documents are archived for compliance and future reference.
Importance of Auditing P2P Process
- Ensure Compliance: Audits confirm correct application of GST, TDS, and other legal requirements. This helps avoid penalties, denied tax credits, and regulatory issues.
- Prevent Fraud & Loss: They detect risks like fake vendors, duplicate or inflated invoices, and unauthorized payments, while ensuring goods or services were actually received.
- Control Costs: Audits help identify and recover duplicate payments, capture missed discounts, and ensure prices match contracts, improving cost control and cash flow.
- Boost Efficiency: They reveal process delays and manual errors, support automation, and ensure accurate vendor and accounting data for smoother operations.
- Improve Reporting: Audits ensure proper expense recognition, accurate accruals, and a clear audit trail, which strengthens the reliability of financial statements.
- Protect Reputation: By ensuring timely payments and ethical sourcing, especially with MSMEs, audits help maintain trust and support responsible business practices.
Key Steps in the P2P Process Audit
The Procure-to-Pay (P2P) process in India is complex due to layered regulations, including GST, TDS, MSME mandates, and corporate governance norms.
Having a step-by-step overview of the process being followed:
1. Planning and Scoping
Begin by defining clear audit objectives such as ensuring GST compliance, preventing fraud, etc..
Conduct a risk assessment to focus on high-risk areas like vendor onboarding, non-PO transactions, and TDS misapplications.
The scope should prioritize critical business units, high-value vendors, and regulated spend categories like imports and services.
2. Process Mapping and Documentation Review
Map the entire P2P workflow, from Requisition → PO → GRN → Invoice → Payment, to understand controls and handoffs.
Review policy compliance including:
- Delegation of Authority (DOA) adherence.
- GST e-invoicing rules (especially IRN generation).
- MSME Act requirements, including the 45-day payment timeline.
3. Vendor Master Audit
Audit vendor onboarding processes to ensure:
- Valid KYC documents, PAN, GSTIN, and banking details.
- Udyam registration status for MSME classification.
- Detection of duplicate, inactive, or shell vendors — particularly those linked to employees or with irregular transaction patterns.
4. Purchase Order (PO) Compliance
Evaluate if POs follow internal approval hierarchies, e.g., CFO sign-off for purchases above ₹5 lakh.
For high-value procurement, verify evidence of competitive bidding.
Confirm inclusion of appropriate GST and TDS clauses.
5. Goods Receipt Note (GRN) Verification
Ensure the GRN matches the PO in terms of quantity and quality, and aligns with physical goods received as per warehouse records.
Watch for missing or backdated GRNs, which can signal process lapses or fraud.
6. Three-Way Matching
This core control compares the PO, GRN, and invoice. Key checks include:
- PO: Item rates, HSN code, GST rate.
- GRN: Delivery confirmation and condition.
- Invoice: Authenticity, duplicate check, bank detail match, correct TDS.
Accuracy of HSN codes is especially important for correct Input Tax Credit (ITC) claims under GST.
7. Invoice and Payment Testing
Sample invoice and payment entries for:
- GST validity (GSTIN, place of supply, 2A/2B reconciliation).
- TDS deductions under relevant sections like 194M, and timely deposit via Challan 281.
- MSME compliance, ensuring payment within 45 days to avoid steep interest penalties.
8. Exception Reporting
Identify non-PO purchases, payments processed without GRNs, or transactions exceeding approval limits.
Quantify potential financial leakage such as duplicate payments or missed early-payment discounts.
9. Compliance Deep Dive
Focus on key regulations:
- GST: Reversals, e-invoicing, return filing reconciliation.
- TDS: Alignment with Form 26Q, avoidance of late fees.
- Companies Act: Related-party transactions and arm’s-length pricing.
- FEMA: Documentation for imports, such as BOEs and FIRC.
10. Technology and Audit Trail Review
Scrutinize ERP logs for user IDs, timestamps, and edit trails. Identify backdated or unauthorized changes.
Assess automation coverage in three-way matching, invoice OCR, and alerts for control breaches.
11. Reporting and Remediation
Classify findings by risk level:
- Critical: Fraud indicators, GST/TDS non-compliance, MSME violations.
- High: Control weaknesses like lack of segregation of duties.
Propose an actionable remediation plan: automate matching, perform quarterly vendor master reviews, and run monthly reconciliation for GST and TDS.
Why Choose PKC for P2P Audits?
✅1500+ satisfied clients across diverse industries
✅Tech-enabled audit solutions with automated MIS reporting
✅End-to-end P2P process restructuring and optimization
✅Procurement cost reduction through vendor management expertise
✅Real-time compliance monitoring preventing revenue leakage
✅ERP integration specialists for seamless audit trails
✅Risk-based audit approach identifying critical control gaps
✅GST and tax compliance expertise for Indian regulations
✅Cost-effective solutions delivering measurable ROI results
Procurement to Payment Process Audit Checklist
A P2P process audit checklist can help you get the audit done efficiently. Here’s what it may look like, although it may vary with your industry and business size:
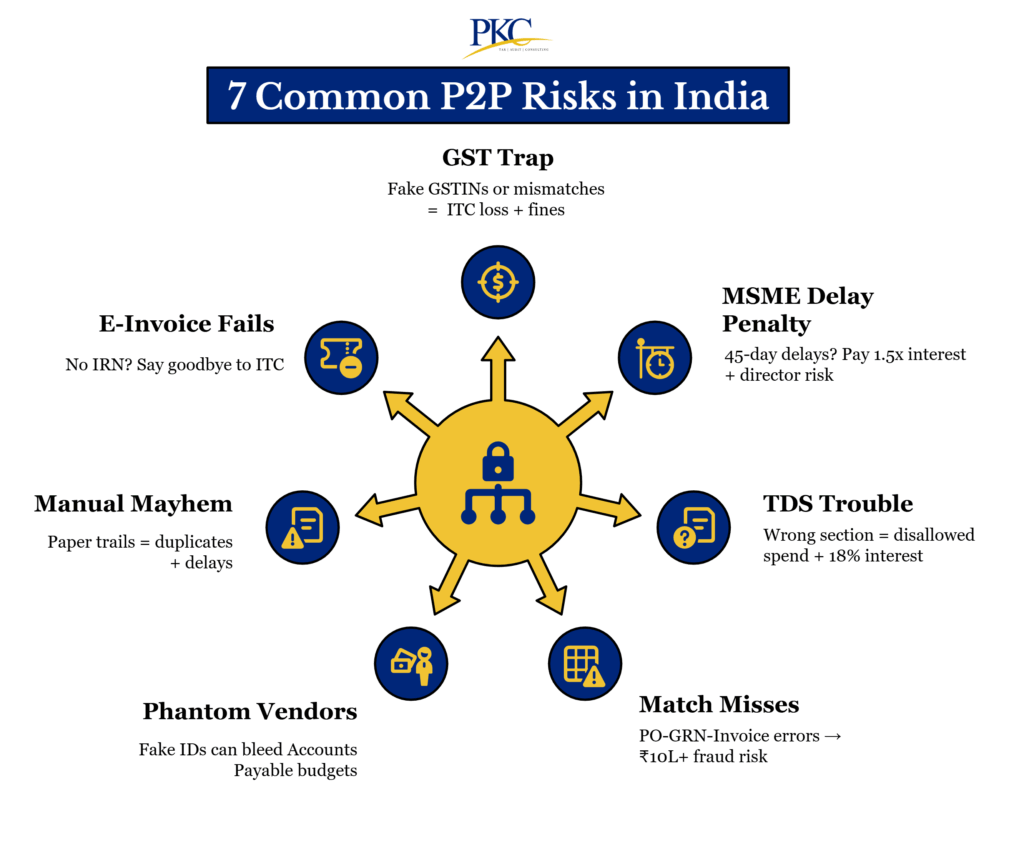
Common Red Flags in Indian P2P Process Audits in India
Here are some of the most common red flags observed in P2P process audits:
- Duplicate Vendor Entries:Multiple vendors sharing the same PAN/GSTIN or bank details indicate potential shell entities or fraud.
- Missing Purchase Orders (POs): Payments processed without a valid PO suggest uncontrolled spending and policy violations.
- Incomplete 3-Way Match: Mismatches between PO, GRN, and invoice (quantity/price/GST) risk overpayment or ineligible Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- GSTIN Validation Failures: Invalid or inactive vendor GSTINs lead to denied ITC and penalties under GST laws.
- TDS Deduction Errors: Incorrect TDS rates (e.g., Sec 194M, 194C) or delayed deposits trigger income tax penalties and disallowances.
- Late MSME Payments: Payments exceeding 45 days to MSME vendors violate the Income Tax Act (Sec 43B(h)) and attract interest liabilities.
- Manual Overrides in ERP: Unauthorized changes to PO/GRN/invoice data or backdated entries signal fraud or control breakdowns.
- Non-Compliant E-Invoices: Missing IRN (Invoice Reference Number) or mismatched e-invoice data result in GST rejection and ITC reversals.
Best Practices for an Effective P2P Audit in India
Let’s take a look at some of the best practices we recommend at PKC Management Consulting for conducting P2P process audits:
Leverage Technology & Automation
- Use AI tools for automated 3-way matching and e-invoicing (IRN) validation to reduce errors.
- Implement blockchain for secure, tamper-proof audit trails—essential for GST-compliant ITC claims.
2. Vendor Master Governance
- Conduct KYC and GSTIN checks via the GSTN portal every quarter to prevent fraud and ITC reversals.
- Flag vendors lacking Udyam registration to ensure MSME payment compliance under Section 43B(h) of the Income Tax Act.
3. Enforce 3-Way Matching
- Automate PO-GRN-Invoice checks to detect mismatches and ineligible ITC.
- Resolve all exceptions before approving payments to reduce duplicate payments.
4. Monthly GST & TDS Reconciliation
- Reconcile internal records with GSTR-2B/2A monthly to avoid ITC clawbacks and daily GST penalties.
- Verify TDS (e.g., Sec 194M) against Form 26Q before quarterly filings to avoid disallowances.
5. Real-Time Exception Monitoring
- Set alerts for non-PO spends, delayed MSME payments, or approvals exceeding limits.
- Investigate anomalies like high-value invoices from new vendors to prevent shell-company fraud.
6. Segregation of Duties (SoD) Controls
- Ensure no single employee can manage vendors, approve POs, and release payments.
- Regularly audit SoD conflicts in ERP systems to avoid override risks—common in large fraud cases.
7. MSME Payment Compliance
- Monitor invoice aging to ensure payments within 45 days, as required under the MSMED Act.
- Focus audits on MSMEs, as most delayed payments affect small suppliers (RBI, 2023).
8. Continuous Audit Trail Monitoring
- Review ERP logs bi-weekly for backdated or unauthorized edits.
- Maintain digital records for 8 years to stay compliant with GST audit requirements.
Uncover P2P inefficiencies with PKC, Call Us Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a P2P process audit in India?
A P2P audit reviews the entire process of purchasing goods and paying for them. It checks for fraud, errors, and compliance with Indian laws like GST and the Companies Act.
2. Why is auditing the P2P process important?
It helps prevent duplicate payments, fraud, and vendor kickbacks. It also makes sure all tax rules are followed properly.
3. How often should companies in India audit the P2P process?
Ideally, companies should audit P2P once a year. Larger or high-risk companies may do it every quarter.
4. What are common P2P risks in India?
Common risks include fake invoices, non-compliant vendors, and missing approvals. These can cost a company a lot if not caught early.
5. What tools can help automate the P2P audit?
Software like SAP, Tally, and Oracle can automate approvals, three-way matching, and data trails. This makes audits faster and more accurate.
6. Can small businesses do a P2P audit in India?
Yes, even small businesses should perform P2P audits. It protects their cash flow and avoids compliance issues..
7. What documents are checked during a P2P audit?
Auditors look at purchase requisitions, POs, GRNs, invoices, payment vouchers, and bank statements. These prove whether the money was spent correctly.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

