Buying a company without proper checks can turn into a costly mistake. That’s why having a due diligence checklist for buying a company in India is essential.
Learn with us the areas a due diligence checklist must cover and download a free sample PDF that can guide to your buying decision.
What is Due Diligence in India?
Due diligence is a structured and comprehensive investigation of a company or asset before entering into a significant transaction. This may mean acquisition, investment, merger, or partnership.
Due diligence process ensures that the buyer or investor has verified all material facts about the target entity and is aware of any likely legal, financial, or operational risks that could result in severe consequences.
Importance of a Due Diligence Checklist When Buying a Company
A due diligence checklist is an essential tool for buying a company in India in the following ways:
1. Uncovers Hidden Risks and Liabilities
A structured checklist helps identify red flags such as:
- Unreported debts or liabilities
- Pending or historical litigation
- Tax defaults or non-compliance notices
- Regulatory or licensing issues
Identifying these risks early helps avoid financial loss, legal exposure, or reputational damage.
2. Verifies Financial Stability and Accuracy
The checklist prompts a thorough review of:
- Audited financial statements
- Cash flow reports
- Accounts receivable and payable
- Asset ownership and encumbrances
This verification ensures the seller’s financial claims are accurate and that the valuation of the business is fair.
3. Ensures Compliance with Indian Laws
India’s legal environment is governed by multiple authorities, including:
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council
- Income Tax Department
The checklist ensures compliance with all applicable laws and mitigates the risk of future regulatory penalties.
4. Strengthens Negotiation and Deal Structuring
Findings from the due diligence process are powerful tools for negotiation. For example:
- Price adjustments for undisclosed liabilities
- Specific indemnities or escrow arrangements
- Deciding between a share purchase and an asset purchase
This leads to better-informed decisions and stronger contractual protections.
5. Supports Post-Acquisition Integration
Due diligence helps assess operational factors such as:
- Supply chain logistics
- Key personnel retention
- Customer and vendor contracts
- IT infrastructure and data security
Understanding these components in advance allows for smoother integration post-acquisition and reduces disruption to the business.
6. Creates a Transparent Record
Maintaining a detailed due diligence file provides:
- Documentation for internal approvals or board reviews
- A defense in case of post-deal claims or regulatory inquiries
- Historical insight for future expansion or divestment strategies
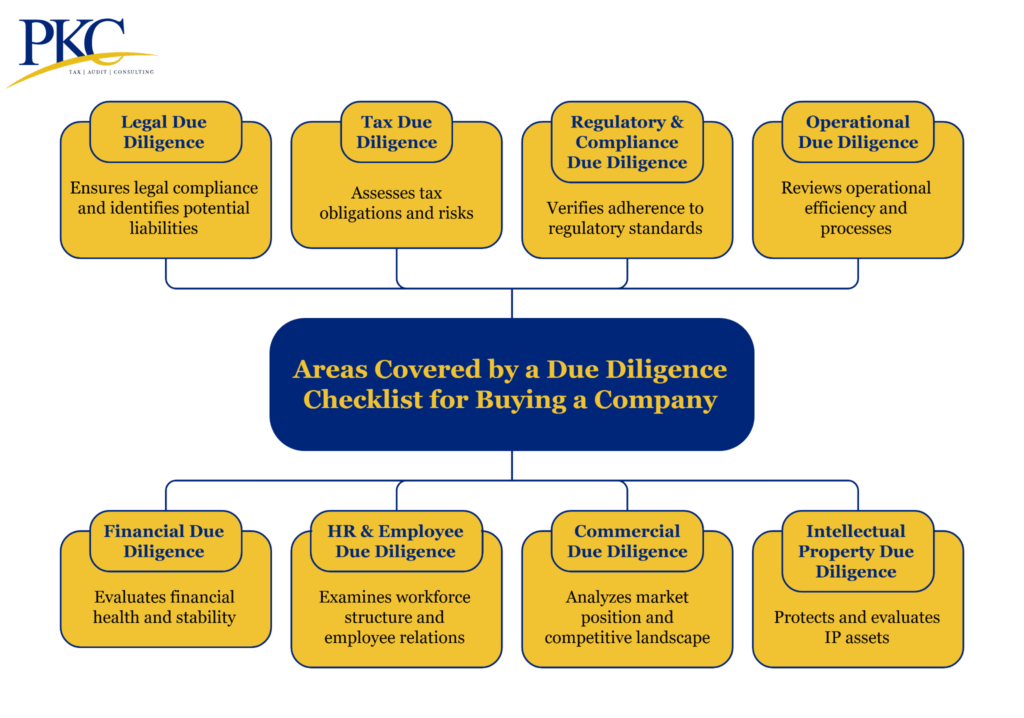
Areas Covered by a Due Diligence Checklist for Buying a Company
A comprehensive due diligence process is needed before buying a company. This involves evaluating different areas including:
1. Legal Due Diligence
Assesses the company’s legal standing and exposure to ensure smooth ownership transfer and regulatory compliance.
Areas Assessed:
- Company Documents: MoA, AoA, incorporation certificate, and amendments.
- Shareholding & Governance: Share patterns, board resolutions, shareholder agreements.
- Contracts & Agreements: Key commercial agreements, leases, vendor/customer contracts, change-of-control clauses.
- Litigation & Disputes: Pending or past legal disputes, arbitration, regulatory cases.
- Licenses & Approvals: Validity of business licenses and approvals.
- Intellectual Property Ownership: Trademark, patent, copyright ownership.
2. Financial Due Diligence
Ensures that the valuation is accurate and that there are no hidden financial risks or overstatements of profitability.
Areas Assessed:
- Audited Financial Statements: 3–5 years of audited balance sheets, P&L, cash flows.
- Working Capital Analysis: Evaluation of working capital cycles, inventory levels, receivables, and payables.
- Revenue & Earnings: Quality of earnings, recurring vs. non-recurring income, margins.
- Assets & Liabilities: Verification of fixed assets, current assets, long-term liabilities, and contingent liabilities.
- Debt Obligations: Loans, guarantees, repayment terms.
3. Tax Due Diligence
Identifies potential tax exposures that may transfer to the buyer post-acquisition. These may carry future financial and reputational risks.
Areas Assessed:
- Income Tax Compliance: Returns, TDS compliance, advance taxes.
- GST & Indirect Tax: GST filings, ITC claims, indirect tax payments, and reconciliations.
- Transfer Pricing: Compliance for cross-border transactions.
- Tax Disputes: Pending assessments, audits, notices.
4. HR & Employee Due Diligence
Helps prevent future employment-related liabilities and ensures workforce continuity post-acquisition.
Areas Assessed:
- Employment Contracts: Review of terms, compensation, non-compete clauses, and termination rights.
- Labor Law Compliance: Verification of compliance with PF, ESIC, Gratuity, Minimum Wages, Bonus Act, Maternity Benefits, etc.
- Employee Disputes: Identification of ongoing or past labor-related litigation or grievances.
- Organizational Structure: Assessment of roles, reporting hierarchy, key personnel, and retention strategies.
5. Regulatory & Compliance Due Diligence
Ensures the company complies with applicable laws and sector-specific regulations to avoid penalties or disruptions.
Areas Assessed:
- Companies Act Compliance: Verification of statutory filings with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Sector-Specific Regulations:
- SEBI: If the company is listed.
- RBI: If it’s a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC).
- FEMA: For companies with foreign investments.
- IRDAI, TRAI, FSSAI, etc., based on the industry.
- Environmental & Safety: Pollution board approvals, workplace safety standards.
6. Commercial Due Diligence
Evaluates the company’s market position, competitive strengths, customer base, and strategic fit.
Areas Assessed:
- Market Dynamics: Industry trends, market size, demand cycles, and growth potential.
- Customer Base: Analysis of major clients, customer contracts, and concentration risks.
- Revenue Streams: Sustainability, diversification, and profitability of different revenue channels.
- Competitor Landscape: Review of market share, pricing strategies, and brand positioning.
7. Operational Due Diligence
Examines internal processes, infrastructure, and systems critical to ongoing business performance.
Areas Assessed:
- Manufacturing & Logistics: Review of production facilities, equipment, and capacity utilization.
- Vendor & Supply Chain: Evaluation of key vendor relationships, dependencies, and risks.
- Real Estate & Leases: Review of property ownership or lease agreements and obligations.
- Technology & IT Systems: Cybersecurity policies, ERP systems, scalability, and compliance with data protection laws (e.g., DPDPA 2023).
8. Intellectual Property (IP) Due Diligence
Confirms ownership and protection of intangible assets, which can be core to company value.
Areas Assessed:
- IP Ownership: Verification of registered trademarks, copyrights, patents, designs, and domain names.
- Infringement Risks: Examination of legal disputes involving IP rights or third-party claims.
- Licensing Agreements: Review of inbound and outbound IP licenses.
- Employee Assignments: Ensuring IP developed by employees or contractors is properly assigned to the company.
Comprehensive Due Diligence Checklist for Buying a Company India
Here’s a sample of how a due diligence checklist for buying a company in India should look like.
You can customize this based on the specific industry, transaction size, and risk profile of your target company.
You can also reach out to professionals at PKC, for complex areas such as tax, legal, and technical due diligence:
How Can PKC Help With Due Diligence Checklist?
✅ 200+ expert consultants across all due diligence verticals
✅ Tax scrutiny and appeals specialists minimize acquisition risks
✅ Technology-enabled MIS reporting for transparent deal evaluation
✅ Industry-specific expertise across 1500+ successful client engagements
✅ Complete statutory compliance verification across all Indian regulations
✅ Advanced automation tools accelerate due diligence timeline
✅ End-to-end implementation support beyond just advisory services
✅ Cost-effective solutions specifically designed for family businesses
✅ Post-acquisition integration consulting for seamless business transition
Sector-Specific Due Diligence in India
While legal, financial, tax, and HR due diligence is standard when acquiring a business in India, some sector-specific diligence is needed to identify hidden risks. Here’s a look at top sectors:
1. Technology & Startups
Startups often depend heavily on IP and venture capital, any gaps here can reduce valuation.
- IP ownership: source code, patents, trademarks, licensing.
- Cap table review and VC investment terms.
- SEZ or DPIIT startup recognition benefits.
- Cybersecurity policies and DPDPA 2023 compliance.
- Export revenue and FEMA compliance.
2. Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
Pharma companies face high compliance scrutiny, missing licenses can shut down operations.
- Drug manufacturing and marketing licenses.
- GMP/WHO/GDP compliance (Schedule M).
- Clinical trial approvals and ethical committee records.
- IP and patent protection of formulations and generics.
- NLEM product pricing under NPPA control.
3. Real Estate & Construction
In India, land disputes are common, title verification is the most critical step.
- Title verification and encumbrance search.
- RERA registration and project compliance.
- Building plan, fire safety, and environmental approvals.
- Land zoning and conversion status (agri to commercial/industrial).
- EPC/construction contracts and pending litigation.
4. Banking, NBFCs & Financial Services
Without proper RBI approval, ownership transfer in NBFCs and banks may not be valid.
- Validity of RBI license (for NBFCs), SEBI registration (brokers/AIFs).
- CRAR and provisioning norms.
- Loan book quality and NPA exposure.
- KYC/AML/UDIN compliance and RBI inspections.
- Fintech: Security of tech platform and data systems.
5. Manufacturing & Industrial Companies
Failure to meet pollution or labor laws can result in shutdowns or penalties.
- CTE/CTO from State Pollution Control Boards.
- Factory Act compliance, worker safety, and EHS protocols.
- Labour law adherence: minimum wages, gratuity, PF/ESI.
- Zoning approvals and electricity/water infrastructure.
- Supply chain contracts and machinery audit.
6. E-commerce & Retail
Foreign investment in multi-brand retail has strict restrictions in India.
- FDI model compliance (marketplace vs. inventory).
- E-commerce Rules, 2020: refund policies, transparency, grievance redressal.
- Seller/vendor contracts.
- Consumer data protection and IT infrastructure.
- Logistics, warehousing, and 3PL agreements.
Common Risks Uncovered During Due Diligence for Buying a Company
Financial Risks
- Inflated revenues, understated expenses, or manipulated EBITDA
- Unrecorded liabilities such as guarantees, related-party dues, or pending loans
- Poor cash-flow management or dependence on a few major customers
- Inaccurate inventory valuation or obsolete stock
Tax & Regulatory Risks
- Unpaid GST, TDS, income tax, or pending assessments
- Non-compliance with MCA/RoC filings and secretarial standards
- Wrong GST classification leading to future tax demands
- Tax exposures from aggressive accounting or transfer pricing
Legal & Contractual Risks
- Undisclosed litigation across commercial, labour, tax, or property matters
- Missing or weak vendor, customer, distributor, or employment contracts
- Unfavourable terms, lock-ins, indemnities, or penalties
- IP gaps including unregistered trademarks or unlicensed software
HR & Labour Risks
- Incorrect payroll, PF/ESI non-compliance, or misclassified contract workers
- Hidden employee disputes or settlements
- Key employees likely to exit due to lack of retention mechanisms
Operational Risks
- Broken processes, missing SOPs, or founder dependency
- Outdated IT, poor data management, or unreliable systems
- Inefficient supply chain or heavy vendor concentration
- Quality control lapses affecting customer satisfaction
Commercial & Market Risks
- Declining revenues, loss of major clients, or falling market share
- Inflated sales pipeline or unverifiable customer relationships
- High churn or negative online reputation
- Over-reliance on a single geography or product segment
Environmental & Industry-Specific Risks
- Expired licences (pollution, factory, FSSAI, etc.)
- Non-compliance with environmental norms or safety standards
- Sector-specific issues such as RERA, pharma GMP, or NBFC regulations
Technology & Data Risks
- Weak cybersecurity, no backups, or outdated infrastructure
- Non-compliance with data-privacy rules under the DPDP Act
- Unlicensed or pirated software
Reputation & ESG Risks
- Negative press, customer complaints, or social media concerns
- Poor ESG practices, unsafe working conditions, unethical sourcing
- Undisclosed related-party transactions or conflicts of interest
Deal-Structure Risks
- Confusion between asset purchase and share purchase implications
- Improper valuation, unrealistic projections, or manipulated performance metrics
- Earn-out risks tied to doubtful or unverifiable milestones
FAQs on Due Diligence Checklist for Buying a Company
Due diligence is the process of reviewing a company’s legal, financial, tax, and operational records before buying or investing. It helps identify risks and confirms that the company is compliant with Indian laws.
It protects buyers from hidden risks/ liabilities, fraud, and non-compliance issues. Without due diligence, buyers risk lawsuits, penalties, or overpaying for a business.
Due diligence may take up to 6 weeks, depending on the complexity of the company and the number of documents. Larger companies or regulated sectors may take longer.
Usually, legal, financial, and tax experts such as law firms, auditors, or consultants handle due diligence. Buyers often hire a specialized team to cover all areas.
Key documents include financial statements, incorporation documents, tax returns, licenses, and contracts. The exact list depends on the sector and deal type.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

