Adopting the right business process reengineering methodology can help businesses be faster, smarter, and more customer-focused.
Delve with us into business process reengineering steps with examples so that you can implement BPR efficiently.
Understanding Business Process Reengineering & Its Core Principles
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is an approach that focuses on rethinking and redesign of core business processes.
It requires rethinking outdated workflows, eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing handoffs, and leveraging digital tools to create more efficient and value-driven processes.
The goal is to achieve significant improvements in performance metrics such as cost, quality, speed, service, and customer satisfaction.
The main difference between BPR and approaches like continuous improvement is that BPR takes a “clean slate” approach. It starts from scratch to completely rethink how work should be done in today’s context, using modern technologies and customer-focused thinking.
Examples:
- A manufacturing company using AI and IoT to revamp its supply chain and minimize delays.
- A government department digitizing legacy processes using platforms like DigiLocker for faster public service delivery.
- An IT services firm restructuring its project delivery model to halve turnaround time through automation and streamlined collaboration.
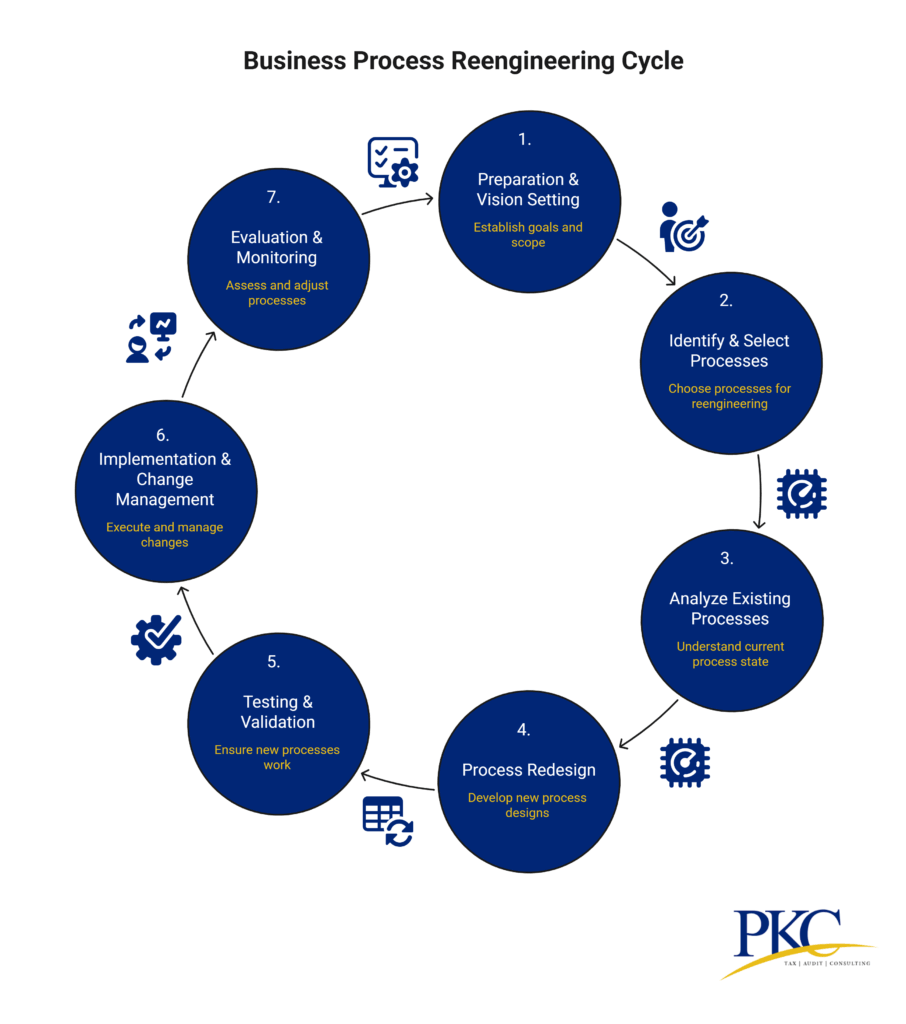
Step-by-Step BPR Methodology: Implementation Phases & Approach
BPR needs a well throughout approach to ensure dramatic performance improvement. Here’s a breakdown of the seven key phases of the BPR methodology:
Phase 1: Preparation & Vision Setting
The main objective of this stage is to establish the foundation for successful BPR by aligning leadership, setting clear goals, and preparing the organization.
Key Activities:
- Secure executive sponsorship and leadership alignment
- Define the strategic vision and goals for the BPR initiative
- Form a cross-functional team with stakeholders from key departments
- Allocate resources: budget, technology, personnel.
- Develop a communication plan to engage all levels of the organization.
Deliverables:
- BPR charter and project plan
- Vision and mission statements
- Defined objectives and KPIs
- Team structure and communication roadmap
Success Factors:
- Strong leadership and commitment
- Clear communication and realistic expectations
- Cross-functional collaboration
Phase 2: Identify & Select Processes for Reengineering
Determines which processes offer the highest value for reengineering based on performance impact and strategic alignment.
Key Activities:
- Create a process inventory across departments.
- Use impact assessment criteria (customer value, cost, cycle time)
- Apply a prioritization matrix or scoring model.
- Conduct feasibility analysis and risk assessments
- Define process boundaries, inputs, and key stakeholders.
Deliverables:
- Prioritized process list
- Scope definitions and feasibility reports
- Risk and impact assessment reports
Success Factors:
- Data-driven decision-making
- Balanced process selection (high impact, feasible implementation)
- Clear ownership and accountability
Phase 3: Analyze Existing Processes
Deeply understand current-state processes to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and performance gaps.
Key Activities:
- Create detailed “as-is” process maps
- Collect baseline data on KPIs: cycle time, costs, error rates, satisfaction
- Conduct root cause analysis (e.g., 5 Whys, fishbone diagram)
- Evaluate technology usage and limitations
- Perform benchmarking against industry best practices.
Deliverables:
- Current-state process documentation
- Performance baseline and KPI dashboards
- Root cause and gap analysis reports
- Technology assessment
Success Factors:
- Honest, accurate documentation
- Engaged stakeholders providing frontline insights
- Benchmarking for objective performance comparison
Phase 4: Process Redesign
Develops future-state processes that eliminate waste, reduce complexity, and maximize value.
Key Activities:
- Apply clean slate thinking: ignore legacy constraints
- Design innovative workflows focusing on:
- Customer-centric outcomes
- Technology integration (e.g., automation, AI)
- Streamlined approvals and fewer handoffs
- Create “to-be” process models and validate feasibility
- Conduct gap analysis to define what’s needed for implementation
Deliverables:
- Redesigned process maps
- Technology requirements
- Improvement projections
- Implementation gap report
Success Factors:
- Bold, innovative thinking
- User involvement and validation
- Focus on measurable performance improvements
Phase 5: Testing & Validation
Test redesigned processes in a controlled environment to validate performance and resolve issues before full-scale rollout.
Key Activities:
- Design and execute a pilot program
- Monitor KPIs and track pilot performance
- Collect user feedback and document issues
- Adjust the process and technology as needed
- Finalize validation with a go/no-go decision
Deliverables:
- Pilot test results and performance data
- Issue logs and resolution actions
- Updated process models
- Validation report and rollout readiness assessment
Success Factors:
- Realistic pilot scenarios
- Structured testing and feedback loops
- Agility in refining the process
Phase 6: Implementation & Change Management
Deploy redesigned processes organization-wide and manage the people’s side of change to ensure adoption and success.
Key Activities:
- Create a detailed implementation roadmap
- Launch communication campaigns to build buy-in
- Provide training programs for all affected roles
- Roll out processes using a phased or big-bang approach
- Set up support systems like help desks and process champions.
Deliverables:
- Implementation and communication plans
- Training curriculum and execution
- New systems and process deployment
- Change readiness and adoption metrics
Success Factors:
- Strong change leadership
- Effective training and support
- Transparent, two-way communication
Phase 7: Evaluation & Monitoring
Track the long-term impact of BPR and establish a framework for continuous improvement and process governance.
Key Activities:
- Monitor performance metrics post-implementation
- Calculate ROI and benefit realization (e.g., cost savings, time reduction).
- Implement continuous improvement cycles and governance
- Capture lessons learned and share knowledge organization-wide
- Identify new opportunities for future BPR efforts
Deliverables:
- Performance evaluation reports
- ROI and benefit realization summary
- Governance and sustainability plan
- Continuous improvement framework
- Lessons learned documentation
Success Factors:
- Ongoing performance tracking
- Culture of continuous improvement
- Shared learning and process ownership
Example of Implementing BPR: Step By Step
Let’s take an example of a company – Gamma Manufacturing, a mid-sized industrial equipment producer.
Problem:
- Order fulfillment averaged 45 days (vs. 15-day industry standard)
- 30% of orders had errors; customer satisfaction was 58/100
- Manual processes led to high rework and operational costs
BPR Goal: Cut order-to-cash (O2C) cycle time by 70%, reduce errors < 2%, and raise customer satisfaction to 90+ within 12 months.
Phase 1: Preparation & Planning
- CEO forms a BPR Steering Committee.
- O2C process scoped
- Targets:
- 45→14 days cycle time
- 30%→<2% error rate
- 58→90+ satisfaction
- Cross-functional team formed
Phase 2: Process Selection for BPR
- Mapped 5 key processes
- O2C prioritized:
- High customer impact (complaints).
- Strategic importance (cash flow delays).
- Severe inefficiencies (manual handoffs between 6 departments).
Phase 3: As-Is Analysis
- Found 34 steps in the process, 12 handoffs, 4 approval layers, redundant data entry.
- Root issues:
- slow credit checks
- manual order entry
- no real-time inventory
- delayed invoicing
Phase 4: To-Be Redesign: Radical Changes
- Instant credit checks via CRM integration
- Self-service customer portal → ERP automation
- Real-time production scheduling using IoT + AI
- Auto-invoicing triggered by shipping
- O2C Process Owners empowered
- Flow simplified to: 34 steps → 5, handoffs: 12 → 2
Phase 5: Testing & Validation
- Ran new process for 10% of customers (key accounts)
- Testing Focus:
- Tech Integration (ERP-CRM-EDI links)
- User Training (sales team on portal)
- Stress Testing (peak order volumes)
- Refinements:
- Simplified invoice dispute button
- Added chatbot for customer queries
Phase 6: Implementation
- Rolled out in phases over 3 months.
- Change Management tactics:
- Workshops
- gamified training
- Incentives
- help desk support
- Tech: Cloud ERP, EDI, customer portal
Phase 7: Results (6 Months)
| Metric | Before BPR | After BPR | Improvement |
| Cycle Time | 45 days | 12 days | ↓ 73% |
| Order Error Rate | 30% | 1.5% | ↓ 95% |
| Customer Sat. | 58/100 | 92/100 | ↑ 59% |
| Operational Cost | $1M/year | $400K/year | ↓ 60% |
Ongoing: Monthly KPIs, AI anomaly alerts, feedback loops.
How Can PKC Assist With BPR Initiatives?
✅ 37 years experience delivering transformation across industries
✅ Radical redesign achieves 90% systematic organizational improvement
✅ Manufacturing, retail, textile industry specialized BPR expertise
✅ Structured requirement gathering prevents costly implementation delays
✅ Real-time MIS reporting enables data-driven decision making
✅ Production time reduction with fabric cost savings
✅ Rigorous implementation methodology delivers measurable business benefits
✅ Process automation reduces people-dependency and increases efficiency
✅ Working capital optimization through streamlined operational workflows
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Business Process Reengineering methodology in India?
It’s a structured approach where companies completely redesign their core processes to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Unlike minor changes, it focuses on radical transformation using modern technology.
2. How does BPR differ from other process improvement methods?
BPR involves starting from scratch, while methods like Kaizen or TQM focus on gradual improvements. It’s more disruptive but can deliver faster, bigger results.
3. What industries in India use BPR the most?
BPR is common in banking, manufacturing, IT services, logistics, and government initiatives. Digital India projects have also applied BPR principles for public services.
4. What are the main challenges of BPR implementation in India?
Common issues include resistance to change, skill gaps, and upfront costs. Strong leadership and training help overcome these barriers.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

