Exporters need to understand GST for export of goods and services to claim benefits and avoid compliance issues.
In this guide, we take you through GST implications of exporting goods or services, the rules, refund process, and compliance requirements.
Exports Under GST Regime
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework, exports of goods and services are treated as zero-rated supplies.
This means that exporters are not required to pay GST on the exported goods or services, yet they are entitled to claim refunds for any GST paid on inputs and input services used in making those exports.
This zero-rated benefit aims to promote Indian exports by removing the domestic tax burden, improving cash flow, and enhancing international competitiveness.
Zero-Rated Supply Under GST
Under Section 16 of the IGST Act, exports are classified as zero-rated supplies, which offers two major tax benefits:
- No GST is charged on export invoices (i.e., 0% tax rate).
- Exporters can claim refunds of Input Tax Credit (ITC) on goods and services used for making those exports.
This mechanism ensures exports are tax-neutral, aligning with global best practices and the destination-based taxation principle, GST is levied where goods or services are consumed, not where they originate.
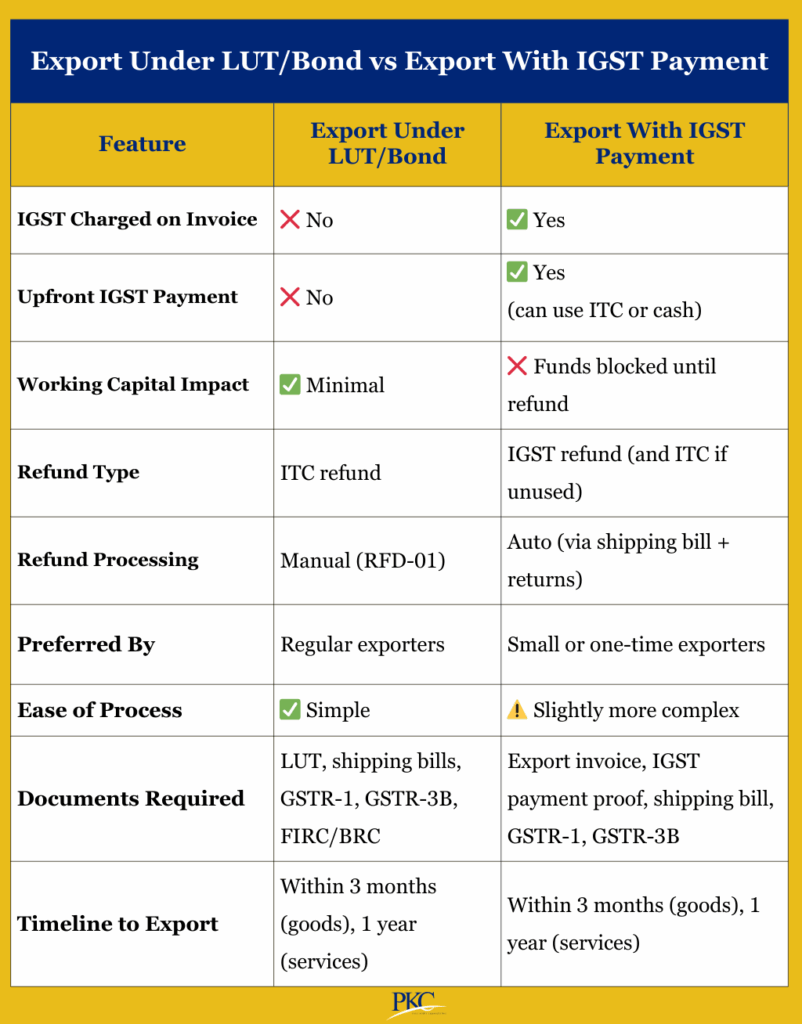
Ways to Export Under GST
Exporters have two methods to avail GST benefits under the zero-rated supply mechanism.
1. Export Under Bond or LUT (Letter of Undertaking)
This is the most preferred and widely used method, especially for regular exporters.
Under this method, exporters are not required to pay Integrated GST (IGST) on their export invoices.
Instead, they must submit a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or Bond to the GST department, committing to fulfill export obligations within prescribed timelines.
Key Steps to Export Under LUT/Bond:
- Apply for LUT/Bond:
- File Form GST RFD-11 online via the GST Portal.
- LUTs are valid for one financial year and easy to renew.
- Exporters not eligible for LUT must furnish a Bond with a bank guarantee.
- Export Without Charging IGST:
- Issue a zero-rated tax invoice.
- Clearly mention it is an export under LUT/Bond.
- Maintain Export Evidence:
- For goods: Shipping bill, customs clearance, Bill of Lading/Airway Bill.
- For services: Receipt in convertible foreign currency, FIRC/BRC, and place of supply outside India.
- File GST Returns:
- Report export details in GSTR-1 (Table 6A/6B).
- Declare eligible ITC and claim refund via Form RFD-01.
Top Benefits:
- No IGST upfront, hence no working capital blockage.
- Single refund process (for ITC only).
- Simple and preferred route for most exporters.
- Ideal for regular exporters who want to optimize cash flow
2. Export With Payment of IGST
This method is often used by new, infrequent, or small exporters or when LUT is unavailable.
Here, the exporter charges and pays IGST on the export invoice and then claims a refund after the export is completed.
Key Steps to Export With IGST Payment:
- Issue Export Invoice with IGST: Charge applicable IGST rate on the invoice.
- Pay IGST Liability: Use Input Tax Credit (ITC) or pay in cash while filing GSTR-3B.
- File GST Returns & Shipping Bill:
- Report export in GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B.
- File shipping bill with customs.
- Claim Refund: No separate application needed. Your shipping bill + GSTR-1 acts as a deemed refund application. Refund is automatically processed after customs-GST system reconciliation.
Top Benefits:
- Streamlined refund (usually faster than ITC route).
- Reduces refund complexity, as ITC and IGST refund can be separated.
- Ideal for small/infrequent exporters who can afford temporary cash outflow
Its major disadvantage is that working capital is blocked until the refund is processed. Also, if ITC is insufficient, IGST must be paid in cash.
GST Rules for Export of Goods & Services
Under the GST regime, both export of goods and export of services are considered zero-rated supplies.
However, the treatment, conditions, and documentation for each differ.
1. Export of Goods As Per GST Rules
Goods are considered exported when they are physically moved from India to a place outside India.
They can be exported as one of the two options:
- Under LUT/Bond: No IGST charged; refund of accumulated Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- With IGST Payment: IGST is paid; refund of IGST after export
GST Conditions for Exported Goods:
- Goods must be exported within 3 months from invoice date (extendable by GST Commissioner).
- The supplier must be in India, while the recipient must be outside India.
- Goods must physically leave India
- Payment must be in convertible foreign exchange or INR (if permitted by RBI)
- Key Documents:
- Tax invoice (mentioning LUT/IGST, as applicable)
- Shipping Bill / Bill of Export
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Export General Manifest (EGM)
- Commercial Invoice
- Customs clearance proof (Let Export Order)
Refund Process:
- Under LUT: Claim refund of ITC via Form RFD-01.
- With IGST payment: Refund is often automatic upon filing GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and customs validation.
2. Export of Services As Per GST Rules
As per Section 2(6) of the IGST Act, a service is considered an export only if all of the following are true:
- Supplier is in India
- Recipient is outside India
- Place of Supply is outside India
- Payment must be received in convertible foreign exchange or INR (if allowed by RBI).
- Supplier and recipient must not be merely different establishments of the same legal entity across countries. IQualifies as an export only when both entities are treated as distinct persons under the law.
Services can be exported the same as goods i.e. under LUT/Bond or with IGST Payment.
GST Conditions for Exported Services:
- Payment must be received within 1 year from the date of invoice
- Place of Supply is the location of recipient and must be outside India
- Key Documents:
- Tax invoice marked as “Export of Services”
- Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) or Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC)
- Contract/Agreement with foreign client
- Proof of recipient location (e.g., client address, registration)
The refund process is the same as goods.
GST Refund Process for Exporters
Exporters can claim GST refunds through two main routes:
1. Automated Refund of IGST Paid on Exported Goods/Services
This is for the exporter who charges IGST on the invoice. In such cases, no separate refund application is required.
Process:
- File GSTR-1: Report export details under Table 6A
- File GSTR-3B: Declare IGST liability on exports
- Shipping Bill Submission: File a shipping bill with matching invoice details
- Customs Verification: ICEGATE matches GSTR-1 data with the shipping bill and Export General Manifest (EGM)
- Refund Credit: Upon successful validation, IGST refund is automatically credited to the exporter’s bank account.
Key Documents:
- GST Invoice (with IGST)
- Shipping Bill
- GSTR-1 & GSTR-3B
- Export General Manifest (EGM)
Timeline:
- Refund is typically credited within 15–30 days after export confirmation.
- Interest at 6% per annum is payable on delays beyond 60 days.
2. Refund of Unutilized Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Applicable when exports are made without payment of IGST, under Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or bond.
Refund is manually processed by the jurisdictional GST officer.
Process:
- File LUT/Bond: Submit online via GST portal.
- File Returns:
- GSTR-1: Report exports in Table 6A (goods) or 6B (services).
- GSTR-3B: Declare zero-rated supply and ITC.
- Submit Refund Application (RFD-01):
- Navigate: GST Portal → Services → Refunds → Application for Refund.
- Select: “Refund of unutilized ITC on export without payment of tax”.
- Upload Supporting Documents.
- Verification & Approval:
- Jurisdictional officer reviews application.
- Provisional refund (up to 90%) may be issued within 7 days.
- Final refund sanctioned after scrutiny.
Key Documents:
- LUT/Bond copy
- Export Invoices
- Shipping Bill / Airway Bill
- Bank Realization Certificate (BRC) / FIRC (for services)
- ITC ledger and GSTR-1/GSTR-3B copies
Timeline:
- Refund sanctioned within 60 days.
- Interest applicable beyond this limit.
Important Deadlines
- Refund Application: Must be filed within 2 years from the relevant date:
- Goods: Date of export/shipping bill.
- Services: Date of receipt of foreign currency or invoice issuance (whichever is later).
- Export Timeframe: Goods must be exported within 3 months of invoice (extendable).
- Realization for Services: Foreign exchange must be received within 1 year of invoice.
Best Practices to Ensure Faster GST Refunds on Exports
- Use matching GSTINs across all documents.
- File all GST returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B) accurately and on time.
- Reconcile ITC using GSTR-2B/2A.
- Keep supporting export documents digitally organized.
- Monitor refund status via GST Portal → Refund → Track Application
Special Cases of GST Applicability on Exports
There are several special cases where the general zero-rated treatment may have specific provisions or exceptions. Here’s a look at these:
1. Deemed Exports
Deemed exports refer to supplies within India that are treated as exports under GST law, even though the goods do not physically leave the country.
GST is charged at the time of supply, but the recipient or the supplier can claim a refund of the tax paid.
Examples of Deemed Exports:
- Supply to Export Oriented Units (EOUs)
- Supplies under Advance Authorization or EPCG schemes
- Supplies to projects funded by UN agencies or foreign governments
2. Supplies to Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
Supplies made to SEZ developers or SEZ units are considered zero-rated supplies under GST, similar to exports.
Conditions:
- Goods or services must be supplied to an authorized SEZ unit or developer
- The exporter can either export without payment of IGST by furnishing a LUT or bond, or pay IGST upfront and claim a refund.
3. Merchant Exports
In cases of merchant exports, traders (not manufacturers) buy goods domestically and export them.
These exporters can purchase goods at a concessional GST rate of 0.1%.
Merchant exporters can claim zero-rated GST on the goods exported by providing the necessary documentation.
Conditions for Merchant Exporters:
- The goods must be exported within 90 days from the date of purchase.
- Proof of export must be provided to the supplier.
4. Supplies to International Tourists (Tax-Free Shopping)
Under India’s Tax Refund Scheme for Tourists, certain goods (not services) sold to foreign tourists can be considered exports if the tourist takes the goods out of India.
GST Treatment:
- Goods purchased by foreign tourists and carried out of the country are treated as exports.
- Tourists can claim a tax refund on eligible purchases under the Tourist Refund Scheme
Key Compliance Requirements for Export of Goods & Services
To benefit from zero rated exports, exporters must meet several compliance requirements.
1. GST Registration: Exporters must have valid GST registration, as exports are treated as inter-state supplies.
2. Documentation: Invoices must be GST-compliant, mentioning “SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT.”
For goods, the shipping bill must match the GST invoice.
For services, a Bank Realization Certificate (BRC) or Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) is required to prove payment in foreign currency.
3. Return Filing: Exporters must report exports in GSTR-1 (Table 6A) and correctly reflect IGST in GSTR-3B. Timely filing ensures smooth refund processing.
4. Export Options: Exporters can choose to export under a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) without IGST or pay IGST and claim a refund. LUTs must be filed annually; otherwise, a bond may be required.
5. Foreign Exchange Compliance: Export proceeds must be realized within 9 months per FEMA rules. BRC is needed to support refund claims.
6. Place of Supply Rules: The place of supply must be outside India, and the supplier must be located in India to qualify as an export.
7. Customs & Data Matching: Invoice and shipping bill details must match with GST and customs filings (ICEGATE) to avoid delays.
8. Refund Process: Refund claims must be filed via GST RFD-01 within two years of export with supporting documents.
9. Record Maintenance: Exporters must maintain auditable records for at least five years and regularly reconcile data for accuracy and audit readiness.
FAQs on GST Implications for Importers and Exporters
1. Is GST required for export business?
Yes, GST registration is generally required for exporters even if turnover is below the threshold. Exports are treated as zero-rated supplies under GST.
2. What is the GST rate for export?
The GST rate for exports is 0% as they are zero-rated supplies. You can export with or without IGST payment and still claim refunds.
3. What is 0.1% GST for export?
It’s a concessional GST rate for merchant exporters buying goods for export.They must export within 90 days and provide proof to claim this benefit.
4. What are the implications of GST in export chain?
GST makes exports tax-free while allowing input tax credit refunds. It also enforces stricter compliance through documentation and return filing.
5. How to calculate GST refund against export of goods?
Refund = GST paid on inputs and services minus GST payable on exports. Since exports are zero-rated, refund is usually equal to input tax credit.
6. Do exporters get GST refunds?
Yes, exporters can claim refunds of IGST paid or unused ITC. The refund process depends on whether they export with or without IGST payment.
7. Is GST registration mandatory for export of services below 20 lakhs?
Yes, GST registration is compulsory for service exporters regardless of turnover. This is because exports are treated as inter-State supplies.
8. Is GST applicable on export of all services?
No GST is charged if conditions of Section 2(6) of the IGST Act are met. These include foreign payment, foreign recipient, and place of supply outside India.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

