BPR in supply chain management is changing how companies are making their complex, diverse, and often slow supply chains more efficient.
Explore with us how BPR works for SCM , its benefits, and how to implement it. We also share a real world example of how a major Indian company used BPR in SCM to its advantage.
What is BPR in Supply Chain Management?
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) in Supply Chain Management (SCM) refers to the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of supply chain processes.
The main aim is to achieve dramatic improvements in performance including cost reduction, improved delivery speed, higher service levels, and increased flexibility.
When compared to traditional process improvement that rely on small tweaks, BPR involves the complete revamp of the supply chain using the latest technology and best practices.
Industries that Benefit most from BPR in SCM
- Manufacturing: High logistics costs and delays hinder manufacturing. BPR streamlines planning, sourcing, and delivery. Example: Tata Steel reengineered its supply chain to integrate suppliers, plants, and distributors for faster deliveries.
- Retail & E-Commerce: Fast delivery is key for platforms like Flipkart and Amazon. BPR improves warehouse layout, inventory tracking, and delivery speed.
- FMCG: Short shelf lives demand speed and precision. BPR aids forecasting, stock management, and distribution.Example: Hindustan Unilever uses digital supply chain platforms to serve rural and urban markets efficiently.
- Pharma & Healthcare: Timely and temperature-controlled deliveries are critical. BPR enables inventory tracking and faster response to demand.
- Automotive: Complex supply chains need coordination. BPR integrates procurement and scheduling to cut delays. Example: Companies like Mahindra & Mahindra have optimized vendor coordination through process reengineering.
- Logistics & Transportation: BPR in logistics focuses on route optimization, real-time tracking, and load management. Third-party logistics (3PL) companies in India use BPR to reduce transit times and fuel costs.
Key SCM Processes That Benefit Most from BPR
| SCM Process | BPR Transformation |
| Procurement | E-sourcing, vendor portals, real-time supplier collaboration |
| Order Fulfillment | Automated warehouses, robotics, route optimization |
| Inventory Management | Demand-driven planning, JIT models, VMI |
| Distribution & Logistics | 3PL integration, GPS tracking, control towers |
| Reverse Logistics | Efficient return workflows, recycling, and reuse programs |
| Demand Planning | Predictive analytics, real-time market sensing |
Role of BPR in Supply Chain Management
Managing supply chains presents unique challenges and opportunities, especially in India. BPR services can help by:
1. Streamlining End-to-End Operations
- Identifies and eliminates redundant steps that slow down movement of goods and information.
- Enables smoother workflows across procurement, manufacturing, inventory, and distribution
- Promotes lean operations by reducing manual processes and cycle times.
2. Reducing Costs Through Process Optimization
- Targets key cost drivers such as overstocking, transportation delays, and warehousing inefficiencies.
- Uses automation, ERP systems, and AI to reduce labour-intensive tasks and human errors.
- Supports Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory models to lower holding costs.
3. Enhancing Customer Service
- Improves order accuracy and speeds up fulfillment times
- Enables real-time tracking and greater transparency, enhancing customer trust
- Reorients supply chain processes around customer needs and expectations
4. Digitizing Traditional Supply Chains & Driving Innovation
- Enables integration of ERP, SCM platforms, and cloud-based solutions for real-time visibility and control
- Supports shift from reactive to proactive supply chain management.
- Leverages the India Stack (e.g., UPI, DigiLocker, GSTN) for streamlined documentation, payments, and compliance.
5. Supporting Strategic and Data-Driven Decisions
- Generates cleaner, integrated data that supports accurate forecasting, demand planning, and risk mitigation.
- Enables faster, more informed decisions through real-time insights and dashboard analytics.
- Improves scenario planning and resilience.
6. Enabling Collaboration Across Organisation
- Fosters collaboration across departments such as sales, procurement, production, and logistics.
- Aligns internal teams and external partners around shared goals and performance metrics.
- Promotes cross-functional integration for a seamless supply chain experience.
7. Improving Scalability and Business Growth
- Redesigns processes that can scale with expansion into new markets, product lines, or geographies.
- Supports standardization, enabling consistent performance across multiple business units.
8. Simplifying Regulatory Compliance
- Reengineers processes to comply with complex regulations like GST, e-way bills, and interstate logistics rules.
- Automates order-to-cash and procure-to-pay processes to reduce compliance delays and penalties.
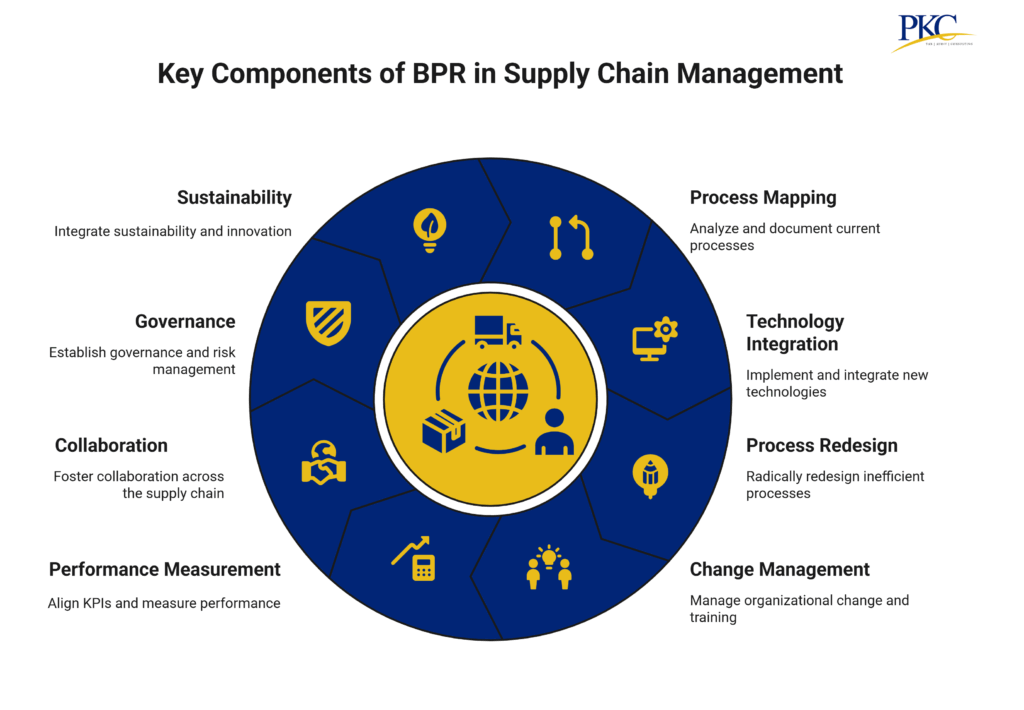
Key Components of BPR in Supply Chain
Successful BPR initiatives especially in India must address both universal supply chain principles and country and region specific issues.
Here are the key components to focus on:
1. Comprehensive Process Mapping and Analysis
The first step in BPR is identifying and documenting every process across the supply chain, from procurement to transportation and last-mile delivery.
Indian supply chains often operate across multiple states, involve cash-on-delivery models, and deal with a mix of organized and unorganized players.
Analysis must consider:
- Multi-layered approvals and manual paperwork still common in Indian operations
- Bottlenecks caused by differing inter-state tax procedures, despite GST
- Reliance on physical documents and fragmented communication across regions
2. Technology Enablement & Integration
Technology adoption and utilisation is central to BPR success.
Supply chains are increasingly adopting ERP platforms, AI-based forecasting tools, and real-time tracking to overcome traditional manual workflows and limited visibility.
Includes:
- ERP systems that unify procurement, finance, logistics, and compliance functions under a single, GST-ready platform.
- IoT sensors and mobile apps that provide real-time shipment data across India’s varied geographies, including rural and remote areas.
- AI and machine learning tools to optimize inventory levels and forecast demand in fast-changing markets.
3. Radical Process Redesign
BPR reimagines existing workflows completely.
For some businesses, this may mean bypassing traditional middlemen, automating GST filing, or shifting to digital proof-of-delivery systems.
Key Changes:
- Removing redundant approval layers in procurement and order fulfillment.
- Automating customs clearance and compliance processes tied to GST and e-way bills.
- Replacing manual ledgers with cloud-based inventory and warehouse management tools.
4. Change Management and Training
This involves preparing the organization, its people, structure, and culture, for a successful transition to reengineered processes.
This is of particular importance in India where supply chain operations often involve a multilingual, semi-skilled, or regionally dispersed workforce.
Involves:
- Executive leadership driving change across departments and locations.
- Multilingual, hands-on training programs tailored to tech adoption in warehouses and logistics hubs.
- Upskilling teams to handle digital platforms and automation tools while addressing concerns about job loss.
5. Performance Measurement & KPI Alignment
Once processes are redesigned, organizations must define success using measurable KPIs.
This also means balancing operational efficiency with regulatory compliance and customer satisfaction.
Examples of KPIs that can be measured include:
| Category | KPI Examples |
| Cost Efficiency | Logistics cost as % of sales, warehouse cost per unit, order fulfillment cost |
| Speed & Agility | Order cycle time, delivery lead time, vehicle turnaround time |
| Service Quality | On-Time In-Full (OTIF) delivery rate, order accuracy, return handling time |
| Regulatory Compliance | GST filing timeliness, e-way bill error rate, document processing time |
| Visibility & Data | % of shipments tracked in real time, data accuracy rate, inventory turnover |
6. Collaboration Across the Supply Chain
For BPR to succeed, collaboration must be embedded in every step, especially where supply chains are long, layered, and involve many informal partners.
Includes:
- Digitally linking suppliers, transporters, and distributors through shared platforms.
- Formalizing relationships with small transporters and local vendors using contracts, UPI payments, and e-invoicing.
- Implementing CPFR (Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment) models to streamline stock management and reduce overstocking or stockouts.
7. Governance, Risk Management, and Implementation Strategy
Effective BPR execution requires structured governance and phased implementation. This becomes more critical given the diversity across regions and changing nature of regulatory requirements.
Best practices:
- Piloting redesigned processes in selected regions or business units before full rollout.
- Embedding regulatory tools (e.g., automated GST filing, e-way bill validation) within the new processes.
- Establishing cross-functional governance teams with clear accountability and escalation mechanisms.
8. Sustainability and Innovation
As global and domestic regulations push for greener operations, supply chains are integrating sustainability directly into their BPR strategies.
Covers:
- Electric vehicle fleets for last-mile delivery and optimized routing to cut emissions.
- Digital documentation to minimize paper usage and manual intervention.
- Circular supply chain practices such as returns reuse, waste reduction, and eco-friendly packaging.
Steps to Implement BPR in Indian Supply Chains
Implementing BPR in the Indian supply chain needs to be done in a planned step by step manner.
Here’s the approach you can take for your business:
Step 1: Laying the Foundation
Start by broadly assessing the current supply chain performance. Based on that, set a bold yet clear objective for change. Eg.: achieving next-day delivery.
Key Tasks:
- Secure strong top-management support
- Assemble a cross functional BPR team with members from logistics, procurement, finance, IT, and operations.
- Select target supply chain process. Prioritize processes with high pain points, strategic impact, or high compliance burden.
- Set measurable KPIs like order cycle time, cost per delivery, etc.
Step 2: Analyze Existing Supply Chain Processes
Document each stage of the process: procurement, production, warehousing, transportation, and distribution, in the “as-is” state.
Use tools and techniques like process flow diagrams, value stream mapping, Value-Added Analysis, bottleneck analysis to analyse and identify root cause of inefficiencies.
Capture pain points like:
- Manual approval loops
- Delays due to GST paperwork
- Poor inter-system integration
- Inefficient routing due to infra constraints
Step 3: Envision & Redesign Supply Chain Process
Redesign the supply chain processes from scratch to eliminate inefficiencies, not just patch existing ones.
This may mean automating tax documentation, digitizing partner interactions, and enabling faster decision-making across distributed teams.
Key Points:
- Challenge every assumption like “Why 7 signatures are needed for approval?”
- Design processes around ERP/WMS/TMS, IoT tracking, AI forecasting, India Stack (GSTN, UPI, eSign).
- Automate compliance including GST invoicing, e-way bills, reporting within the flow.
- Create vendor/transporter portals, standardize interfaces for small partners.
- Replace manual tasks with automation in warehouse management, approvals invoicing, and reporting.
- Design for real-time tracking & data sharing across partners
- Quantify impact of BPR initiatives like projected savings, revenue impact. risk reduction.
- Develop a detailed rollout plan with phases, timelines, resources, budget, risk mitigation.
Step 4: Pilot Testing
Implement the redesigned process in a limited scope. This may mean a particular region, product category, or warehouse.
Example: A logistics firm could test RFID-based tracking or AI-powered route optimization in a metro before extending it to Tier-2/3 cities.
Monitor KPIs closely, gather user feedback, identify glitches, especially compliance or tech integration issues, refine design & training.
Step 5: Change Management and Training
Traditional businesses may face high resistance to change, particularly among frontline employees and middle management.
A strong communication strategy can ease this transition.
Actions:
- Share the “why” of BPR across the organization.
- Conduct multilingual training sessions for warehouse staff, drivers, and field agents.
- Offer simulations and digital literacy programs to ease technology adoption.
- Train employees on new systems (e.g., ERP, WMS, TMS)
- Help vendors or transporters use portals for order tracking and payment status.
Step 6: Full-Scale Implementation
Roll out the redesigned process in stages, state by state, or business unit by business unit, to accommodate infrastructure variation, bandwidth limitations, and regional compliance norms.
Ensure seamless integration with upstream/downstream processes. Maintain a close watch and track defined KPIs religiously against baseline and targets.
Best Practices:
- Maintain parallel systems briefly to ensure business continuity.
- Use dashboards for real-time KPI tracking .
Step 7: Monitoring, Optimization & Continuous Improvement
Now that the new system is live, track performance rigorously against baseline metrics. Focus on:
- On-time in-full (OTIF) delivery
- Reduction in logistics cost per unit
- GST filing accuracy and documentation speed
Create structured feedback loops from field staff, warehouse operators, and transporters to continuously tweak and improve operations.
Mechanisms:
- Weekly review meetings
- Real-time feedback via mobile reporting tools
- Regular customer and vendor satisfaction checks
Challenges of BPR in Supply Chain Management in India
Implementing BPR in Indian supply chains often faces significant challenges which include:
1. Resistance to Change: Deep-rooted reliance on legacy systems, fear of job losses, and lack of change management hinder adoption. Traditional, family-run businesses often resist process innovation.
2. Siloed Operations: Departments operate in isolation, obstructing cross-functional collaboration critical for BPR. Poor data integration reduces visibility and slows decision-making.
3. Outdated IT Infrastructure: Many companies still use legacy or paper-based systems. Integration with modern platforms like GSTN or digital payments is often limited, especially in rural areas.
4. High Implementation Costs: BPR demands heavy investments in technology, training, and consulting. SMEs struggle to justify costs without clear ROI or external support.
5. Infrastructure Gaps: Weak transport networks, limited cold chains, and patchy internet access in remote areas disrupt supply chain reliability and digital integration.
6. Regulatory Complexity: Frequent policy changes and inter-state compliance hurdles increase operational risks. Manual documentation further complicates audits and reporting.
7. Talent and Skill Shortages: There’s a scarcity of professionals with BPR and digital expertise. Low digital literacy among frontline workers hampers tech adoption.
8. Vendor Misalignment: MSMEs and informal vendors often lack the resources or systems to align with reengineered processes, leading to inefficiencies and inconsistency.
9. Strategic Execution Gaps: Unrealistic scopes, lack of pilot scalability, and pressure for quick wins often derail BPR initiatives before they mature.
Mitigation Strategies to Battle Supply Chain BPR Implementation Challenges
| Challenge | Solutions |
| Cultural Resistance | Top-down leadership advocacy; early inclusion of employees in redesign; upskilling programs |
| Legacy Systems | Phased tech modernization; API-led integration with India Stack |
| Partner Fragmentation | Simplify interfaces (SMS/mobile apps for transporters); collaborative training. |
| Infrastructure Gaps | Hybrid models (e.g., digital + manual fallbacks); hub-and-spoke networks |
| Regulatory Uncertainty | Dedicated compliance cell; agile process design with modular updates. |
Example of BPR in SCM: Flipkart’s Big Supply Chain Makeover
Here’s a real-world example of BPR in Supply Chain Management, for e-commerce company Flipkart.
Challenges Before Reengineering (Early 2010s)
- One big warehouse where all orders came from, caused slow deliveries 5 to 7 days.
- Delivering to smaller cities was very expensive
- Majority orders were Cash on Delivery (COD), leading to cash flow and fraud issues.
- Reliance on third-party logistics with poor tracking and high damages.
- Peak sales events caused system crashes, order losses and bad customer feedback.
Major BPR Interventions
Distributed Fulfillment Network
- Shifted to “Mother Hub + Delivery Stations” near demand centers
- AI-driven inventory forecasting to position stock closer to customers.
- Result: Delivery time cut to under 2 days, approx 30% reduction in last-mile costs
Digital Payment and Cash Flow Innovations
- Introduced Flipkart Wallet and Card-on-Delivery to reduce COD.
- Drivers used devices for real-time COD reconciliation.
- Result: COD dependency reportedly reduced significantly, working capital cycle shortened by approx 40%.
Automation & Robotics
- AI-powered sortation centers sorting 4,500 parcels/hour (vs. 600 manually).
- Robots improved picking accuracy; error rate under 0.1%.
Kirana Store Partnerships for Last-Mile Delivery
- 50,000+ kirana stores onboarded with dedicated app for pickups/payments.
- Coverage extended to about 99% of pin codes.
- Rural delivery costs lowered by nearly 25%.
Data-Driven Dynamic Routing
- AI optimized delivery routes considering traffic, weather, vehicle locations.
- IoT sensors enabled live tracking.
- Result: Estimated fuel consumption reduction of approx 18%, on-time delivery rates reportedly above 95%.
BPR in SCM Results Summary
| Metric | Before | After | Improvement |
| Delivery Time | 5-7 days | 1-2 days | 70% faster |
| COD | Over 70% | Below 30% | 40% reduction |
| Peak Orders Capacity | 500,000 orders/day | > 8 million/day | 16X bigger |
| Delivery Cost | ₹120 per order | ₹80-90 per order | 25% cheaper |
| Reach | 500 cities | 20,000+ pin codes | 40X wider |
Sources Include: Flipkart Tech Blogs, News Coverage (Business Standard, Inc 42, etc.)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is BPR in supply chain management?
BPR in supply chains means redesigning processes from scratch to make them faster, cheaper, and more efficient. It focuses on eliminating waste and improving overall performance.
2. How does BPR improve supply chain efficiency in India?
It removes unnecessary steps, digitizes processes, and integrates technology to speed up deliveries and reduce costs. It also helps overcome infrastructure and logistics challenges.
3. Which industries in India benefit most from BPR in supply chain management?
Manufacturing, retail, e-commerce, and FMCG sectors see the biggest gains. These industries rely on fast, accurate, and cost-effective supply chains.
4. Is BPR expensive to implement in India?
Yes, it can involve high upfront costs for technology and training. However, the long-term savings often outweigh the investment.
5. Does BPR in supply chains require new staff skills?
Yes, employees need training in new systems and workflows. In India, this often includes multilingual and digital literacy programs.

 Expert verified
Expert verified