SOPs for manufacturing play a vital role in the success of the business. They provide a clear framework for employees to follow, reducing confusion and errors while enhancing productivity.
Learn with us why manufacturing SOPs are essential, what guides them and what kinds of SOPs do different manufactures need
What Are SOPs for Manufacturing?
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) in manufacturing are step-by-step, well structured, written instructions that outline how to correctly and consistently perform specific tasks or processes on the factory floor.
SOPs guide operators, technicians, and quality personnel on what needs to be done, how it should be done, who is responsible, and what standards must be met.
They ensure that manufacturing activities are carried out in an efficient, safe, and compliant manner.
Importance of SOPs for Manufacturing in India
As a fastest-growing manufacturing economy, India contributes significantly to both domestic consumption and global exports.
This makes SOPs critical tools for operational success, regulatory compliance, and global competitiveness:
1. Ensuring Consistency Across Operations: India’s manufacturing spans diverse states, languages, and skill levels. SOPs standardize processes, ensuring consistent product quality be it Gujarat or Tamil Nadu.
Result: Fewer defects, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced variability.
2. Improving Worker Safety and Onboarding: With a large, rotating workforce, SOPs ensure quick, repeatable training and embed safety protocols.
Result: Fewer accidents, better risk mitigation, and stronger safety culture.
3. Regulatory and Quality Compliance SOPs help manufacturers comply with bodies like FSSAI, CDSCO, BIS, and ISO standards, easing inspections and certification processes.
Result: Regulatory readiness, reduced legal risks, and increased credibility.
4. Boosting Efficiency and Cost Control: SOPs optimize task execution, cutting waste, rework, and raw material loss, especially for cost-sensitive SMEs and MSMEs.
Result: Increased output, reduced costs, and higher profitability.
5. Enabling Global Trade and Export Growth: SOPs meet global standards required for certifications and contracts, especially in pharmaceuticals, food, and automotive sectors.
Result: Improved global buyer confidence, fewer rejections, and better market access.
6. Supporting Continuous Improvement and Innovation: SOPs evolve with technology and methods, enabling seamless integration of changes while supporting long-term growth.
Result: Higher agility, process improvement, and sustainable innovation.
7. Accountability and Traceability: SOPs help trace product failures and deviations, enabling quick corrective actions and audit trails.
Result: Faster troubleshooting, better compliance, and enhanced customer trust.
Key Regulatory Bodies in India for SOP Compliance
Let’s quickly take a look at the key regulatory bodies overseeing SOP compliance across industries in India:
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
- Sector: General manufacturing
- SOP Requirements: IS codes set product standards; manufacturers must follow SOPs for quality, testing, and certification. The ISI mark is required for many products.
- Role: Provides a base for standardized manufacturing practices across industries like electronics, textiles, chemicals, and steel.
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Sector: Food & Beverages
- SOP Requirements: Mandates strict SOPs for food safety, hygiene, handling, storage, and packaging, ensuring products meet standards for both domestic and export markets.
- Role: Ensures food products are safe for consumption and compliant with hygiene standards.
Ministry of Labour & Employment
- Sector: All industries
- SOP Requirements: SOPs for worker safety, health, fire drills, and accident prevention are required under the Factories Act, 1948 to protect workers’ health and safety.
- Role: The Ministry of Labour enforces labor laws to ensure factories provide a safe working environment.
Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO)
- Sector: Pharmaceuticals
- SOP Requirements: Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential. SOPs govern drug manufacturing from raw material procurement to packaging and quality testing.
- Role: Ensures pharmaceutical products meet safety and efficacy standards through proper SOP implementation.
Ministry of Commerce & Industry (DPIIT)
- Sector: Manufacturing & Exports
- SOP Requirements: Exporting manufacturers must maintain SOPs to comply with international quality control standards for global market expansion.
- Role: Promotes export readiness of manufacturers by setting guidelines and encouraging standardization.
State & Central Pollution Control Boards
- Sector: Industrial manufacturing
- SOP Requirements: Environmental SOPs are critical for pollution control, waste management, and emission reduction. Factories must follow these SOPs to get necessary environmental clearances.
- Role: Enforce environmental protection laws and ensure compliance with sustainability practices.
International Certification Bodies (ISO)
- Sector: All industries
- SOP Requirements: SOPs are key to obtaining certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001, ensuring quality, environmental, and safety management.
- Role: ISO certifications boost global competitiveness and are often required by international clients and regulatory bodies.
| Regulatory Body | Industry / Sector | SOP Requirement |
| BIS | General manufacturing | Product quality & IS standards compliance |
| FSSAI | Food & beverages | Hygiene, packaging, storage, and safety SOPs |
| Ministry of Labour | All industries | Worker safety & health SOPs (Factories Act, 1948) |
| CDSCO | Pharmaceuticals | GMP & drug manufacturing SOPs |
| DPIIT | Manufacturing & exports | Export readiness & compliance with international standards |
| CPCB / State Boards | Industrial manufacturing | Pollution control, waste management, and environmental SOPs |
| ISO | All industries | International quality, safety, and environmental standards |
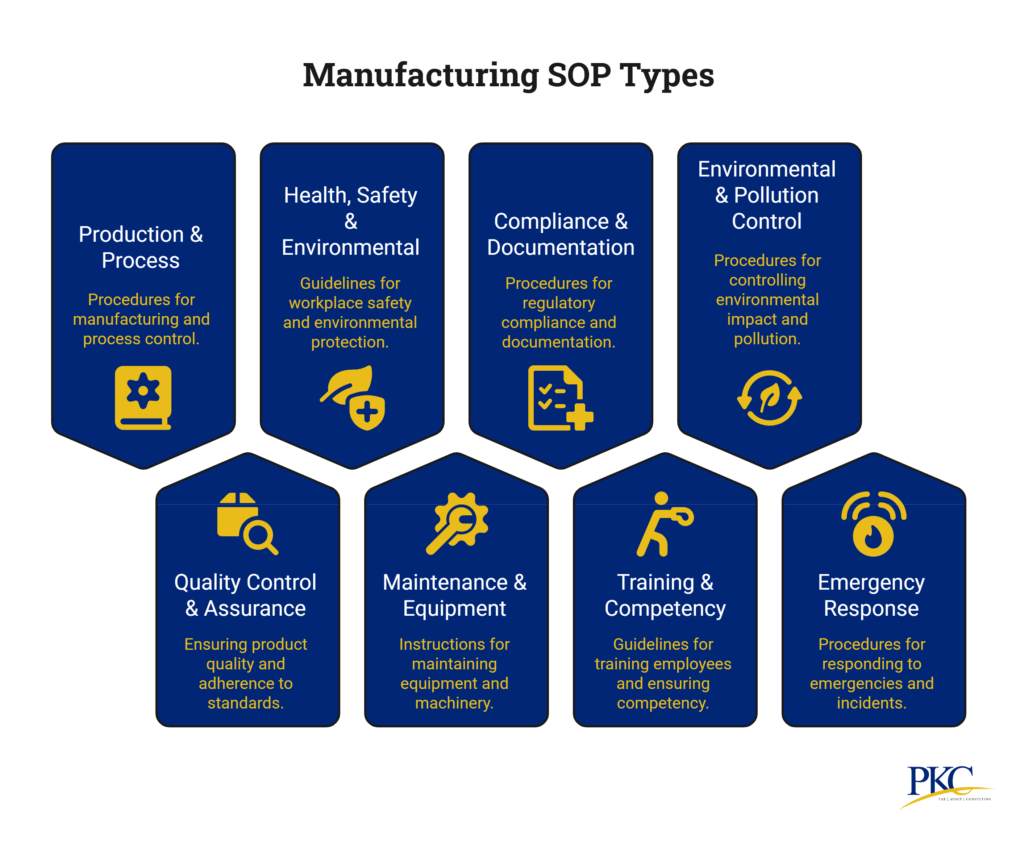
Fundamental Manufacturing SOP Categories in India With Examples
Manufacturing has several kinds of processes and most require well defined SOPs. Here a look at the types of SOPs manufactures need:
1. Production & Process SOPs
Define shop floor operations, from raw material handling to machine use, ensuring smooth, efficient, and safe production.
Clear SOPs prevent errors, ensure quality, minimize delays, and maintain compliance with industry regulations for product integrity and legal requirements..
Key Areas:
- Raw Material Handling: Procedures for inspecting, verifying, and storing incoming materials.
- Machine Operation: Step-by-step instructions on operating machines and equipment safely.
- Process Control: Monitoring and adjusting production parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, speed).
- In-Process Quality Checks: Continuous checks throughout the production cycle.
- Assembly Line: Instructions for efficient and defect-free assembly operations.
- Packaging & Maintenance: Detailing packaging processes and equipment upkeep.
Example: Automotive manufacturers have SOPs that guide workers through each step of welding car body parts, specifying temperature, duration, safety checks, and inspection points to ensure consistent, defect-free frames.
2. Quality Control & Assurance SOPs
Ensure products meet quality and safety standards, from raw material testing to final inspection.
By following QC and QA SOPs, manufacturers reduce defects, maintain certifications (e.g., ISO, BIS, FSSAI), and build trust, driving business success.
Key Areas:
- Material Inspection: Pre-production material checks to ensure they meet quality standards
- In-Process Testing: Continuous checks during production to prevent defects
- Final Product Testing: Ensures the final output meets specifications.
- Calibration: Regular calibration of machines and testing equipment.
- Non-Conformance Handling: Procedure for managing defective products.
Example: Pharma SOP details process for testing tablet purity and weight, covering sample collection, lab analysis, and acceptance criteria to ensure compliance with Indian and international standards like WHO and US FDA.
3. Health, Safety & Environmental SOPs
Focus on protecting employees and the environment while meeting legal requirements.
Ensuring worker health and safety prevents accidents and complies with laws like the Factories Act.
Environmental compliance, especially with waste and hazardous materials, avoids fines, legal issues, and damage, ensuring smooth operations and maintaining licenses.
Key Areas:
- PPE Usage: Guidelines for using protective equipment like helmets, gloves, and safety shoes.
- Fire & Emergency Evacuation: Procedures for fire safety, chemical spills, and medical emergencies.
- Hazardous Material Handling: Safely storing and handling chemicals or dangerous goods.
- Waste Management: Procedures for waste segregation, treatment, and disposal to comply with environmental laws.
Example: In paint factories, SOPs require workers to wear protective gear (gloves, goggles, masks) and follow ventilation guidelines to prevent inhaling toxic fumes, reducing accidents and ensuring compliance.
4. Maintenance & Equipment SOPs
These preventive and corrective maintenance SOPs reduce downtime, extend equipment life, and lower repair costs.
By keeping equipment well-maintained, factories improve production efficiency, minimize disruptions, and comply with industry standards for smooth operations.
Key Areas:
- Preventive Maintenance: Schedules and procedures for routine maintenance to prevent breakdowns.
- Corrective Maintenance: Protocols for repairing faulty equipment and minimizing downtime.
- Equipment Calibration: Ensuring that machinery and testing equipment are calibrated regularly for accurate performance.
- Spare Parts Management: Guidelines for tracking and managing critical spare parts to avoid production delays.
Example: Electronics factories follow SOPs for regular calibration of circuit assembly machines, ensuring correct wiring and functionality in smartphones.
5. Compliance & Documentation SOPs
Ensure factories meet legal, environmental, and regulatory requirements through effective record-keeping.
Well-managed records demonstrate compliance with safety, quality, and regulations, preventing fines, recalls, or license loss.
Key Areas:
- Record-Keeping: Proper documentation of all production activities, material receipts, inspections, and maintenance actions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Procedures for maintaining compliance with local and international regulatory bodies like BIS, FSSAI, and ISO.
- Audit Trail: Maintaining a traceable record of all actions taken during production process.
- Document Control: Guidelines for version control, approvals, and access to critical documentation.
Example: Amul maintains daily cleaning records of milk tanks and pipelines, which are checked during FSSAI audits to avoid license suspension.
6. Training & Competency SOPs
Ensure employees are well-trained and competent, maintaining high production standards.
It also aids scalability in factories with high turnover, making employees more productive and fostering continuous process improvement.
Key Areas:
- Employee Onboarding: Processes for introducing new hires to company policies, and equipment.
- Role-Specific Training: Guidelines for training workers on specific machines, tasks, or processes.
- Ongoing Skill Development: Regular programs to upgrade skills of employees and ensure they are aware of new methods.
- Trainer Qualifications: Ensuring trainers are competent and capable of transferring knowledge effectively.
Example: Garment factories train new workers using SOPs with pictorial guides, ensuring fast skill transfer and fewer errors.
7. Environmental & Pollution Control SOPs
Make sure manufacturing processes comply with environmental regulations, managing pollution, waste, and resource conservation.
Compliance avoids penalties, shutdowns, and environmental harm. Sustainable practices also enhance consumer trust, offer a competitive edge, and help achieve CSR goals.
Key Areas:
- Pollution Control: Procedures for managing air, water, and noise pollution
- Waste Disposal: Guidelines for proper disposal of hazardous and non-hazardous waste.
- Resource Conservation: Methods to minimize resource consumption (e.g., energy, water).
- Emissions Monitoring: Regular checks on emissions to ensure compliance.
Example: Chemical factories follow SOPs for waste segregation and safe disposal, ensuring CPCB compliance and preventing environmental harm.
8. Emergency Response SOPs
Provide clear procedures for managing emergencies in the workplace, from fire outbreaks to chemical spills.
This ensures that workers know what to do in the event of an emergency and also helps in compliance with safety regulations.
Key Areas:
- Fire Safety: Procedures for preventing fires, evacuating personnel, and using fire suppression systems
- Chemical Spill Response: Steps to contain and clean up hazardous chemical spills.
- First Aid: Instructions for providing immediate medical care in case of accidents
- Emergency Evacuation: Defined routes and procedures for evacuating employees during a crisis
Example: Factories handling gases like ammonia or chlorine maintain SOPs for gas leaks, covering alarms, evacuation, and first-aid, reducing damage and fatalities during emergencies.
Sector-Specific SOP Types Manufactures Need in India
Here’s a quick look at the types of SOPs manufactures should have as a manufacturer based on their industry:
| Industry | Core SOP Types Manufacturers Need |
| Pharmaceuticals |
– Production SOPs (tablet pressing, capsule filling) – Quality Control SOPs (sampling, calibration) – Cleaning & Sanitation SOPs – Packaging & Labeling SOPs – Storage & Distribution SOPs |
| Food & Beverages |
– Raw Material Inspection SOPs – Processing SOPs (pasteurization, blending) – Hygiene SOPs – Pest Control SOPs – Packaging & Allergen SOPs |
| Automotive |
– Assembly SOPs (welding, painting) – Safety Check SOPs (brakes, airbags) – Maintenance SOPs for equipment – Supply Chain SOPs – Lean Manufacturing SOPs |
| Textiles & Garments |
– Fabric Inspection SOPs – Cutting & Sewing SOPs – Dyeing & Printing SOPs – Finishing SOPs (washing, ironing) – Worker Welfare SOPs |
| Chemicals & Paints |
– Material Handling SOPs – Mixing & Blending SOPs – Waste Disposal SOPs – Fire & Emergency SOPs- PPE SOPs |
| Electronics & Electricals |
– Component Assembly SOPs – Static Control (ESD) SOPs – Product Testing SOPs – Packaging & Export SOPs – E-waste Recycling SOPs |
Key Components/ Structure of a Manufacturing SOP
SOPs in manufacturing can vary with the process, purpose, industry and other factors. However, they follow the same basic structure that includes:
1. Title Page
Ensures clear identification of the SOP, aids in version control, and facilitates compliance during audits.
- SOP Title (e.g., Welding Procedure for Automotive Assembly)
- SOP Number/Code
- Department Name (e.g., Production, Quality, Safety)
- Date of Issue and Revision History
2. Purpose
Clearly defines the reason for the SOP’s existence and its overall objective. Helps employees understand why the procedure exists, aligning everyone with its importance for maintaining quality, safety, and operational standards.
Example: This SOP ensures consistent welding of car body parts to maintain safety and quality standards.
3. Scope
Specifies the boundaries of the SOP, detailing which tasks, processes, or areas the SOP applies to and who must follow it. It helps prevent misapplication and maintain focus.
Example: This SOP applies to all welding operations in the assembly unit at the Chennai plant.
4. Responsibilities
Clearly assigns accountability by outlining the roles and individuals responsible for carrying out, monitoring, and approving the process. Promotes ownership and reduces risk of errors.
Example:
- Operator: Perform welding according to SOP.
- Supervisor: Ensure compliance with SOP.
- Quality Officer: Inspect and approve the finished welds.
5. Definitions & Abbreviations
Defines technical terms, acronyms, or jargon used within the SOP to ensure clarity.
Helps everyone, including new or unskilled workers, fully understand the SOP without confusion, promoting better adherence to procedures and reducing misunderstandings.
Example: PPE = Personal Protective Equipment
6. Materials & Equipment Required
Specifies the necessary tools, raw materials, safety gear, and machinery needed to carry out the procedure.
Ensures that the correct materials and equipment are available, reducing delays and maintaining process efficiency.
Example: Welding machine, gloves, helmet, steel sheets, inspection gauges.
7. Step-by-Step Procedure
Detailed, numbered instructions that guide the worker through each step of the task, ensuring consistency and precision.Guarantees that the process is executed consistently and without deviation.
Example:
- Put on PPE before starting work
- Switch on welding machine and check calibration
- Align steel sheets according to design specifications
- Perform welding following standard parameters
8. Safety & Precautions
Outlines safety warnings, hazard controls, and accident prevention measures during the procedure.
Critical to prevent accidents and injuries, ensuring a safe working environment.
Example: Ensure a fire extinguisher is nearby. Do not weld without protective mask.
9. Quality Control Checks
Specifies the necessary inspection steps and acceptance criteria to verify the quality of work.
Helps in detecting errors before they reach customers, reducing rework and ensuring product reliability.
Example: Weld joints must be free of cracks and must undergo X-ray testing.
10. Documentation & Records
Details the forms, checklists, or logs that must be filled out after completing the procedure.
Essential for audit trails, compliance with regulatory bodies (BIS, ISO, FSSAI, CDSCO, etc.), and maintaining a record of process execution.
Example: Production logs, machine calibration sheets, defect reports.
11. References
Provides guidance on where to find supporting documentation and regulations. Lists any related standards, regulations, or manuals referenced in the SOP.
Example: BIS welding standards, ISO 9001 guidelines, company quality manual.
12. Approval & Review Section
Shows signatures of responsible authorities (e.g., Manager, QA Head, Safety Officer) and includes review frequency.
Ensures that the SOP is approved by the right authorities, and sets expectations for periodic review to keep the SOP up-to-date with changing processes, technologies, or regulatory requirements.
Example: This SOP must be reviewed every 12 months.
How Can PKC Help With Manufacturing SOPs
✅ 37+ years manufacturing process optimization expertise
✅ Proven 5-step SOP methodology reduces implementation risks
✅ Industry-specific regulatory compliance across all manufacturing sectors
✅ Fresh outside perspective identifies hidden process gaps
✅ Immediate specialist access without lengthy hiring processes
✅ Faster delivery with dedicated SOP development resources
✅ Ongoing monitoring and testing ensures SOP relevance
✅ ISO certification support through compliant documentation
✅ Scalable solutions grow with your manufacturing expansion
✅ Core business remains uninterrupted during SOP implementation
Case Studies: How PKC Helped Manufacturers Implement SOPs Successfully
PKC can be your trusted partner for designing and implementing manufacturing SOPs.
Here is an overview of our SOP implementation across different manufacturing sectors:
Pet Bottle Manufacturing Company
- Implemented SOPs to improve production planning and reduce management involvement.
- Resulted in 95% better order fulfillment, higher production, and lower defects.
Textile Manufacturing Startup
- Created SOPs for order processing, inventory, and customer management.
- Achieved 42% faster order handling and easier branch expansion.
Food Manufacturing Company
- Introduced SOPs for procurement, reporting, and process clarity.
- Led to 95% improved order fulfillment, cost reduction, and time savings.
FAQs on SOPs for Manufacturing India
1. What are SOPs in manufacturing?
SOPs are step-by-step written instructions that guide workers on how to perform tasks consistently and safely in a factory. They help maintain product quality, ensure worker safety, and meet compliance standards in India.
2. What is an example of a manufacturing SOP?
An example is a welding SOP in an automotive plant that explains the exact steps, safety checks, and inspection points for welding car frames. This ensures every vehicle is produced with the same quality and safety standards.
3. How do you write a SOP for manufacturing process?
To write a manufacturing SOP, define the purpose, scope, responsibilities, required tools, and then list step-by-step instructions in clear language. Always include safety guidelines, quality checks, and documentation requirements.
4. What is the purpose of SOP in manufacturing?
The main purpose of an SOP is to standardize operations so every worker performs tasks in the same, correct way. This improves efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with Indian and global regulations.
5. What are the main benefits of an SOP manual in manufacturing?
An SOP manual improves consistency, enhances worker training, boosts safety, ensures legal compliance, and reduces production errors. Together, these benefits save costs and help Indian manufacturers compete globally.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

