Process automation in manufacturing in India is transforming productivity, reducing costs, and boosting global competitiveness.
Learn all about trends, types, examples, and importance of process automation in manufacturing in India
What is Process Automation in Manufacturing?
Process automation in manufacturing refers to the use of technology, machinery, and control systems to perform tasks that were once performed by hand.
It aims to minimize human intervention and include using robots, software, sensors, and AI to streamline production, improve efficiency, and reduce errors.
It includes machines, software, and systems that can do things like:
Examples:
- Robotic arms assembling car parts
- Automated conveyor belts moving products without manual handling
- AI-powered quality checks detecting defects faster than humans
Importance of Process Automation in Manufacturing in India
- Boosts Productivity: Enables round-the-clock operations with minimal downtime. This significantly boosts productivity and processing capacity. Machines complete repetitive tasks faster and with higher accuracy than manual labour.
- Reduces Operational Costs: Reduce reliance on manual labour and minimize material waste. Over time, this contributes to substantial savings in labour, rework, and production costs.
- Enhances Product Quality: Improves consistency in production processes, reducing defects and variation. This results in uniform product quality and improved customer satisfaction.
- Strengthens Global Competitiveness: By improving speed, accuracy, and scalability, Indian manufacturers can better compete with global players. Automation helps meet international quality and compliance standards.
- Supports “Make in India” Vision: Advanced automation strengthens local manufacturing capabilities and attracts both domestic and foreign investments. It drives India toward becoming a global manufacturing hub.
- Enables Real-Time Monitoring & Control: With IoT and AI integration, manufacturers gain real-time insights into operations. This improves responsiveness, decision-making, and reduces downtime.
- Facilitates Scalability: Automated systems can be scaled easily with growing demand. Manufacturers can expand production without proportionately increasing workforce or infrastructure.
- Enhances Compliance & Traceability: Automated record-keeping ensures accurate documentation for audits and regulatory compliance. It also enables traceability across the production chain.
Comparison Between Traditional and Automated Manufacturing in India
| Aspect | Traditional Manufacturing | Automated Manufacturing |
| Labor | Manual work | Machine operated |
| Speed | Slower output | High speed |
| Consistency | Varies by worker | Highly consistent |
| Scalability | Hard to scale | Easily scalable |
| Cost | Higher over time | Lower long-term |
| Flexibility | Custom friendly | Less adaptable |
| Maintenance | Low tech needs | Requires upkeep |
| Data Use | Minimal tracking | Real-time insights |
| Safety | More risk | Safer environment |
| Training | Manual skills | Tech-based skills |
10 Common Types of Process Automation Used in Indian Manufacturing
Here’s an overview of the common types of process automation widely adopted in Indian manufacturing, along with their applications/ examples and benefits:
1. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs are industrial computers used to control machinery and production lines through pre-programmed logic.
They can handle harsh factory conditions while running control programs instantly, making them essential for automated manufacturing.
Example Use: Robotic welding at Tata Motors, bottling lines at Hindustan Unilever.
Benefits: Reliable, cost-effective, and easy to reprogram for evolving tasks.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based back-office tasks like data entry and invoice processing.
They can run continuously without breaks, handling large amounts of data while working with existing company software systems.
Example Use: Drug inventory in pharma (e.g., Sun Pharma), e-commerce invoicing.
Benefits: Cuts clerical errors and speeds up digital workflows.
3. Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs)
HMIs are touchscreen dashboards that allow operators to interact with and control machines visually and intuitively.
These interfaces turn complex machine data into easy-to-understand graphics, helping operators monitor processes, make adjustments, and respond to problems quickly.
Example Use: Turbine monitoring at NTPC, temperature control in food processing.
Benefits: Boosts operator efficiency and reduces manual error.
4. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
SCADA systems provide centralized control and real-time monitoring across industrial operations.
Operators are able to see entire facility operations from one control room and make smart decisions based on live information.
Example Use: Pipeline monitoring at Reliance, water treatment automation.
Benefits: Enables predictive maintenance and remote oversight.
5. Material Handling Automation
Automated systems like AGVs, conveyors, and cranes handle raw materials and finished goods movement.
They improve warehouse operations by automatically moving materials based on production schedules, reducing manual work while tracking inventory accurately.
Example Use: Amazon India’s Kiva robots, automated cranes at JSW Steel.
Benefits: Improves speed, safety, and lowers labour dependency.
6. Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
DCS manage continuous, complex industrial processes involving multiple machines and control loops.
Excellent at coordinating connected processes where timing is critical, providing backup systems and safe operations for important manufacturing environments.
Example Use: Fertilizer batch control at IFFCO, cement kiln optimization at Ultratech.
Benefits: Seamless plant integration and high precision.
7. Industrial Robotics
These are high-performance robots used in tasks like welding, painting, and heavy-duty assembly.
Modern industrial robots combine advanced sensors, smart vision systems, and precise motors to perform complex manufacturing tasks with consistency and accuracy.
Example Use: Robotic paint shops at Maruti Suzuki, PCB assembly at Samsung Noida.
Benefits: Operate 24/7 with high-speed precision.
8. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are safe, flexible robots designed to work alongside humans.
They have advanced safety sensors and easy programming, making them perfect for small-batch production and tasks requiring human-robot teamwork.
Example Use: Packaging in small food units, assembling medical devices like at Trivitron.
Benefits: Ideal for SMEs, easy to set up, and worker-friendly.
9. IoT Smart Sensors
These sensors collect real-time operational data (temperature, vibration, etc.) to enhance machine intelligence.
Enable predictive analysis by continuously monitoring equipment health and environmental conditions, feeding data to smart systems for pattern recognition and problem detection.
Example Use: Predictive maintenance at Tata Steel, soil moisture sensing in agri-manufacturing.
Benefits: Prevents breakdowns, saves energy, and improves uptime.
10. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machines
CNC machines automate the cutting, shaping, and finishing of components with micron-level accuracy.
Read digital blueprints and execute complex machining operations automatically, ensuring consistent quality while reducing material waste and production time.
Example Use: Aerospace part machining at HAL, custom jewelry by Tanishq.
Benefits: Minimizes waste, ensures repeatable precision in complex parts.
How Indian Manufacturers Can Start with Process Automation: Step By Step Guide
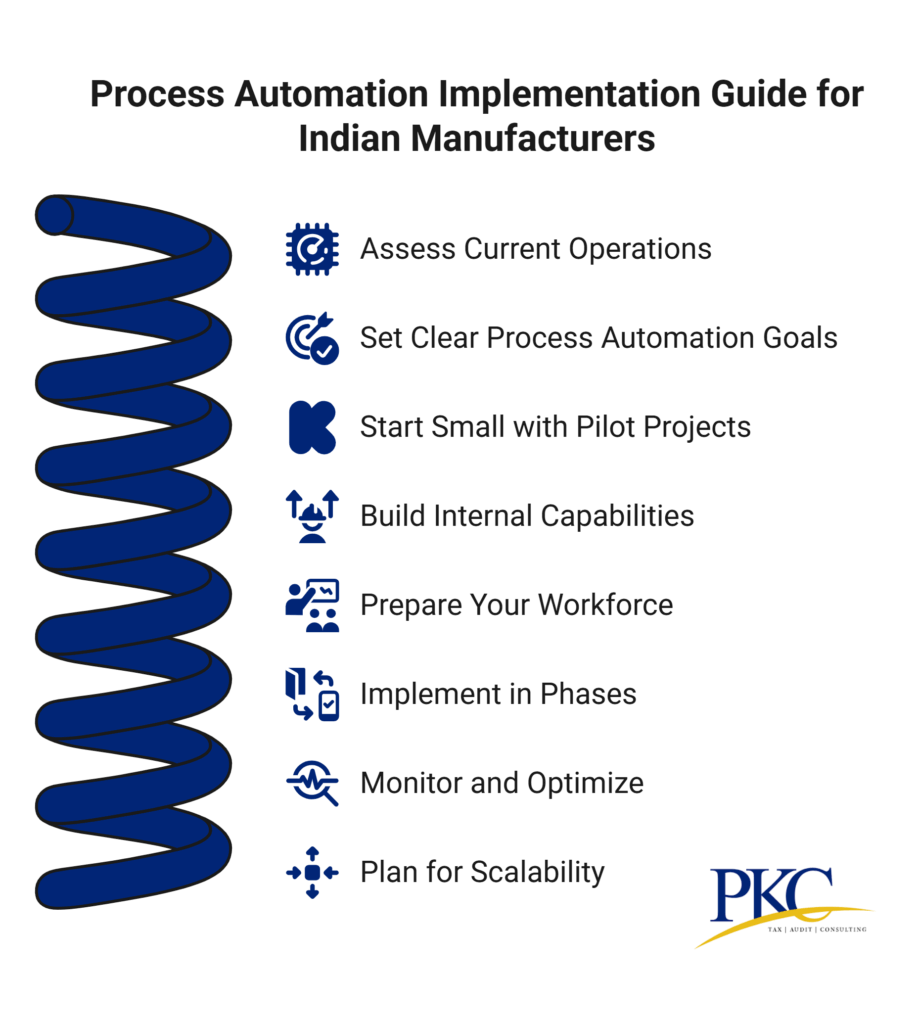
Here’s a 9 step process to implement process automation
Step 1: Assess Current Operations
Conduct a Process Audit
- Map all manufacturing processes from raw material intake to product dispatch
- Measure time for each step and identify manual, repetitive tasks
Identify Pain Points
- Look for quality issues, safety risks, or delays caused by manual work
- Focus on areas with high labour costs or frequent human errors
Step 2: Set Clear Process Automation Goals
Define specific outcomes that align with your business needs and available resources.
Common Goals:
- Reduce production time by 30-40%
- Improve product quality and consistency
- Lower labour costs in specific departments
- Increase overall equipment effectiveness
- Enhance workplace safety standards
Step 3: Start Small with Pilot Projects
Begin with a focused, low-risk automation project to test feasibility and learn.
Ideal Starting Points:
- Material handling tasks (conveyors, automated storage)
- Quality inspection processes (vision systems, sensors)
- Simple assembly operations (pick-and-place robots)
- Data entry and reporting tasks (RPA for administrative work)
Step 4: Build Internal Capabilities
Train your team and hire automation specialists like PKC Management Consulting to make the process easy.
Selection Criteria:
- Experience with similar manufacturing processes
- Local presence and support capabilities
- Training and knowledge transfer programs
- Flexible financing options
- References from other Indian manufacturers
Step 5: Prepare Your Workforce
Invest in training your employees to work with automated systems rather than replacing them entirely.
Training Focus Areas:
- Operating and monitoring automated equipment
- Basic troubleshooting and maintenance
- Data interpretation and decision-making
- Safety protocols for human-machine interaction
- Continuous improvement mindset
Step 6: Implement in Phases
Roll out automation gradually to ensure smooth integration and issue resolution.
Implementation Phases:
- Phase 1: Install and test core automation equipment
- Phase 2: Integrate with existing systems and processes
- Phase 3: Train operators and optimize performance
- Phase 4: Monitor results and make improvements
- Phase 5: Scale successful solutions to other areas
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize
Use real-time data to evaluate performance and make improvements.
Key Metrics to Track:
- Production efficiency and throughput
- Quality metrics and defect rates
- Equipment uptime and maintenance costs
- labour productivity and safety incidents
- Overall return on investment
Step 8: Plan for Scalability
Extend automation to more areas based on pilot success.
Scaling Strategies:
- Standardize successful automation solutions
- Create internal automation expertise
- Develop supplier relationships for ongoing support
- Build automation considerations into new equipment purchases
- Share best practices across different production lines
Success Tips & Mistakes to Avoid With Process Automation in Manufacturing in India
Automation can bring a number of benefits for manufacturing businesses. Here are some tips to ease the journey:
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Don’t Automate Bad Processes: Fix inefficient processes before automating them. Automation will only make bad processes consistently bad at a faster rate.
Avoid Over-Engineering: Don’t invest in complex automation for simple problems. Sometimes a basic conveyor system is better than an expensive robotic solution.
Don’t Ignore Change Management: Prepare your workforce for changes and address concerns about job security. Involve employees in the automation planning process to gain their support.
Avoid Setting Unrealistic Expectations: Don’t expect overnight efficiency gains. It can lead to disappointment. Set phased milestones (e.g., 20% productivity increase in 6 months).
Ignoring Existing Systems: Many factories forget to check if new tech works with old machines or software. This creates downtime, wasted spending, and poor performance.
Choosing the Cheapest Vendor/ Automation Partner: Cheap can become very expensive. Pick partners based on support, customization, and proven results, not just the lowest quote.
Success Tips for Indian Manufacturers
Start with government incentives: Explore schemes like PLI (Production Linked Incentive) that support automation investments.
Consider local conditions: Choose automation solutions that work well in Indian environmental and infrastructure conditions.
Focus on flexibility: Select systems that can adapt to changing product requirements and market demands.
Build internal capabilities: Develop in-house expertise to reduce dependence on external support over time.
Measure everything: Track detailed metrics to demonstrate ROI and justify future automation investments.
How Can PKC Help Manufacturers With Process Automation?
✅Dedicated onsite process excellence teams for implementation
✅Automated workflows eliminate manual handoffs completely
✅Real-time dashboards provide instant production visibility
✅Paper-less manufacturing even on shop floors achieved
✅AI-powered audit techniques identify hidden inefficiencies
✅End-to-end order-to-delivery time reduction guaranteed
✅Automated quality control and inspection processes
✅Machine throughput optimization removes production bottlenecks
✅Inventory management automation reduces dead stock
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is automation important for Indian manufacturers?
Automation helps Indian manufacturers compete globally by increasing speed, efficiency, and product quality. It also reduces labour dependency and production downtime.
2. Is automation affordable for small manufacturers?
Yes, with cloud-based tools, government incentives, and modular systems, even SMEs can start small and scale automation over time. Many affordable solutions are designed for Indian businesses.
3. Will automation reduce jobs in Indian manufacturing?
Automation may replace repetitive tasks, but it creates new jobs in programming, maintenance, and system monitoring. It also drives the need for upskilling workers.
4. What technologies are used in manufacturing automation in India?
Common technologies include robots, IoT sensors, PLCs, SCADA systems, AI, and cloud software. These tools help control and monitor production with minimal human input.
5. What are common mistakes when implementing automation in India?
Rushing automation, ignoring existing systems, and skipping worker training are major pitfalls. Poor vendor choices and unrealistic ROI expectations also cause failures.

 Expert verified
Expert verified