Internal audit of supply chain management is a must for businesses to survive as it impacts everything from costs and compliance to risk and customer satisfaction.
Explore with us all you need to know about this along with a look at its process and our sample supply chain management internal audit checklist that you can download for free.
What is the Internal Audit of Supply Chain & Why it Matters?
An Internal audit of supply chain management is a review of a company’s supply chain operations. It is either conducted by an in-house team or hired specialists like PKC Management Consulting.
It’s purpose is to:
- Examine supply chain processes including procurement, manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, inventory management, supplier management, etc.
- Assess how well these processes are working. Check them for efficiency, effectiveness and compliance
- Identify potential problems before they cause major damage like fraud, stockouts, delivery delays, quality failures, or safety issues.
- Verify that operations follow internal company policies, external regulations (like tax laws, safety standards), and customer contracts.
- Test the “safety nets” (procedures, checks, systems) designed to prevent errors and fraud. Are they working properly
- Provide practical suggestions to fix weaknesses, reduce risks, cut costs, and boost performance.
Importance of Internal Audit for Internal Supply Chains
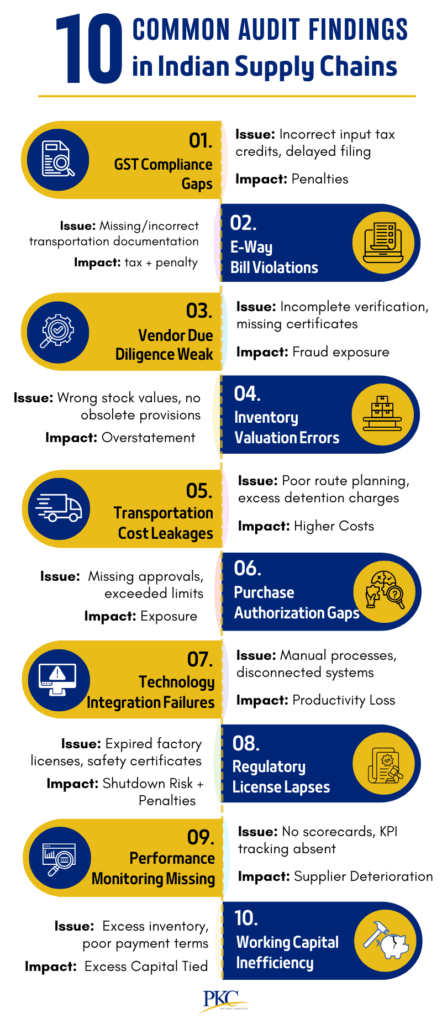
- Regulatory Compliance: Internal audits help navigate India’s evolving regulations (GST, labour laws, MSME rules), preventing fines and disruptions.
- High Risk of Mistakes: Indian supply chains often rely on manual processes, old software, or outdated systems. That means more chances of errors, especially with billing, orders, or GST filings.
- Fraud & Loss Prevention: Audits deter fraud (fake invoices, theft) and reduce leakage, protecting assets and margins.
- Supplier Risk Management: With many MSMEs involved, audits assess supplier reliability and quality, reducing disruption risk.
- Efficiency & Cost Control: Audits spot inefficiencies (waste, bottlenecks), leading to leaner, more cost-effective operations.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures consistent quality control across the supply chain, protecting brand reputation.
- Risk Resilience: Audits identify vulnerabilities (e.g., single-source risks), helping supply chains handle shocks.
- Stakeholder Trust: Strong audit systems build confidence with investors, customers, and regulators.
- Global Readiness: They align operations with global standards, supporting exports and global supply chain participation.
Top Industries in India Needing Supply Chain Audits
Many industries in India face high risks within their supply chain operations, which makes supply chain audits essential. Here’s a look at some of these sectors:
FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods)
This industry deals with High volume, perishable goods with thin margins, and fragmented distribution.
Apart from this they also have a huge number of vendors and distributors with high risk of inventory mismatch
Audit priorities:
- FIFO/LIFO compliance to reduce waste
- Supplier adherence to safety standards (e.g., FDA/FSSAI)
- Cold chain integrity for perishables
Pharmaceuticals
Medicines must be tracked and stored correctly, especially with India being a global pharma hub.
Audit priorities:
- Temperature-controlled logistics validation
- Strict quality and storage checks (cold chains, expiry dates
- Regulatory compliance (e.g., WHO-GMP, GDP)
- Anti-counterfeiting measures via blockchain traceability
E-commerce & Retail
This sector is witnessing explosive growth, complex reverse logistics, and intense customer expectations.
Audit priorities:
- Last-mile delivery efficiency and cost controls
- Inventory accuracy across multi-warehouse networks
- Ethical labour practices for gig workers (e.g., delivery agents)
- Cybersecurity of customer data
Automotive & Auto Components
Global OEM partners require stringent supplier quality and technical compliance.
The sector faces complex multi-tier supplier structures, increasing risk of disruptions.
Audit priorities:
- Supplier quality management (ISO/TS 16949)
- Resilience to geopolitical disruptions
- Verifies vendor contracts and quality standards
- Avoids delays on assembly lines
Logistics & Warehousing
Integral for handling, warehousing, customs compliance, and last-mile delivery.
Asset visibility and regulatory compliance are persistent challenges.
Audit priorities:
- Reduce damage, misrouting, and storage delays
- Improve delivery accuracy
- Track inbound and outbound shipments
- Ensures contracts and SLAs are followed
Manufacturing (General & Heavy Industries)
Includes consumer goods, electronics, engineering, and capital goods.
Internal supply chain audits are crucial for quality control, safety, environmental compliance, and process optimization.
Audit priorities:
- Supplier financial health monitoring
- IoT-enabled predictive maintenance
- Product recalls and operational inefficiencies
- Non-compliance with ISO and safety standards
Agriculture & Food Processing
India’s food industry relies on timely and safe supply of perishable items.
Food safety, traceability, and compliance with export/import rules require thorough auditing across complex and widespread supply chains.
Audit priorities:
- Pesticide residue testing
- Perishable supply chain breaks
- Cold storage infrastructure gaps
- International trade requirements
Key Components of a Supply Chain Audit in India
A supply chain audit looks into everything from purchasing to delivery.
It looks for problems, errors, or fraud, and makes sure you’re following Indian laws like GST and customs rules.
Here are the key components every audit must cover:
Governance & Strategy
Auditors examine how your supply chain is managed. Without clear governance, supply chains become disorganized and prone to costly mistakes.
Checks:
- Supply chain strategy alignment with business goals
- Clarity in roles, accountability, and escalation protocols.
- Top management review of supply chain performance
- Board oversight of ESG compliance (BRSR reporting) and climate resilience plans.
Procurement and Vendor Management
Here, the main aim is to verify if vendors are ethically sourced and reliable. Poor vendor management risks disruptions, fraud, or compliance failures.
Checks:
- Vendor selection criteria is transparent and documented
- Valid MSME registration, GSTIN, and financial health checks for suppliers
- Matching purchase orders and invoices properly
- Signs of fraud or favoritism
- Ethical sourcing compliance (no child labour, fair wages under India’s labour Codes).
- Contract adherence for quality, delivery, and pricing
Inventory and Warehouse
Auditors inspect stock accuracy and storage safety. Inefficient warehousing inflates costs and risks perishable goods.
Checks:
- Physical stock counts vs. system records
- Storage compliance (especially perishables or electronics)
- Waste management per CPCB norms
- Expired, obsolete, or stolen items
Process Efficiency & Controls
Weak controls cause delays, errors, and revenue leakage. Therefore, auditors check how efficient and controlled your operations are.
Checks:
- Use of standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- ERP/WMS automation (e.g., Tally, SAP)
- Order-to-delivery cycle times
Risk Management & Resilience
This evaluates how well your supply chain handles unexpected disruptions.Unmanaged risks disrupt operations during monsoons or supplier bankruptcies.
Checks:
- Business continuity plan
- Risk assessments for vendors and locations
- Backup suppliers for critical items
- Climate disaster plans (floods/droughts)
- MSME financial health monitoring
- Cyberattack response protocols
Logistics and Transportation
This is to ensure goods move efficiently and legally. Transport failures damage goods or trigger penalties.
Checks:
- Whether transportation is cost-effective and compliant
- Correct E-Way bills, lorry receipts, and freight documents
- Vehicle fitness (FASTag, BS-VI emissions)
- IoT sensor data for perishables/electronics
- Fuel theft detection; toll evasion audits
GST and Tax Compliance
Auditors reconcile taxes to avoid penalties. GST errors attract 18% interest plus fines under Section 50 of the CGST Act 2017.
Checks:
- GSTR-2B vs. GSTR-3B reconciliation
- E-invoicing (IRN) compliance
- HSN code accuracy
Customs and Import/Export Compliance
For global supply chains, this part focuses on cross-border compliance. Auditors validate cross-border shipments.
Checks:
- Goods cleared on time to avoid detention
- Complete documentation (Invoice, Packing List, Bill of Lading)
- HS code accuracy for duty optimization
- FTA benefit utilization (e.g., India-UAE pact)
- Anti-dumping duty evasion risks
- SEZ documentation checks
Contracts and Payment
This area checks financial transactions and legal agreements. Contract breaches spark disputes, while delayed payments violate laws.
Checks:
- Accurate and timely payment records
- Penalty clauses for delivery/quality failures
- Subcontractor approval workflows
- Vendor payments as per contract terms
Sustainability & Ethical Standards
Modern audits also check if supply chains are ethical and eco-friendly.Violations damage brand reputation and attract lawsuits.
Check:
- Vendors using fair labour practices
- Environmental regulations being followed
- Packaging and transport methods sustainable
- CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) policies implementation
- EPR compliance for plastic/e-waste
Step-by-Step: How to Conduct an Internal Audit of Supply Chain Management
Let’s take a quick look at the process of conducting a supply chain audit:
1. Define Audit Objectives and Scope
- Set clear objectives (e.g. verify GST compliance, reduce logistics leaks)
- Define audit boundaries (e.g. focus on high-risk warehouses or MSME suppliers)
- Prioritize India-specific risks (e.g. monsoon disruptions, tax penalties)
- Avoid overly broad scopes to maintain focus and depth
2. Map the Full Supply Chain
- Sketch out the full journey of your product from vendor to warehouse to customer
- Document all tiers of suppliers, logistics partners, and warehouses
- Identify hidden risks (e.g. unregistered subcontractors, China-dependent vendors)
- Use the UDYAM portal to validate MSME registrations
3. Develop an Audit Plan
- Assign specific roles (e.g. CA for tax checks, local auditors for Tier-2 visits)
- Align timelines with compliance cycles (e.g. GST filing dates)
- Schedule surprise checks for warehouses during monsoon/ busy season
4. Gather Documentation and Data
- Collect GSTR-2B, GSTR-3B, e-way bills, and supplier contracts
- Verify contracts for MSME payment compliance (45-day clause)
- Include temperature logs for cold chains
- Digitize records using tools like E-Invoice portals
5. Evaluate Processes, Test Controls and Compliance
- Match physical stock with system records
- Verify e-way bill routes using FASTag data
- Reconcile GST input credits
- Check compliance with FSSAI (food), DPCO (pharma), and labour codes
6. Perform Supplier Assessments
- Audit MSME suppliers for financial health and UDYAM registration
- Assess ethical practices (e.g. no child labour, fair wages)
- Prioritize high-risk vendors (e.g. single-source electronics suppliers)
7. Interview Stakeholders
- Speak with warehouse staff about monsoon preparedness
- Discuss e-way bill issues with truck drivers
- Address GSTR-2B reconciliation with finance teams
- Use local languages with Tier-3 or rural suppliers to ensure clarity.
8. Conduct Risk Assessment
Identify India-specific risks such as:
- Monsoon flooding
- GST non-compliance
- Cyberattacks on logistics systems
- MSME payment delays beyond 45 days
9. Analyze Findings and Prepare Report
- Quantify issues (e.g. ₹25L GST mismatch, 30% stock variance)
- Benchmark against Indian industry standards
- Summarize key insights for actionable decision-making
10. Report Findings and Corrective Actions
- Highlight critical issues (e.g. delayed MSME payments)
- Set deadlines for resolution.
- Recommend fixes (e.g. automate GST reconciliation, diversify suppliers)
- Assign responsible owners for each corrective action
11. Follow-up and Close-Out
- Verify implementation of fixes within 90 days
- Track progress using digital tools
- Re-test high-risk areas
- Close audit only after full verification
Why Choose PKC for Supply Chain Internal Audits?
✅100+ expert team with specialized knowledge
✅ERP implementation experts solve supply chain challenges
✅Process consulting integrated with supply audit expertise
✅Inventory management inefficiencies identified and corrected quickly
✅Operational problems solved through implementable audit solutions
✅Revenue growth strategies embedded within audit recommendations
✅Cost optimization focus maximizes supply chain profitability
✅Profitability improvement through supply chain audit insights
✅Digital transformation capabilities modernize traditional supply audits
Internal Audit Checklist for Supply Chains
Having a supply chain audit checklist is essential to keep your audit structured and ensure you don’t miss critical areas.
Here’s a sample checklist that you can customize based on your industry, company size, and complexity of operations:
FAQs About Internal Audit of Supply Chain Management
1. What is a supply chain internal audit in India?
A supply chain internal audit in India checks the entire process from procurement to delivery for compliance, fraud, and efficiency. It ensures the company is following GST laws, managing inventory properly, and avoiding financial risks.
2. Why is supply chain auditing important for Indian businesses?
It helps businesses catch issues like tax misreporting, vendor fraud, and inventory losses. Regular audits improve transparency, reduce risk, and ensure compliance with Indian regulations.
3. How often should supply chain audits be conducted in India?
At least once a year is recommended, but high-risk industries may need quarterly reviews. The frequency depends on business size, volume, and complexity.
4. Are internal supply chain audits mandatory in India?
They aren’t legally required for all businesses, but public companies and large private firms often must comply. It’s also a best practice to prevent operational and financial risks.
5. Who conducts internal audits in Indian companies?
Internal audit teams, chartered accountants, or third-party consultants like PKC Management Consulting usually conduct these audits. They follow ICAI and GST standards when applicable.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

