From statutory to labour, and environmental audits, understanding different types of compliance audits in India is needed for running a legally safe and successful business.
Find out the main types of compliance audits for businesses and see which one you may need.
What are Compliance Audits?
A compliance audit is a formal, independent review conducted to determine whether a business or organization is adhering to applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies.
During the audit, experts (like CAs or compliance officers) review documents, processes, and financial records. They see whether everything is done legally and ethically.
A typical compliance audit assesses the organization’s conformity to:
- External laws such as Companies Act, 2013, GST, Income Tax Act, Labour laws, etc.
- Internal policies and procedures, such as employee handbooks, codes of conduct, corporate governance frameworks, etc.
These audits are usually conducted by:
- Internal Auditors: Employees within the organization
- External Auditors: Independent CAs or legal consultants
- Government Authorities: Regulatory bodies like the Income Tax Department, EPFO, SEBI, or Pollution Control Boards
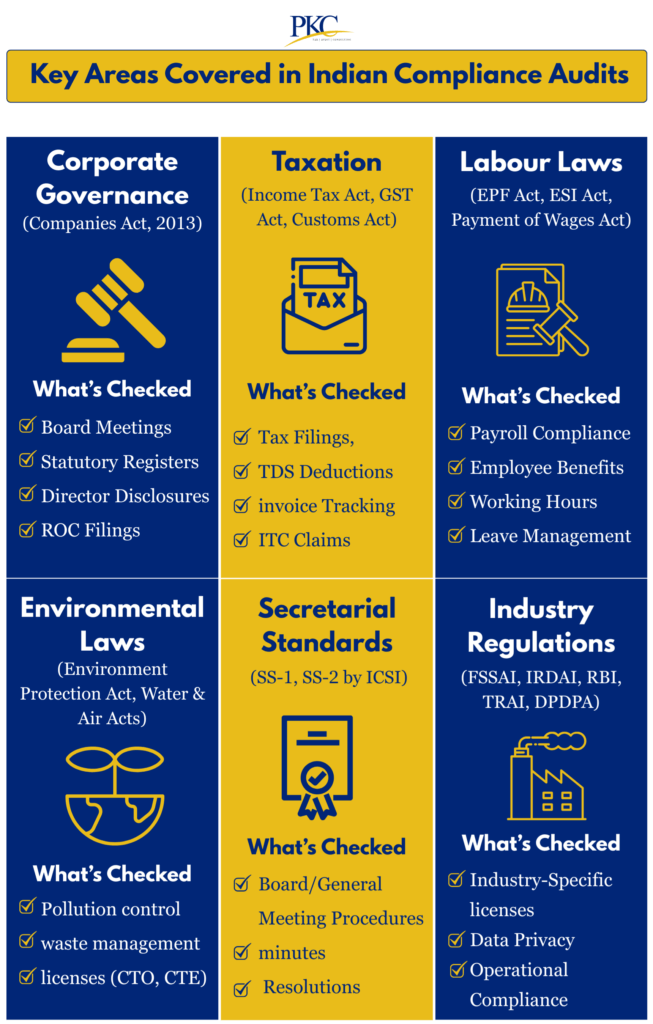
7 Main Types of Compliance Audits Businesses Must Consider in India
Compliance audits help identify legal gaps, prevent penalties, and demonstrate corporate responsibility to stakeholders.
Here are the key types of compliance audits for businesses in India:
1. Statutory Compliance Audits
Statutory audits are legally mandated audits under various Indian laws such as the Companies Act, 2013, Income Tax Act, and other financial statutes.
These audits aim to verify whether a company complies with statutory reporting and disclosure requirements.
These audits cover the following sub categories:
A. Financial (Statutory) Audit
A financial audit checks whether the company’s financial statements (balance sheet, profit & loss account, cash flow statement) are accurate and fair.
It is usually conducted by chartered accountants and is mandatory for all companies except dormant or small companies meeting exemption criteria
Focus Areas:
- Verification of financial statements (Balance Sheet, P&L, Cash Flow)
- Compliance with Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS)
- Evaluation of internal financial controls and fraud risks
Outcome: Audit Report (Clean(Unmodified), Qualified, Adverse, or Disclaimer) submitted to shareholders and filed with MCA
B. Tax Audit
Under Section 44AB of the Income Tax Act, businesses with turnover above certain limits must undergo a tax audit.
The audit prevents underpayment of taxes and avoids penalties from the Income Tax Department.
The auditor examines:
- Accuracy of income tax returns
- Proper filing of GST returns
- Compliance with TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
- Transfer pricing for international transactions
Applicability:
- Businesses with turnover exceeding ₹1 crore (₹10 crore if cash transactions ≤5%)
- Professionals with gross receipts over ₹50 lakh
Outcome: Form 3CA/3CB with Form 3CD submitted electronically to the Income Tax Department
C. Secretarial Audit (Section 204, Companies Act, 2013)
A secretarial audit is conducted by a Practising Company Secretary (CS). It ensures compliance with corporate governance rules and company law.
It improves transparency and ensures that companies are managed ethically and in line with the law.
It is applicable for all listed companies, public companies meeting defined requirements and private companies that are a Subsidiary of a secretarial audit applicable public companies.
The audit covers:
- Board meetings and shareholder meetings
- Maintenance of statutory registers
- Compliance with SEBI regulations for listed companies
- Adherence to secretarial standards
Outcome: Secretarial Audit Report in Form MR-3 attached to Board’s Report
D. Cost Audit (Section 148, Companies Act, 2013)
The audit ensures pricing transparency, cost control, and compliance with cost accounting standards
It is mandatory for companies in specified industries like cement, fertilizers, steel, electricity, etc.
Key Requirements:
- Maintenance of cost records as per prescribed formats
- Filing of CRA-3 report with MCA
2. Regulatory Compliance Audits
These audits ensure that businesses adhere to sector-specific regulations prescribed by regulatory authorities such as RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, TRAI, and others.
A. SEBI Compliance (for Listed Entities & Market Intermediaries)
- Annual secretarial compliance audit
- Insider trading compliance
- Corporate governance audit
- Audit of brokers, mutual funds, credit rating agencies
B. RBI Compliance (Banks & NBFCs)
- Risk-based supervision
- Asset Liability Management audit
- KYC/AML compliance
- Concurrent and statutory audits
C. IRDAI Compliance (Insurance Companies)
- Actuarial audit
- Investment and solvency compliance
- Policyholder protection audit
D. TRAI Compliance (Telecom Operators)
- Tariff compliance
- Quality of Service (QoS) audit
- Spectrum and interconnection usage compliance
3. Labour Law Compliance Audits
Labour law compliance audits assess whether a company complies with applicable employment laws that govern wages, benefits, working conditions, and employee rights.
They cover central and state laws including:
- Factories Act, 1948: Safety, health, and welfare of workers
- Employees’ Provident Funds Act, 1952 (EPF): Provident fund contributions and returns
- Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 (ESI): Health and medical benefits
- Payment of Wages Act, 1936: Timely and fair wage disbursement
- Contract Labour Act, 1970: Engagement and welfare of contract workers
- Payment of Bonus Act, 1965: Bonus calculation and disbursement
- PoSH Act, 2013: Prevention of sexual harassment at the workplace
- Shops and Establishments Acts (State-wise): Working hours, leave, and employee benefits
- Professional Tax & Labour Welfare Fund Acts
These audits help companies avoid labour disputes, ensure employee welfare, and build a healthy workplace culture.
4. Environmental Compliance Audits
This is a structured evaluation of whether an organization is following applicable environmental laws and regulations.
This is especially critical for industries with significant environmental impact, such as manufacturing, mining, chemicals, and energy.
These audits are primarily governed by environmental laws like:
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- Hazardous Waste Management Rules
- Various rules related to e-waste, plastic waste, and noise pollution
Environmental audits assess whether:
- Required environmental clearances and consents (CTE, CTO) are in place and valid.
- Air and water emissions are within permissible limits.
- Waste, especially hazardous waste, is stored, treated, and disposed of lawfully.
- Pollution control equipment (like ETPs, scrubbers, stacks) is functioning effectively.
- Legal filings and environmental reports are submitted to the relevant State or Central Pollution Control Boards.
Failure to comply can result in heavy penalties, plant closures, criminal liability for management, and reputational damage.
These audits also demonstrate an organization’s commitment to sustainable and responsible business practices.
5. IT & Data Protection Compliance Audits
An IT and Data Protection Audit evaluates how well an organization protects its information systems and manages personal and sensitive data.
These audits have become critical with rising cybersecurity threats and the introduction of India’s new digital data protection law.
Key laws and frameworks include:
- Information Technology Act, 2000
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDPA)
- SPDI Rules, 2011
- International standards like ISO/IEC 27001 for information security
These audits typically look into:
- Data privacy compliance (lawful consent, data minimization, individual rights).
- IT security controls, including access restrictions, firewalls, encryption, and network monitoring
- Readiness to respond to cyber incidents, including data breach protocols.
- Compliance with requirements related to data localization and cross-border data transfers.
- Review of IT policies, backup and disaster recovery systems, and user access management
6. Internal Compliance Audits
An Internal Compliance Audit is an internal review of a company’s operations, controls, and risk management practices.
Unlike external audits, these are conducted proactively by management to improve internal governance and efficiency.
Internal audits act as an early warning system, helping management correct issues before they are caught by regulators or external auditors.
While not governed by a specific statute, internal audits are supported under:
- Companies Act, 2013 (for certain classes of companies)
- Guidelines from the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA)
Internal audits can be wide-ranging, depending on the company’s focus, and may include:
- Reviewing financial controls and accounting accuracy
- Checking for efficiency in procurement, production, and sales processes
- Assessing risk management and fraud prevention systems
- Ensuring compliance with the company’s own policies, codes of conduct, and delegations of authority
- Identifying operational inefficiencies or vulnerabilities
7. Industry-Specific Compliance Audits
Compliance audits are mandatory in sectors that operate under unique or sensitive regulatory environments.
These audits ensure that companies follow rules specific to their industry, often enforced by sectoral regulators.
Non-compliance in these sectors can lead to loss of license, regulatory sanctions, public backlash, or even a ban on operations.
Governing Bodies and Examples:
| Industry | Regulator | Audit Focus / Compliance Areas |
| Banking & NBFCs | RBI | Capital adequacy, NPA classification, KYC/AML norms, lending practices |
| Insurance | IRDAI | Solvency margins, policyholder protection, investment compliance |
| Capital Markets | SEBI | Insider trading prevention, board governance, disclosure norms |
| Food & Beverage | FSSAI | Food safety, hygiene, labeling, adulteration controls |
| Pharmaceutical | CDSCO | GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), GLP (Good Laboratory Practices), clinical trials |
| Telecom | TRAI | Service quality, tariff compliance, customer grievance redressal |
| Export/Import | DGFT & Customs | Compliance with foreign trade policy and customs regulations |
These audits check whether:
- Regulatory filings and disclosures are timely and accurate.
- Operational practices comply with industry-specific norms and safety standards
- Licensing, approvals, and authorizations are in place and valid
- Consumer and investor protection standards are being followed
What Sets PKC’s Compliance Audit Services Apart?
At PKC, we believe compliance isn’t a checklist—it’s a strategic advantage. Our audit services are engineered to be a proactive shield and a growth catalyst for your business.
Here’s what sets us apart:
✅The PKC Ecosystem: Your 360-Degree Shield
We are your single-point compliance partners. Our integrated team of CAs, CSs, and MBAs works in unison, offering a holistic view that covers financial, legal, and strategic risks.
This eliminates the inefficiency of managing multiple consultants and ensures no compliance gap goes unseen.
✅Tech-Enabled, Not Just Tech-Assisted
We use our proprietary checklists and smart workflow tools that go beyond standard practices.
This translates to deeper forensic analysis, predictive risk insights, and real-time tracking, transforming your compliance from a reactive cost into intelligent, data-driven governance.
✅Business-Aligned Compliance
We dive deep to understand your unique industry and business model. Our compliance audits protect your specific operational risks and strategic goals.
We provide actionable, business-savvy recommendations that enhance efficiency and support your growth trajectory.
✅Clarity as a Core Promise
Our reports are renowned for their unmatched clarity and actionable insights, presented in a straightforward manner.
We empower your leadership to make confident, strategic decisions.
Get in touch for a FREE Consultation
Why Compliance Audits in India Are Important
Apart from regulatory obligation, Compliance audits are essential for long-term sustainability, reputation management, and operational efficiency for the following reasons:
1. Legal Protection and Risk Mitigation: Businesses in India have to follow multiple rules, and there are heavy penalties for non-compliance. Proactive audits help prevent financial, operational, and reputational risks.
Compliance audits help
- Avoid fines for late GST or income tax filings.
- Prevent disruptions like license revocation or business shutdowns.
- Reduce legal exposure by identifying issues early.
2. Builds Trust with Stakeholders: A strong compliance record signals transparency and good governance.
Regular audits enhance credibility and build stakeholder confidence.
- Investors favour low-risk, compliant businesses.
- Banks require audit reports before lending.
- Partners and clients prefer working with law-abiding companies.
3. Enhances Efficiency and Governance: Compliance audits also improve internal operations. The result is a leaner, more agile, and accountable organization.
- Spot inefficiencies in payroll, procurement, taxation
- Strengthen controls to prevent fraud and mismanagement
- Ensure accurate records and policy enforcement
4. Critical for Growth and Transactions: Poor compliance can delay or derail these opportunities. Compliance is essential during strategic milestones:
- M&A due diligence requires full compliance
- IPOs demand ongoing regulatory adherence
- Government tenders often require clean compliance histories
- VC/PE funding depends on thorough compliance checks
5. Protects Brand Reputation: Compliance breaches can quickly damage brand value.
- Audits prevent public scandals and legal actions
- Reflect a commitment to ethical, transparent business
FAQs on Types of Compliance Audits in India
A compliance audit in India checks if a company is following all the laws, regulations, and internal policies that apply to its business. It helps prevent legal trouble and builds trust with stakeholders.
Compliance audits are usually carried out by CAs, company secretaries, cost accountants, or internal compliance teams depending on the type of audit. Sometimes regulators also conduct inspections.
Not all audits are mandatory. Some, like statutory audits and tax audits, are required by law, while others like internal audits are voluntary but highly recommended.
Most mandatory audits are annual, but many companies conduct quarterly or half-yearly audits to stay updated with changing regulations.
Yes, startups must also follow laws such as GST, labour laws, and tax regulations. While they may not need all types of audits, certain compliance checks are mandatory.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

