Using key performance indicators for internal audit is essential for measuring their effectiveness, efficiency. KPIs offer a structured way to track performance, set expectations, and demonstrate accountability.
Explore with us the most relevant KPIs for internal audit in India, how they can be implemented, and why they are critical for aligning the audit function with organizational goals.
Why are KPIs Essential for Internal Audit?
KPIs in Internal Audit are indicators that evaluate the effectiveness, efficiency, and quality of an internal audit function.
These measurable values help audit departments demonstrate value, improve performance, and align with organizational goals.
Here’s why it is important to define them:
- Proving Value & Building Trust: KPIs show how internal audits add real value by protecting assets and strengthening governance.
- Ensuring Quality & Consistency: Internal audit KPIs ensure that all audits meet professional and regulatory standards, keeping quality must be consistent across teams.
- Aligning with Strategy & Risk: KPIs can help measure how well internal audits are designed to support long-term business goals.
- Improving Stakeholder Communication: A KPI dashboard turns internal audit results into simple, data-driven insights for better decision-making and accountability.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: Tracking KPIs over time helps identify what’s working, where to improve, and how to stay relevant and effective.
- Increasing Accountability: With KPIs, everyone in the audit team knows what’s expected. The team is productive, measurably effective, and if there’s a problem, it’s easier to spot and fix.
How to Define Effective KPIs for Internal Audit India?
Before you can start tracking KPIs for your internal audit department, you must lay groundwork. Here are the steps to determine what KPIs to track:
1. Align with Strategy & Risk:
Link KPIs directly to your organization’s goals and top risks.
Here are a few examples of aligning Audit KPIs with risks/ goals.
| Risk Area / Goal | KPI Example |
| Regulatory Compliance (SEBI/RBI) | % of audits covering SEBI/RBI controls |
| Fraud Prevention | INR value of frauds detected/prevented |
| Operational Resilience | % of key processes audited for continuity controls |
| Digital Transformation | % of digital/IT audits covering cyber and data risks |
2. Focus on Outcomes, Not Just Outputs:
Move beyond counting audits completed. Measure impact and value such as:
- Effectiveness: % High-Risk Issues Resolved Timely, Stakeholder Satisfaction Score
- Efficiency: Actual vs. Planned Audit Days, Average Report Issuance Time.
- Quality: “% QAIP Recommendations Implemented, Findings Re-opened Rate.
3. Apply SMART Framework:
Good KPIs follow the SMART model:
| Element | Meaning | Example |
| S | Specific | % of audits completed on time |
| M | Measurable | Count the number of repeat audit findings |
| A | Achievable | Don’t set goals no one can meet |
| R | Relevant | Focus on what matters to your business |
| T | Time-bound | Set monthly or quarterly targets |
4. Prioritize & Limit:
Select 5-8 critical KPIs across key dimensions:
- Strategic Coverage: % Audit Plan addressing top enterprise risks.
- Operational Efficiency: Cycle time, budget adherence.
- Quality & Compliance: QA results, adherence to Standards.
- Stakeholder Value: Action closure rates, satisfaction.
5. Involve Stakeholders:
Consult the Audit Committee and Senior Management especially critical in promoter-driven firms to ensure KPIs reflect their expectations of an internal audit’s value.
6. Use a KPI Dashboard or Scorecard
Use a simple Excel dashboard or an audit management tool like Zoho, MetricStream, or TeamMate to manage KPIs
- Update it regularly
- Share it in audit meetings
- Use it to guide decisions
7. Review & Adapt:
Regularly assess KPI relevance and effectiveness.
Adjust based on changing risks, business strategy, or stakeholder feedback.
Common Key Performance Indicators for Internal Audit in India
Here are some of the most common KPIs that can determine the efficacy of your internal audit function divided under different sections:
Strategic Alignment & Value Creation
- % audit plan coverage of top enterprise risks
- % audits covering key regulatory requirements (SEBI/RBI/Companies Act)
- Number/ Value of significant control improvements identified
- Number/ Value of fraud detected or prevented
- Value additions identified (Cost savings/Revenue leakage plugged)
Operational Efficiency & Resource Optimization
- Actual vs. Budgeted audit hours/Days
- Utilization rate of audit staff
- Average audit cycle time (Planning → report)
- Audits completed vs. Approved plan
- Cost per audit
Audit Planning, Coverage & Execution Quality
- % high-risk areas audited annually
- % audit plan delivered on schedule
- Average days from fieldwork completion to draft report
- % workpapers meeting quality standards
- Number of repeat findings
Compliance, Regulatory & Standards Adherence
- % Critical regulatory controls audited (e.g., GST, DPDPA, RBI Circulars)
- Results of quality assurance reviews (QAR Scores)
- % Quality Assurance and Improvement Program (QAIP) recommendations implemented
- % Audits compliant with IIA/Regulatory standards
- Number of regulatory inspection findings related to Internal Audit
Risk Management & Advisory Focus
- Number of proactive advisory engagements
- % Time spent on assurance vs. Advisory
- Coverage of critical it/Cybersecurity controls
- Number of risk assessments facilitated for business units
- Third-Party risk coverage
Technology & Process
- % Audits using data analytics
- Process improvement impact (e.g., “TAT Reduced by X Days Post- Internal Audit”)
- Coverage of digital transformation initiatives
- Automation rate of audit workflows
- System implementation review coverage
Stakeholder Engagement & Satisfaction
- Stakeholder satisfaction score (Audit committee/Senior management)
- % Agreed management actions implemented (Timely/Overall)
- % High-priority recommendations accepted
- Number of management requests for IA input
- Auditee feedback rating
Talent Development & Human Resource Effectiveness
- Training hours per auditor (Technical/Regulatory)
- Staff turnover rate
- % auditors with relevant certifications
- Succession plan readiness score
- Employee engagement index (Internal Audit team)
Emerging KPIs
- ESG risk coverage (% ESG framework elements audited)
- Carbon footprint reduction impact from Internal Audit recommendations
- Data privacy (DPDPA) Compliance Gap closure rate
- Cloud security controls audited
- AI/ML implementation review coverage
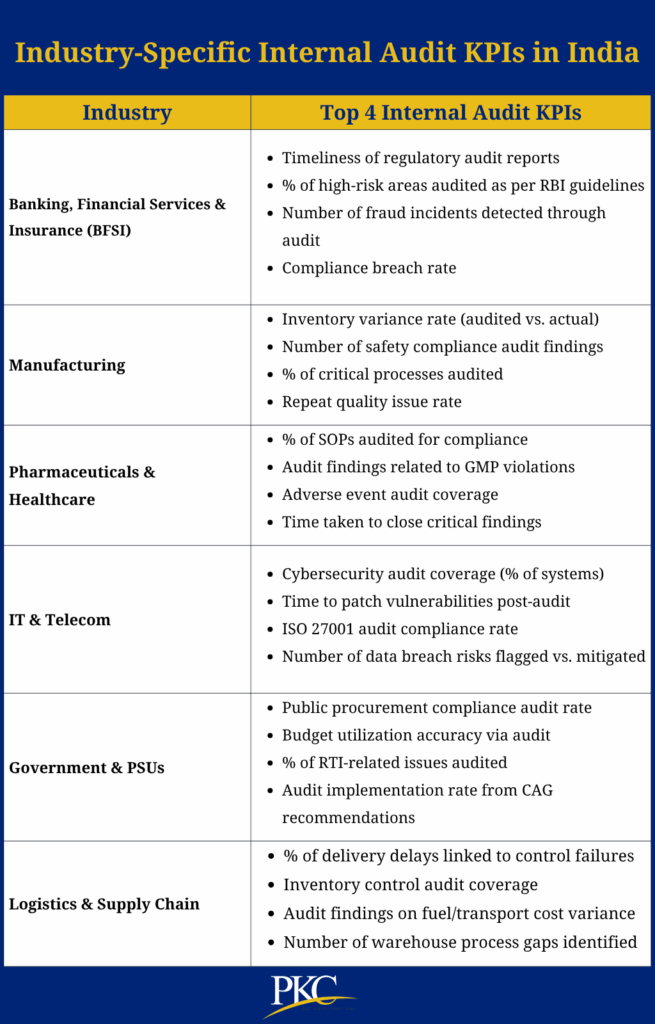
Industry-Specific Internal Audit KPIs in India
Different businesses have different needs and challenges, which is why they may need industry-specific KPIs for internal audit.
Here’s a look at some industries and their most important KPIs
How to Measure and Track Internal Audit KPIs?
Once you have an idea about the KPIs you want to track, you would need to measure and track them.
Here’s a simple overview of the way it can be done:
Here’s a concise, under-300-word version of your guide with a clear structure:
1. Define KPIs & Baselines
- Clearly define each KPI (e.g., % Agreed Actions Implemented = (# Closed ÷ Total Due) × 100).
- Set baselines (e.g., audit cycle time = 45 days) for comparison.
2. Assign Ownership & Embed in Workflow
- Allocate KPI owners (e.g., Audit Manager for Cycle Time).
- Integrate tracking across the audit lifecycle:
- Planning: % Plan Delivered
- Fieldwork: Budget vs. Actual Hours
- Reporting: Report Issuance TAT
- Follow-up: Action Closure Rate
3. Use Technology Wisely
| Tool | Use Case | Top Options |
| GRC Software | Dashboards, tracking | MetricStream, Zoho Analytics |
| Analytics Tools | Quantify savings/fraud | Power BI, IDEA |
| Basic Tools | For small teams | Excel, Google Sheets, Tally Add-ons |
4. Collect & Validate Data
- Automate from ERP/HRMS (e.g., SAP, Tally, greytHR).
- Validate samples quarterly with process owners.
- Align sources with management for credibility.
5. Monitor & Report
- Monthly: Operational KPIs
- Quarterly: Strategic KPIs
- Annually: Talent/Quality KPIs
- Use dashboards (heatmaps, RAG status).
6. Review & Improve
- Present KPIs quarterly with root cause analysis
- Use feedback tools (e.g., SurveyMonkey)
- Retire irrelevant KPIs; add emerging ones (e.g., ESG)
How Can PKC Help With Internal Audit KPIs?
✅Achieve 100% audit plan completion with structured methodology
✅Automated email alerts for KPI target deviations
✅Multi-industry benchmarking data for KPI standardization
✅On-site audit teams ensuring quality KPI achievement
✅Dedicated knowledge team tracking regulatory KPI changes
✅Business advisory for KPI improvement and optimization
✅Cost-effective audit solutions improving efficiency KPIs
✅Technology-enabled audit processes enhancing productivity KPIs
✅Ongoing support ensuring sustained KPI performance excellence
KPI Mistakes to Avoid in Indian Internal Audit
Setting up Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is great but it can only bring good results, if done right.
Here are some mistakes to avoid:
1. Using Vanity Metrics
Tracking numbers that look good but lack meaning — like counting the number of audits without looking into their impact. Focus on results, not just activity.
2. Measuring Quantity Over Quality
Fast audits aren’t useful if they miss key risks. Track impact, client feedback, and whether issues are resolved.
3. Setting Unrealistic Targets
Goals like 100% implementation or zero findings can lead to false reporting. Set challenging but realistic benchmarks and adjust them over time.
4. Ignoring Industry Needs
One-size KPIs don’t fit all. For example, internal audits in BFSI need different KPIs than in manufacturing. Customize your KPIs to reflect regulations, sector-specific risks, and business priorities.
5. Not Updating KPIs
Business risks evolve. Review and update KPIs yearly to keep them relevant. Drop irrelevant ones and add new risk-focused indicators.
6. Excluding Key Stakeholders
KPIs created only by the audit team may miss business context. Involve management, the audit committee, and even business units when defining KPIs.
7. Tracking Too Many Metrics
Too many KPIs cause confusion. Focus on 8–12 that truly guide decisions.
8. Weak Data Collection
Good KPIs need good data. Use consistent templates, audit tools, or dashboards to track performance accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why are KPIs critical for Internal Audit in India?
They objectively prove its value to promoters & regulators, justify resources in cost-sensitive environments, and ensure focus on top risks like fraud and compliance. Without KPIs, internal audit’s impact remains invisible and undervalued.
2. What are the most important KPIs for Indian Internal Audit functions?
Some of the most important KPIs include – % High-Risk Actions Implemented, Stakeholder Satisfaction, Coverage of Key Regulations , and Audit Cycle Time. These demonstrate risk mitigation, relevance, and efficiency.
3. How often should we track and report Internal Audit KPIs?
Track operational KPIs (e.g., cycle time, budget) monthly, strategic/value KPIs (e.g., risk coverage, action closure) quarterly, and talent/quality KPIs annually. Report key trends to the Audit Committee quarterly.
4. What tools can we use to track KPIs affordably in India?
Start with Excel/Google Sheets trackers or Power BI dashboards. For automation, explore GRC modules in ERPs or cost-effective Indian audit tools like Zoho Analytics integrated with Tally.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

