Written By – PKC Desk, Edited By – Krithika Mohan, Reviewed By – Vignesh
A business operations audit could be the one tool that saves you money, time, and legal trouble. Learn about these audits with this guide.
We explore their importance, process and industry -specific areas of focus. We also share a downloadable free sample business process audit checklist.
What are Business Operations Audits & Why Are They Needed?
A business operations audit a detailed review of a company’s non-financial processes.
It looks at how efficient, cost-effective, risk averse and compliant the business is with Indian laws and standards.
Unlike financial audits, it focuses on operational mechanics:
- Operational workflows (e.g., supply chain, production, sales)
- Compliance with Indian laws
- Resource optimization (cost, time, manpower)
- Risk management (fraud, disruptions, reputation)
They provide actionable insights for enhanced efficiency and sustainable growth.
Importance of Business Operations Audits With Examples
Operations audits can benefit your business in the following ways:
Uncover Hidden Inefficiencies
Identifies wasted time, money, or resources in daily processes.
Example: An operations audit of a Surat-based garment manufacturer discovered its factory machines run at 50% capacity due to poor maintenance schedules. Fixing this could boost output without new investments.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance:
Verifies adherence to Indian laws (GST, labour, tax, data privacy) to avoid penalties.
Example: A Bengaluru IT startup business operations audit revealed missed TDS filings on freelance payments, preventing over heavy fines from the Income Tax Dept.
Reduce Operational Risks:
Finds weaknesses that could lead to fraud, errors, data breaches, or supply failures.
Example: A Delhi retailer’s audit showed no CCTV in its warehouse, allowing employee theft. Installing cameras cut stock losses substantially.
Improve Customer Experience:
Pinpoints process flaws causing delays, errors, or poor service quality.
Example: A Mumbai restaurant chain’s audit linked slow service to kitchen layout. Reorganizing stations reduce order delivery time and improve overall customer experience.
Support Growth & Scalability:
Reveals bottlenecks that hinder expansion, especially for MSMEs relying on temporary fixes (“jugaad”).
Example: A Chennai auto-parts MSME struggles to fulfill pan-India orders. An operations audit found its manual inventory system couldn’t scale. Implementing ERP software would enable 2x growth.
Enhance Profitability:
Directly lowers costs and boosts revenue by optimizing resource use and output.
Example: A Hyderabad e-commerce firm’s audit shows high return rates due to poor packaging. Using better materials would reduce return rates and save lakhs annually.
Build Stakeholder Trust:
Demonstrates to investors, banks (like SBI/HDFC), and regulators (RBI/SEBI) that the business is well-managed.
Example: A Vadodara pharma company used its clean operations audit report to secure a lower-interest loan from a Bank for a new plant.
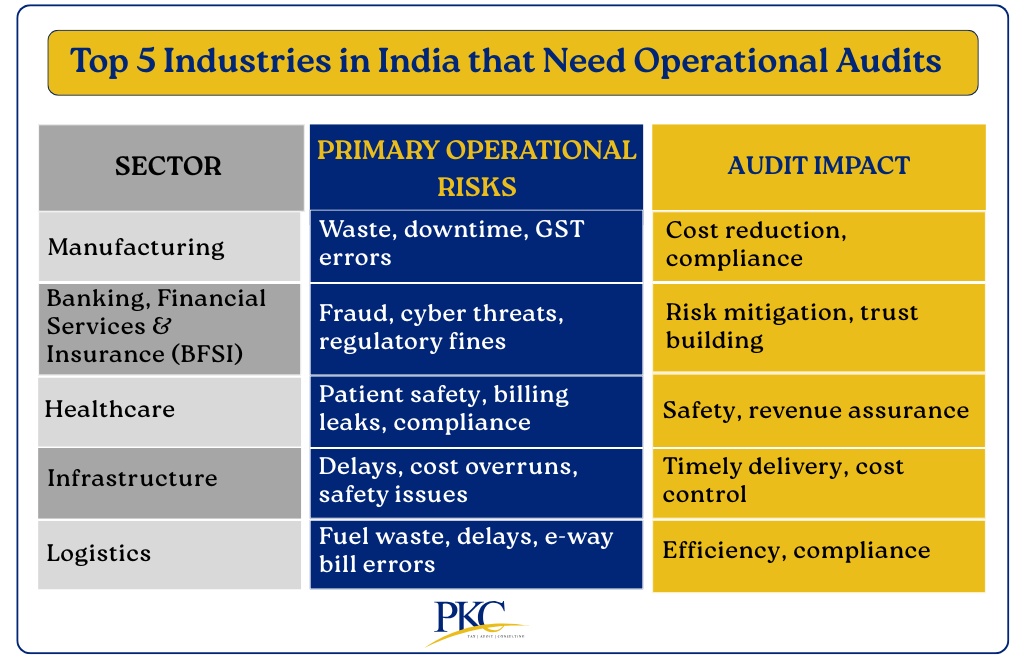
Business Sectors in India That Need Operational Audits Most
Although all kinds of industries can benefit from an operations audit, here are key sectors that need them the most.
They face complex, high-impact operational challenges where audits deliver significant value:
Manufacturing (Especially MSMEs):
Have a high exposure to supply chain disruptions, waste, energy inefficiency, quality lapses, and complex GST/tax compliance.
Key Focus Areas:
- Raw material inventory & wastage tracking
- Machine downtime & maintenance efficiency
- Energy/fuel consumption optimization
- GST input credit reconciliation
- Quality control adherence
Banking & Financial Services (BFSI):
Strict RBI/SEBI regulations, high fraud risk (loans, KYC), cybersecurity threats, and NPA (bad loan) management pressures.
Key Focus Areas:
- Loan appraisal processes & NPA management
- KYC/AML compliance workflows
- Digital transaction security protocols
- TDS/TCS deduction accuracy
- Branch service efficiency
Retail & E-Commerce:
Thin margins, inventory shrinkage (theft/damage), complex logistics, high return rates, and multi-channel sales challenges.
Key Focus Areas:
- Stock reconciliation & shrinkage analysis
- Warehouse layout & space utilization
- Last-mile delivery cost optimization
- GST e-way bill compliance
- Returns management efficiency
Healthcare (Hospitals, Pharma, Diagnostics):
Critical patient safety risks, drug inventory expiry, billing inaccuracies, NABH/regulatory compliance, and medical equipment downtime.
Key Focus Areas:
- Medicine inventory expiry tracking
- Patient billing & revenue leakage points
- Medical equipment maintenance logs
- Infection control protocol adherence
- Data privacy (DPDP Act) compliance
Information Technology (IT) & IT-Enabled Services (ITES):
Project cost/time overruns, resource underutilization, data security risks (DPDP Act), SLA breaches, and remote work challenges.
Key Focus Areas:
- Project resource utilization & burn rates
- Cybersecurity controls & incident response
- SLA (service level agreement) compliance
- Employee billable/non-billable hours
- Cloud infrastructure cost leaks
Infrastructure & Construction:
Chronic project delays, cost overruns, safety violations, subcontractor mismanagement, and material pilferage.
Key Focus Areas:
- Project progress vs. deadlines
- Material procurement & wastage control
- Subcontractor payment compliance
- Safety protocol enforcement
- Labour regulation (wages/PF/ESI) adherence
Logistics & Supply Chain:
Fuel inefficiency, fleet underutilization, shipment delays, warehouse management flaws, and GST e-way bill compliance risks.
Key Focus Areas:
- Route optimization & fleet utilization
- Fuel consumption patterns
- Warehouse throughput efficiency
- GST e-way bill/documentation accuracy
- Vendor performance management
Agriculture & Food Processing:
Post-harvest losses (up to 40% in India), supply chain gaps, FSSAI compliance, adulteration risks, and MSP/procurement inefficiencies.
Example: An audit at a Punjab rice mill identified outdated drying techniques causing 12% spoilage. Modern dryers cut losses and increased farmer payments.
Key Focus Areas:
- Cold chain management & spoilage rates
- FSSAI hygiene & licensing compliance
- MSP procurement efficiency
- Warehouse storage conditions
- Farmer payment transparency
Step By Step Business Operations Audit Process in India
Here’s how a business operations audit is conducted:
Step 1: Define the Audit Objectives
Begin by clearly identifying the purpose of the audit.
Objectives may include improving operational efficiency, ensuring compliance with Indian regulations, identifying cost-saving opportunities, or streamlining workflows.
Establishing clear goals helps guide the scope and focus of the audit.
Step 2: Collect Internal Data
Gather all relevant internal documents such as process manuals, financial records, SOPs, employee handbooks, and previous audit reports.
This data serves as a foundation for understanding how the business currently operates and whether it aligns with internal policies and legal standards in India.
Step 3: Interview Key Stakeholders
Engage with team members across departments—operations, finance, HR, compliance, and others—to gain first-hand insights.
These interviews help identify practical challenges, uncover inefficiencies, and understand employee perspectives on current processes.
Step 4: Map Out Current Processes
Visually document business workflows and processes using flowcharts or diagrams.
This mapping allows auditors to see how each process works, where responsibilities lie, and how different departments interact.
It also helps highlight redundancies or bottlenecks.
Step 5: Measure Performance With KPIs
Compare actual performance with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as turnaround time, error rates, cost per unit, or customer satisfaction.
This step quantifies how well each business area is functioning and identifies areas needing improvement.
Step 6: Identify Gaps & Risks
Analyze the data to pinpoint operational gaps, compliance issues, or risks such as fraud, process delays, or policy violations.
This includes assessing risks specific to the Indian business environment, such as taxation issues, labour law non-compliance, or industry-specific licensing gaps.
Step 7: Create an Improvement Action Plan
Based on the findings, develop a clear and actionable plan.
This should include recommendations, resource allocation, deadlines, and responsible personnel.
Prioritise tasks based on urgency and impact, ensuring compliance with Indian laws and best business practices.
Step 8: Share the Audit Report with Stakeholders
Prepare a detailed yet easy-to-understand audit report and present it to key decision-makers—owners, directors, or department heads.
The report should highlight findings, risks, recommendations, and the proposed action plan.
Step 9: Follow-Up & Monitor Progress
Conduct regular follow-ups to ensure that recommended actions are being implemented.
Track progress through updated KPIs and periodic reviews.
This ongoing monitoring helps sustain improvements and ensures accountability.
Sample Business Operational Audit Checklist
Here’s how a business operational audit checklist should look like:
Who Should Perform a Business Operations Audit in India?
A business operations audit needs to be done in the most efficient ways to get the maximum benefit.
Here’s a look at the best options:
Internal vs. External Auditors
Internal Auditors:
- Provide continuous monitoring and deep organizational knowledge
- Cost-effective for ongoing assessments
- May lack objectivity due to internal relationships
External Auditors:
- Offer independent, unbiased perspectives
- Bring cross-industry expertise and best practices
- Ensure regulatory compliance and stakeholder confidence
Role of Chartered Accountants and Consulting Firms
CAs form the backbone of business operational audits, combining financial expertise with operational insights. Consulting firms add strategic value through:
- Process optimization methodologies
- Technology integration assessment
- Risk management frameworks
- Industry-specific solutions
Credentials to Look for When Choosing an Audit Partner:
- Professional qualifications: CA, CMA, CIA certifications
- Regulatory expertise: GST, Companies Act, labor law compliance
- Industry experience across multiple sectors
- Technology proficiency in ERP systems and digital processes
Why Choose PKC Management Consulting?
Established 1988 with 1,500+ clients, PKC combines:
- Holistic approach: Business + finance + compliance integration
- Proven results: Enhanced efficiency, risk management, cost reduction
- Multi-industry expertise: Manufacturing, retail, healthcare, IT/ITES
- Risk-based auditing: Identifies critical operational risks proactively
- Process optimization: Streamlines operations and reduces costs
- Value-driven outcomes: Actionable insights beyond traditional compliance
At PKC, we deliver independent, comprehensive operational audits that drive operational excellence while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Reach Out to Us For a Customized Audit Plan
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a business operations audit?
A business operations audit is a full review of how your business runs beyond finances.It checks your systems, people, tools, and daily operations.
2. Is a business operations audit mandatory in India?
It is not always mandatory, but it’s often required under GST, Companies Act, or for investor-backed businesses. Even when not required, it’s highly recommended for efficiency.
4. Who conducts business operations audits in India?
Usually external consultants, CA firms like PKC Management Consulting, or internal audit teams with expertise conduct these audits. For small businesses, even independent professionals can do it.
5. Will business operations audits disrupt daily work?
No, most audits run in the background and involve short interviews. Experienced audit firms like PKC Management Consulting ensure that there are minimal disruptions.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

