An HR compliance audit in India is one of the most important tools to avoid costly penalties and protect employee rights.
If you’re running a business in India, this guide will help you understand compliance audits and what they cover. We also provide a sample HR compliance audit checklist PDF, you can download for free.
What is an HR Compliance Audit?
An HR Compliance Audit is an in-depth review of a company’s human resource policies, procedures, documentation, and practices.
It is performed to ensure alignment with applicable labour laws, statutory regulations, and internal HR policies.
The HR compliance audit serves as a risk mitigation tool, helping companies avoid penalties, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Importance of HR Compliance Audits
1. Avoid Legal Penalties & Government Action: Non-compliance can result in fines, lawsuits, criminal liability, or even shutdowns. An audit helps you catch compliance gaps early and fix them.
2. Safeguard Employee Rights: Ensure that your workforce receives fair wages, social security benefits, safe working conditions, and protection against discrimination or harassment. This leads to a more engaged and loyal workforce.
3. Strengthen Employer Branding & Reputation: Companies demonstrating compliance and ethical practices are seen as trustworthy by employees, investors, customers, and regulatory bodies. This boosts your employer brand and market credibility.
4. Keep Pace with Changing Labour Laws: Labour laws are subject to frequent amendments. Regular audits ensure that your policies stay up-to-date and legally sound, especially with the implementation of new Labour Codes.
5. Improve Operational Efficiency: Audits often uncover inefficiencies, outdated processes, and documentation gaps in HR systems. Addressing these can improve internal workflows and reduce administrative overhead.
6. Prepare for Inspections or M&A Due Diligence: Whether it’s a labour department inspection or a merger/acquisition deal, having audit-ready HR compliance can make or break business outcomes.
7. Foster a Safe and Inclusive Work Culture: An HR audit also verifies compliance with laws like the POSH Act, ensuring your workplace is free from harassment and discrimination.
Key Labour Laws Covered in an HR Compliance Audit India
An HR Compliance Audit assesses whether a business is complying with a wide range of central and state labour laws including
Code on Wages, 2019
This Code combines four major wage laws, including the Minimum Wages Act and Payment of Wages Act. It ensures:
- Timely payment of wages
- Compliance with minimum wage standards
- Equal pay for men and women
Audit Focus:
- Adherence to state-specific minimum wage rules
- Issuance of wage slips
- Proper documentation of bonuses and deductions
Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 (EPF Act)
This Act requires employers to contribute to employees’ provident fund accounts for retirement benefits.
Audit Focus:
- EPF registration
- Correct contribution rates
- Timely deposits
- UAN (Universal Account Number) linkage
Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 (ESI Act)
Applies to specific establishments and provides health, maternity, and disability benefits to employees.
Audit Focus:
- ESI registration and accurate deductions
- Timely contribution filings
- Maintenance of employee records
Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
Ensures eligible employees receive annual bonuses based on company profitability.
Audit Focus:
- Bonus eligibility and calculation
- Timely disbursement
- Maintenance of statutory registers (e.g., Form C)
Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
Provides gratuity to employees who complete at least 5 years of continuous service.
Audit Focus:
- Employee eligibility verification
- Accurate gratuity calculation
- Timely payments during exits
- Policy compliance
Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
Grants paid maternity leave, nursing breaks, and other benefits to women employees. Establishments with 50+ employees must have crèche facilities.
Audit Focus:
- Leave and benefit records
- Crèche compliance
- Policy communication and implementation
Factories Act, 1948 & Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
Regulates health, safety, and welfare of workers, especially in manufacturing.
Audit Focus:
- Availability of safety equipment
- Working hours and overtime records
- Leave policies
- Facilities like restrooms, ventilation, and canteens
Shops and Establishments Act (State-specific)
Applies to commercial establishments, with rules varying by state.
Audit Focus:
- Registration and licensing
- Compliance with working hours and holidays
- Overtime provisions
- Employment of women and minors
Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 & Industrial Relations Code, 2020
Covers employment termination, disputes, strikes, and lockouts.
Audit Focus:
- Proper termination procedures
- Documentation of retrenchments
- Grievance redressal systems
- Implementation of Standing Orders
Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970
Applies to employers using contract workers via third-party contractors.
Audit Focus:
- Valid contractor licenses
- Wage parity with regular employees
- Statutory benefits for contract staff
- Documentation (e.g., Form V, Muster Rolls
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013 (POSH Act)
Mandates a safe workplace for women and the formation of an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC).
Audit Focus:
- ICC formation and functioning
- Awareness and training programs
- Policy display and accessibility
- Proper complaint handling
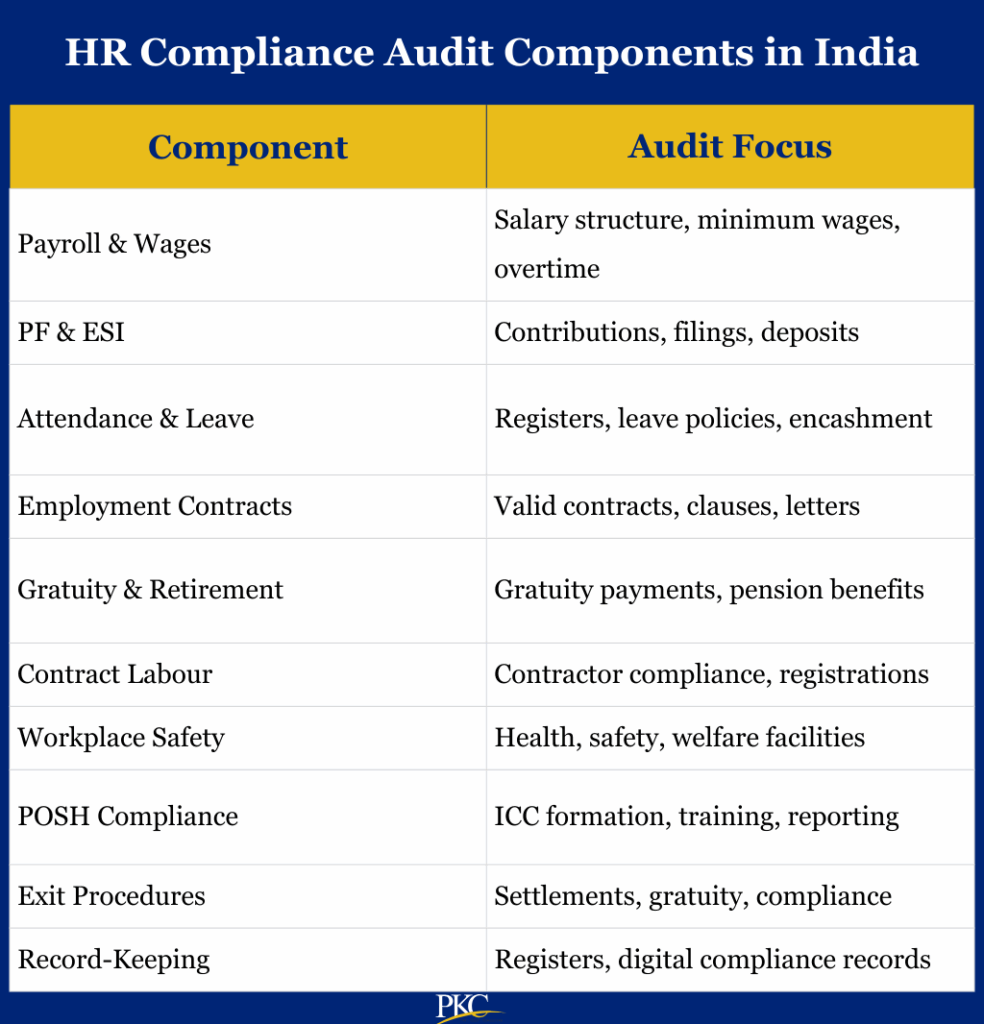
Components of an HR Compliance Audit in India
An HR compliance audit spans the entire employee lifecycle, from hiring to retirement or exit.
It includes checks on regulatory registrations, social security, safety standards, and workplace ethics.
Here are the key components that are covered under the HR compliance audit in India:
1. Statutory Registrations and Licensing
The audit first verifies whether the organization has all the required legal registrations to operate in compliance with Indian labour laws.
- Registration under state-specific Shops and Establishments Act
- EPF and ESIC registration (where applicable)
- Professional Tax (PT), Labour Welfare Fund (LWF), and other state-mandated registrations
- Factory License under the Factories Act (for manufacturing units)
- Contract Labour Registration and License (if contractors are engaged)
2. Payroll and Compensation Compliance
This component ensures employees are paid legally and fairly.
- Adherence to the Minimum Wages Act and Code on Wages, 2019
- Timely and accurate salary disbursement under the Payment of Wages Act
- Overtime and bonus payments as per legal entitlements
- Correct salary structure, wage slips, and statutory deductions (PF, ESI, TDS)
- Annual bonus compliance under the Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
3. Provident Fund (PF), ESI, and Social Security Compliance
Social security benefits are a mandatory component of employee welfare in India.
- Verifying registration and coverage under the EPF Act and ESI Act
- Ensuring correct employer and employee contributions
- Timely deposits, filing of returns (ECR, ESIC Challans)
- Gratuity eligibility and payment compliance under the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
- Pension and insurance contributions (if applicable)
4. Employee Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintaining proper records is both a legal obligation and a compliance indicator.
- Offer letters and appointment contracts with all required clauses
- KYC documents (PAN, Aadhaar, bank details)
- Employment agreements with confidentiality or non-compete clauses (if relevant)
- Maintenance of statutory registers: Muster Roll, Wage Register, Leave Register, etc.
- Record of background checks and verification for new hires
5. Attendance, Leave, and Working Hours
Audits assess whether the organization is following statutory norms for attendance and leave.
- Biometric/manual attendance systems and daily attendance records
- Leave policy compliance under the Factories Act, Shops and Establishments Act, and Maternity Benefit Act
- Overtime records and limits under the Factories Act
- Leave encashment and carry-forward practices
- Holiday and weekly rest day policies
6. Contract Labour and Outsourced Employees
If contractors or third-party service providers are employed, additional checks are necessary.
- Licensing under the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970
- Form V issuance by the principal employer
- Verification that contractors comply with PF, ESI, and wage payments
- Record of outsourced employees’ working hours and welfare entitlements
7. Workplace Health, Safety, and Welfare
Ensuring safe and humane working conditions is critical to compliance.
- Safety protocols and hazard identification under the Factories Act or Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code
- Availability of first-aid kits, fire extinguishers, safety gear, and emergency exits
- Canteen, drinking water, sanitation, and crèche facilities (as applicable)
- Health check-ups for workers, especially in hazardous roles
- Display of safety signages and legal notices at the workplace
8. POSH Compliance (Prevention of Sexual Harassment)
Ensuring a respectful and harassment-free workplace is not only legally required but also vital for employee trust.
- Compliance with the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013
- Formation and functioning of the Internal Complaints Committee (ICC)
- Regular training and sensitization programs
- Documentation of complaints, inquiries, and resolutions
- Display of POSH policy in prominent areas
9. Exit and Full & Final Settlement
A smooth, lawful exit process reflects HR compliance maturity.
- Proper documentation for resignations, terminations, and retirements
- Timely full & final settlements covering salary, gratuity, leave encashment, etc.
- Issuance of relieving letters and experience certificates
- Adherence to notice period and termination clauses
- Settlement of statutory dues and handover processes
10. HR Policies and Handbook Compliance
HR policies must align with current labour laws and be implemented consistently.
- Review of the Employee Handbook: leave policy, disciplinary policy, code of conduct, grievance redressal, remote work, etc.
- Verification that policies are clearly communicated and acknowledged by employees
- Policy implementation consistency across all departments
- Regular policy updates based on legislative changes
11. Audit Trail, Reporting & Corrective Actions
The final part of the audit process ensures accountability and continuous improvement.
- Documenting audit findings and identifying compliance gaps
- Assigning risk scores based on the severity of non-compliance
- Recommending corrective actions and timelines
- Developing a compliance calendar for future monitoring
- Training HR teams and line managers to close gaps and improve adherence
HR Compliance Audit Checklist India
Let’s take a look at how a HR compliance audit checklist looks like in India.
The checklist ensures comprehensive coverage of Indian labour law requirements. However, some laws vary by state.
Before using this make sure, that state-specific compliance requirements are met. You can also reach out to PKC’s experts for a checklist specific to your industry and your business size.
Steps to Conduct an HR Compliance Audit in India
Here’s a quick guide to conducting an HR compliance audit in India:
1. Pre-Audit Planning and Scope Definition
Set Clear Objectives
- Identify the purpose: Is it a routine check, or a response to a compliance concern
- Define what’s being audited, compliance with EPF/ESI, POSH Act, or a full-spectrum HR audit.
Establish the Scope
- Include all applicable laws: Shops and Establishments Act, Factories Act, Payment of Wages Act, Minimum Wages Act, etc.
- Factor in state-specific requirements and industry variations.
- Cover all employee types: full-time, part-time, contractual, and temporary workers.
Form the Audit Team
- Internal: HR, payroll, legal, finance, and compliance staff.
- External : Labour law consultants or firms like PKC with expertise in Indian employment laws.
Develop an Audit Checklist
Create a compliance checklist that suits the needs of your business. You can check and download the free sample checklist shared above.
2. Document Collection and Record Review
Gather Relevant HR Documents
Collect historical and current documentation such as:
- Offer letters, joining forms, and employee agreements
- Payroll records, salary slips, and paysheets
- Attendance and leave registers
- PF, ESI, PT, and gratuity records
- Licenses and registrations under various labour laws
- Compliance returns filed under different statutes
- Policy documents (POSH, grievance redressal, whistleblower)
Organize and Digitize
Ensure records are accessible and systematically maintained, especially for remote audits or inspections by government authorities.
3. Field-Level Verification and Interviews
Conduct Random Interviews
- Speak with employees across departments to verify adherence to policies.
- Ask about awareness of grievance redressal mechanisms and the ICC under POSH.
Check for Implementation Gaps
- Compare documented policies with actual practices.
- Verify salary disbursement timelines, PF deductions, overtime payouts, and leave calculations.
POSH and Workplace Safety
- Ensure mandatory POSH training is conducted.
- Confirm the Internal Committee is properly constituted with both internal and external members.
4. Identify Gaps and Non-Compliance Areas
Perform a Compliance Gap Analysis
Evaluate all collected data against applicable Indian labour laws.
Common issues found:
- Delayed or incorrect PF/ESI contributions
- Non-issuance of appointment letters
- Incomplete or missing statutory registers
- Incorrect payment of minimum wages or overtime
Categorize Risks
- High Risk: Violations that may lead to legal action or significant fines.
- Medium Risk: Lapses that could trigger audits or minor penalties.
- Low Risk: Administrative oversights that are easy to correct.
5. Draft the Compliance Audit Report
Create a Detailed Audit Report
Include:
- Executive Summary: Key findings and implications
- Methodology: Steps followed during the audit
- Detailed Observations: Legal references, specific issues, and current gaps
- Risk Assessment: Categorization of non-compliance severity
- Recommendations: Corrective measures with prioritization
Include a Compliance Scorecard
Provide a risk score (low, medium, high) for quick management review and decision-making.
6. Create and Implement a Corrective Action Plan
Develop a CAP (Corrective Action Plan)
Each issue must be matched with:
- Responsible team or individual
- Specific actions to be taken
- Target completion dates
Examples of Actions
- Amend outdated HR policies
- Conduct mandatory compliance training (e.g., POSH awareness)
7. Monitor Progress and Ensure Continuous Compliance
Follow-Up Audits
- Schedule quarterly, bi-annual, or annual audits based on company size and industry risks.
- Recheck whether all action items have been implemented.
Ongoing Monitoring
Use an HRMS or payroll compliance tool to automate tracking of:
- Statutory payments (PF, ESI, TDS)
- Return filing deadlines
- Employee documentation
Stay Updated on Labour Law Changes
Revisit policies and processes whenever new labour law codes or amendments come into effect.
Penalties for Non-Compliance to HR Compliance Audits in India
| Category | Details |
| Heavy Monetary Fines |
|
| Criminal Liability & Imprisonment |
|
| Business Restrictions |
|
| Reputation & Employee Trust |
|
Why Should You Outsource HR Compliance Audit to PKC
With 37 years of expertise and over 1,500 satisfied clients, PKC Management Consulting transforms your compliance challenges into competitive advantages.
1. Zero-Risk Guarantee: 100% compliance records across industries. Every labour law, PF/ESI requirement, and statutory obligation covered.
2. Proactive Problem Prevention: Identify violations before they become costly legal issues. Spot what internal teams miss.
3. Industry-Specific Intelligence: Tailored solutions for manufacturing, healthcare, IT, and retail. Specialized expertise beats generic advice.
4. Continuous Partnership: Ongoing monitoring, training, and implementation support. Your compliance partner for life.
5. Reputation Protection: Enhanced credibility with stakeholders through demonstrated ethical business practices.
Ready to eliminate compliance risks? Call PKC’s specialists today.
FAQs on HR Compliance Audit India
An HR compliance audit is a review of company policies, employee records, and statutory filings to ensure compliance with labour laws. It helps businesses avoid penalties and maintain legal and ethical HR practices.
Yes, HR compliance audits are essential for companies to meet labour law requirements. While the audit itself may not always be legally mandated, compliance with laws is mandatory, making audits necessary.
Most businesses in India conduct compliance audits annually. However, large companies or industries with frequent inspections often conduct them quarterly.
They can be performed internally by HR teams or externally by professional compliance consultants. Outsourcing audits ensures unbiased results and expert guidance.
Auditors check payroll records, employee contracts, PF/ESI filings, leave registers, gratuity records, and POSH compliance documents. The checklist depends on industry and state laws.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

