From fraud prevention to protecting patient lives, solid internal controls for healthcare are the backbone of a safe, legal, and trustworthy health sector.
Explore with us the basics of internal controls for healthcare businesses in India. We cover everything, right from its components to steps of implementation.
Understanding Internal Controls in Healthcare Its Importance
Internal controls in healthcare basically refer to the systems, processes, and rules that a hospital or clinic uses to keep its operations clean, safe, and efficient.
It main purpose is to:
- Prevent theft, fraud (like fake billing), and errors in payments, receipts, and payroll
- Ensure right medicine reaches right patient, equipment works correctly, and procedures are followed
- Meet regulations (like Clinical Establishment Act, Data Privacy Bill, GST, Tax laws, NABH standards)
- Reduce waste, avoid stock-outs of medicines, and make sure appointments and records are managed properly
- Trust your financial reports and patient data for smart decisions.
Importance of Internal Controls in Healthcare
High Risk of Fraud & Theft:
Cash payments, expensive medicines/supplies, complex billing (insurance, CGHS, etc.) create opportunities. Controls act as a deterrent and early warning system.
Strict & Evolving Regulations:
- NABH Accreditation: Requires robust controls for patient safety, medication management, and infection control.
- Clinical Establishments Act: Mandates standards and record-keeping.
- Data Privacy (Digital Personal Data Protection Act – Coming Soon): Demands strict security for sensitive patient health information (PHI).
- GST & Income Tax: Accurate invoicing, input tax credit tracking, and financial reporting are essential to avoid penalties.
Patient Safety is Paramount:
A single error in medication dosage, patient identification, or procedure can be catastrophic. Controls provide systematic checks.
Protecting Your Reputation:
News of fraud, data breaches, or patient harm spreads fast and destroys trust. Good controls build trust with patients, insurers, and partners.
Financial Health:
Preventing revenue leakage (unbilled services, under-billing), controlling costs (preventing pilferage, optimizing inventory), and ensuring accurate financial reporting are vital for profitability.
Insurance Company Requirements:
Efficient and accurate claim processing with proper documentation relies heavily on internal controls. Rejections cost money.
Building Investor/Partner Confidence:
Demonstrating strong controls makes your business more attractive for funding or collaborations.
Streamline Insurance Claims
Proper documentation and processes reduce claim rejections and delays, improving cash flow.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Internal Controls in Healthcare
There are several laws and regulations in India that force healthcare providers (hospitals, clinics, labs, pharmacies) to implement strong internal controls.
Non-compliance means hefty fines, lawsuits, license cancellation, or even jail time.
Here’s a quick overview of some core regulations:
- Clinical Establishments (Registration and Regulation) Act, 2010 (CE Act): Sets basic standards for registration, record-keeping, and quality in healthcare facilities. Adoption differs by state.
- National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH): Voluntary accreditation for hospitals, covering patient care, infrastructure, and management. Recognized for quality assurance.
- Indian Medical Council Regulations / NMC Act, 2019: Define ethical conduct, patient consent, confidentiality, and professional behavior for doctors.
- Indian Nursing Council (INC) and State Nursing Councils: Regulate nurse education and practice. Hospitals must ensure nurse registration and compliance.
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules, 1945: Controls drug storage, labeling, and dispensing in hospitals to ensure safety and compliance.
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances NDPS Act, 1985: Regulates controlled drug use in hospitals, requiring double-lock storage, special prescriptions, separate registers, regular stock checks, authorized access, and mandatory reporting.
- Information Technology Act, 2000 and DPDPA, 2023 Rules: Protection of electronic health records and sensitive personal data.
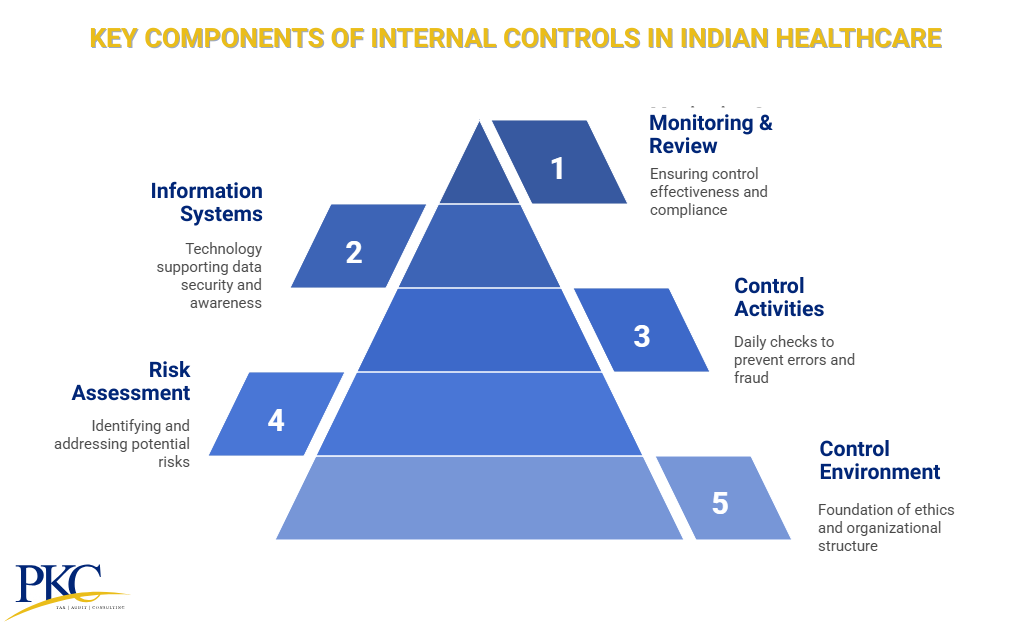
Key Components of Internal Controls in Healthcare India
Effective internal controls in healthcare are essential to protect patients, finances, and regulatory compliance.
Here are its most essential components
1. Control Environment
This is the foundation of your internal control system, set by leadership and reflected in the organization’s ethics, structure, and people.
- Leadership Matters: Management must model ethics, safety, and compliance (NABH, DPDPA, GST, NDPS).
- Structure & Clarity: Define reporting lines, roles, and responsibilities
- Policies & Training: Enforce a code of conduct and regularly train staff on laws and procedures.
2. Risk Assessment
Healthcare businesses must proactively identify where things can go wrong and address those risks based on their impact and likelihood.
- Identify Risks: Spot vulnerabilities like billing fraud, drug theft, data breaches, non-compliance.
- Evaluate & Prioritize: Focus on risks with high impact and high likelihood.
- Link to Law: Align controls with specific legal standards (e.g., DPDPA, NABH, GST).
3. Control Activities
These are the day-to-day checks and safeguards that prevent or detect errors, fraud, and misuse.
- Approvals & Limits: Set clear sign-offs for purchases, prescriptions, data access.
- Segregation of Duties: Separate key functions like billing, dispensing, and payment.
- Safeguards: Lock medicine stores (especially NDPS), use CCTV, secure cash handling.
- Documentation: Keep accurate medical records, invoices, NDPS registers, and consent forms.
- Reconciliations: Regularly match cash, bank, inventory, and patient records.
4. Information Systems & Communication
Technology and communication support control effectiveness, data security, and staff awareness.
- Access Control: Use strong passwords and role-based permissions—no shared logins.
- Backups & Security: Ensure secure, tested data backups. Encrypt patient data.
- DPDPA Readiness: Have breach plans, consent systems, and vendor agreements in place.
- Reliable Data Flow: Ensure timely reporting and department coordination.
- Clear SOPs: Document key processes (admission, billing, claims).
- Training & Reporting: Conduct regular training and enable whistleblower reporting.
5. Monitoring & Review
This ensures that the controls are regularly reviewed to stay effective and compliant.
- Daily Oversight: Managers should actively review reports and spot-check controls.
- Internal Audits: Periodic checks to test control effectiveness.
- Regulatory Reviews: Stay audit-ready for NABH, DPDPA, GST, etc.
- Act on Issues: Address control failures promptly and update procedures.
Types of Internal Controls in Healthcare in India
In Indian hospitals and clinics, internal controls can be categorised under different types. Here’s a classification based on what they are intended for:
1. Clinical Controls
Ensures patient safety, accurate diagnosis, and ethical treatment through standardized medical practices.
Examples:
- Confirm patient identity using ID band and verbal check before procedures
- Match medication lists at admission, transfer, and discharge
- Use signed consent forms, translated if needed, before procedures
- Follow sterilization protocols and audit hand hygiene regularly
- Use standard treatment plans for common conditions
2. Financial Controls
Protects assets, prevents fraud, and ensures accurate financial reporting.
Examples:
- Reconcile daily OPD/IPD collections with billing system.
- Validate GST invoices and reconcile input tax monthly
- Audit insurance claims before submission to reduce rejections
- Get manager approval for purchases above ₹20K
- Match bank statements with ledger entries monthly.
3. Regulatory Compliance Controls
Ensures adherence to Indian healthcare laws and standards.
Examples:
- Log narcotic drug use with witness signatures
- Submit Form F and secure ultrasound logs within 24 hours
- Maintain audit-ready NABH documentation
- Display registration and fee structure publicly
- Follow waste segregation rules and keep disposal records
4. Administrative & Operational Controls
Streamlines day-to-day operations and resource management.
Examples:
- Limit OPD appointments using scheduling software
- Monitor bed occupancy in real time
- Issue timed visitor passes for patient areas
- Tag equipment with QR codes for maintenance tracking
- Conduct fire drills and emergency response training
5. Data Privacy & Security Controls
Protects sensitive patient information under India’s DPDP Act.
Examples:
- Restrict EHR access based on user roles
- Encrypt telehealth data end-to-end
- Collect digital consent for data sharing
- Track who accessed patient data and when
- Report data breaches immediately as per law
6. Quality Assurance Controls
Monitors and improves clinical/service standards.
Examples:
- Gather patient feedback and review monthly
- Audit 5% of patient records for accuracy
- Calibrate lab equipment daily
- Monitor surgical site infection rates monthly
- Hold case discussions every two weeks
7. Risk Management Controls
Proactively identifies and mitigates operational and clinical risks.
Examples:
- Score elderly inpatients for fall risk
- Inspect fire safety equipment monthly
- Use hotline to report fraud risks anonymously
- Allow staff to report medication errors confidentially
- Maintain backup power and cloud-based data recovery
8. Human Resource Controls
Ensures qualified, compliant, and ethical staffing.
Examples:
- Verify medical licenses at the time of hiring
- Conduct police checks for staff handling drugs
- Track training certifications for all staff
- Approve overtime to manage workload and burnout
- Collect access cards and disable logins during exit process
9. Procurement & Supply Chain Controls
Manages ethical sourcing and inventory integrity.
Examples:
- Compare three bids for purchases over ₹50,000
- Monitor vaccine temperatures during transport
- Flag medicines nearing expiry 30 days in advance
- Match goods received to purchase orders
- Avoid suppliers with GST compliance issues.
10. Information Technology Controls
Secures digital infrastructure and data integrity.
Examples:
- Use multi-factor authentication for remote data access
- Auto-lock workstations after 5 minutes of inactivity
- Apply software updates weekly
- Test data backups every quarter
- Run quarterly phishing simulations to train staff
How Can PKC Help With Internal Controls in Healthcare?
✅2 decades of supporting hospital growth trajectories
✅End-to-end revenue tracking from admission to discharge
✅Leak-proof revenue collection and reconciliation systems
✅Process audit creating standardized plug-and-play operations
✅ERP implementation with integrated process training
✅Zero penalties through comprehensive compliance auditing
✅Business reports enabling data-driven decision making
✅Procurement restructuring reducing costs and improving availability
✅Examining, testing, and evaluating management control systems
How to Implement Internal Controls in Healthcare Industry?
Here’s a step by step guide on how to identify and implement internal controls in the healthcare sector:
Identify Applicable Laws
Your first action is to map out every legal and regulatory rule that applies to your facility.
- If you’re running a small clinic, you’ll face different rules than a giant multi-specialty hospital.
- Consider the Clinical Establishments Act, NABH accreditation standards, Drugs and Cosmetics Act, Biomedical Waste rules, NDPS for controlled substances, GST, the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA), etc.
- Document these laws so you know what you’re up against before you build controls.
Conduct a Compliance Gap Analysis
Once the laws are clear, compare them to your current systems. Identify
- Where are you already in compliance
- Where are the gaps
- Build a checklist to view where your weaknesses lie
For example, if your hospital uses handwritten records instead of a secure EMR, that’s a gap under data protection rules.
Prioritize
It’s impossible to fix everything at once. So, start by focussing on high-risk, high-penalty areas first.
These usually mean:
- Patient data privacy (DPDPA readiness)
- NABH or JCI if you’re seeking accreditation
- NDPS (safe handling of controlled drugs)
- GST and billing compliance
Rank them and build your control program in phases depending on the hierarchy
Embed Controls in SOPs
Document control procedures required by law clearly in your Standard Operating Procedures.
For example, if you have a rule about who can approve high-value purchases, include that in your procurement SOP.
That way, staff can reference the rules anytime, not just in training sessions.
Train Relentlessly
Even the best controls fail if your team doesn’t follow them.
- Set up role-based training so staff only learn what is relevant to them.
- Teach new hires during onboarding
- Run refresher trainings every year (or more often)
- Use real-life scenarios to show why these controls matter, like fraud cases or data breaches.
Audit Regularly
A control is worthless if it’s not tested.
- Schedule regular internal audits with your compliance or finance team
- Check that staff are following your SOPs
- For high-risk areas (like data privacy, drug storage, patient billing), bring in an external audit firm
- Fix any issues fast, and document every fix so you can show regulators.
Stay Updated
Indian healthcare laws are changing constantly, so staying updated is not a choice.
- Designate one person to monitor the latest rules
- Check government health ministry portals
- Follow industry associations like the Association of Healthcare Providers India (AHPI) or NABH newsletters
- Update your SOPs whenever rules change
Challenges & Solutions For Implementing Internal Controls in Indian Healthcare
| Challenge | Solution |
| Lack of Standardization | Create national guidelines, adopt accreditation standards, and develop sector-wide SOPs. |
| Poor IT Infrastructure | Build basic digital systems, implement HIS, and support government health platforms. |
| Staff Shortages | Train staff, include compliance in education, and offer online upskilling. |
| Resistance to Change | Run training, involve staff in changes, and incentivize compliance. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Simplify rules, provide checklists, and hold policy briefings. |
| Limited Funding | Use low-cost tech, access government aid, and form public-private partnerships. |
| Corruption/Fraud | Enforce anti-fraud rules, add whistleblower systems, and audit regularly. |
| Weak Documentation | Standardize formats, digitize records, and train on proper data entry. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are internal controls legally required in Indian healthcare?
Yes, many controls are required under Indian health laws and accreditation standards. These include data privacy, drug safety, and financial transparency.
2. What happens if a hospital fails internal controls?
They could face huge fines, legal action, or lose accreditation. Patient trust and safety would also take a serious hit.
3. Who is responsible for healthcare internal controls in India?
Hospital owners and managers hold the ultimate responsibility. They can appoint compliance officers to handle the details.
4. How often should internal controls be reviewed in the healthcare sector?
They should be reviewed at least once a year through internal audits. High-risk areas should be checked even more frequently.
5. Can technology improve internal controls in Indian hospitals?
Absolutely, tools like EMR, biometrics, and digital audits strengthen controls. They help track data and prevent fraud more easily.

 Expert verified
Expert verified