For many taxpaying entities including an audit report with ITR is mandatory. However, sometimes, certain audit triggers can cause income tax scrutiny.
In this blog, we take you through some of the most common reasons for audit-related tax scrutiny notices.
What Are Audit-Related Tax Scrutiny Notices?
Audit-related tax scrutiny notices are official letters sent by the Income Tax Department when they find something suspicious or inconsistent in your tax audit report or income tax return.
These notices often ask for:
- Books of accounts
- Copies of audit reports (Form 3CD & 3CB)
- Bank statements
- Explanation for mismatches
- Details of expenses and deductions
Also Read,
Common Reasons for Income Tax Scrutiny
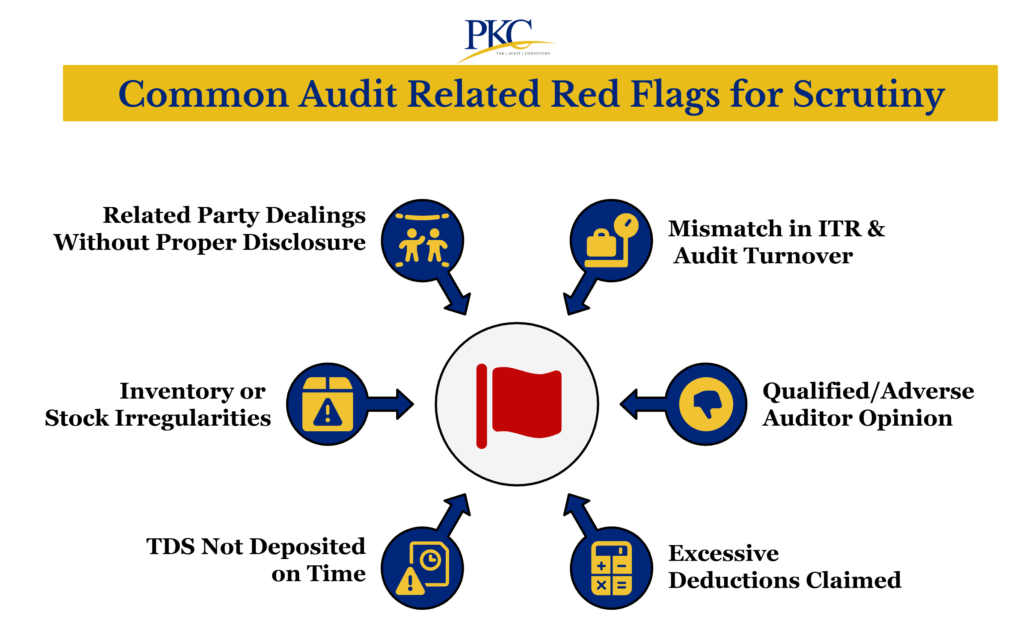
Top Reasons for Audit-Related Income Tax Scrutiny Notices
Here are the key audit report triggers that can lead to income tax scrutiny in India:
- Tax Audit Applicability Breach
If your turnover or professional receipts exceed audit thresholds (like ₹1 crore for business or ₹50 lakh for profession), but you don’t get audited, it is a default.
This not only invites a penalty but also automatic scrutiny.
- Defects in the Audit Report or Tax Return
Errors, omissions, or incomplete audit reports can raise suspicion under Section 139(9).
Missing signatures, incomplete disclosures, or wrongly selected audit clauses in Form 3CD are also common issues.
Failure to submit audit reports by the due date (September 30) or incomplete filings may result in penalties and scrutiny notices.
- Non-Compliance with Accounting Standards (AS/Ind AS):
Failure to follow Accounting Standards or Ind AS results in unreliable financials.
If the auditor notes deviations from these standards, especially in recognition of income, valuation, or presentation, it can become a serious trigger.
Such deviations usually attract a qualified or adverse opinion, which automatically raises a red flag.
- Qualified/Adverse/Disclaimer of Opinion:
When the auditor is not satisfied with the financials, they may issue:
- Qualified Opinion: Financials are mostly correct, but a few areas are problematic
- Adverse Opinion: Financials are materially misstated
- Disclaimer: The Auditor could not obtain sufficient evidence to form an opinion
Any of these indicates to the tax department that something is wrong, often leading to scrutiny.
- Auditor’s Report Qualifications
Specific qualifications in the auditor’s report – where the CA says “subject to” or “except for” – indicate doubt or disagreement.
This also includes notes on non-maintenance of books, non-compliance with tax laws, or internal control weaknesses in the audit report.
This alerts the department to review the issues in detail.
- High-Priority Disclosures in Form 3CD:
Form 3CD has specific clauses that the IT department monitors closely:
- Clause 21 – Expenses disallowed under the Income Tax Act
- Clause 34 – TDS defaults
- Clause 40 – Details of deductions claimed
- Clause 44 – Break-up of total expenditure into GST-registered/unregistered parties
If these are left blank, incomplete, or show suspicious patterns, scrutiny is almost certain.
- Specific Tax-Related Disclosures:
Items like payments to related parties, cash transactions, and foreign remittances are watched closely by the tax authorities.
Disallowable expenses or unverifiable donations are also common triggers if improperly disclosed.
Incorrect set-off of brought-forward losses or unabsorbed depreciation can also invite scrutiny.
- Mismatch of Audit Financials Vs ITR
Differences between audited financials and ITR-reported income (e.g., underreported revenue or overstated expenses) are also something tax officials may look into.
It suggests misreporting or manipulation, making it a top reason for scrutiny.
- Abnormal Financial Ratios
Unusual ratios like:
- Negative current ratio
- Very low net profit margin
- Extraordinarily high debtor days
These suggest poor financial health or manipulation, which are taken very seriously by the tax authorities.
- Transactional Red Flags
High cash payments, unsecured loans without agreements, and frequent related-party transactions also raise red flags.
These are closely monitored by the tax authorities.
- Profitability Variations
If your profits fluctuate widely year-over-year without a business justification, the auditor may highlight it.
Tax officials see this as a red flag and often select such cases for detailed scrutiny.
- Revenue and Sales Fluctuations
Big jumps or drops in sales, turnover, or revenue without corresponding explanations can be suspicious.
For example:
- Two times revenue growth, but five times expense growth
- Major drop in sales without a loss in cost base
Such trends are often called out in the audit report and attract scrutiny.
- Expense & Dedication Triggers
Overstated or suspicious deductions, especially:
- Excessive salaries to directors
- High advertising or consultancy expenses
- Frequent Section 80C/80G donations
If expenses don’t match the nature or size of the business, the tax officer will dig deeper.
- Cash Flow Statement Anomalies
Discrepancies between cash profits and net profits can signal hidden cash transactions or underreporting.
Examples:
- Huge cash flow from operations despite showing accounting losses
- Excessive cash purchases or sales
Such red flags are easily detected and flagged in the audit.
How Can PKC Help With Audit Scrutiny Notices for Businesses?
✅360-degree audit coverage: statutory plus tax compliance
✅Proactive red flag identification prevents escalating notices
✅Data reconciliation across GST, 26AS, and statutory liabilities
✅Preemptive documentation strengthening before scrutiny hits
✅Related party transaction arm’s length pricing expertise
✅Internal control evaluation prevents future audit triggers
✅Fast-track response preparation for immediate notice compliance
✅Multi-source financial data validation reduces scrutiny risks
✅Chartered accountant team specializing in scrutiny defense
✅Balance sheet optimization improves audit scrutiny outcomes
✅Post-scrutiny process improvements prevent recurring department attention
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are audit-related tax scrutiny notices?
Audit-related scrutiny notices are sent by the Income Tax Department when issues are found in your audit report or tax return. These notices ask for documents or clarification on inconsistencies.
- Can a clean audit report still lead to tax scrutiny?
Yes, even a clean report can trigger scrutiny if the department flags unusual deductions, high transactions, or a mismatch with other data sources. The audit is only one part of the full review.
- What audit triggers raise red flags?
Frequent triggers include mismatches between ITR and audit reports, qualified audit opinions, large deductions, or cash transactions. Any sign of non-compliance can lead to a detailed review.
- Can related party transactions attract scrutiny?
Absolutely. If they’re not disclosed properly or seem inflated/unusual, they raise suspicion and can be disallowed under Section 40A(2)(b).
- Can low profit or revenue fluctuations cause scrutiny?
Yes. Sudden drops in profit or wide revenue swings without explanation often indicate manipulation or tax avoidance, attracting scrutiny.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

