Written By – PKC Desk, Edited By – Farith, Reviewed By – Sanjana
Tax planning vs tax advice, may seem names for the same kind of service, but they are different in many respects.
Let us help you understand the difference between tax planning and tax advice, helping you choose the right kind of services for your needs.
Tax Planning vs Tax Advice: Breaking Down the Differences
Here’s a quick look at the one on one comparison of the two approaches:
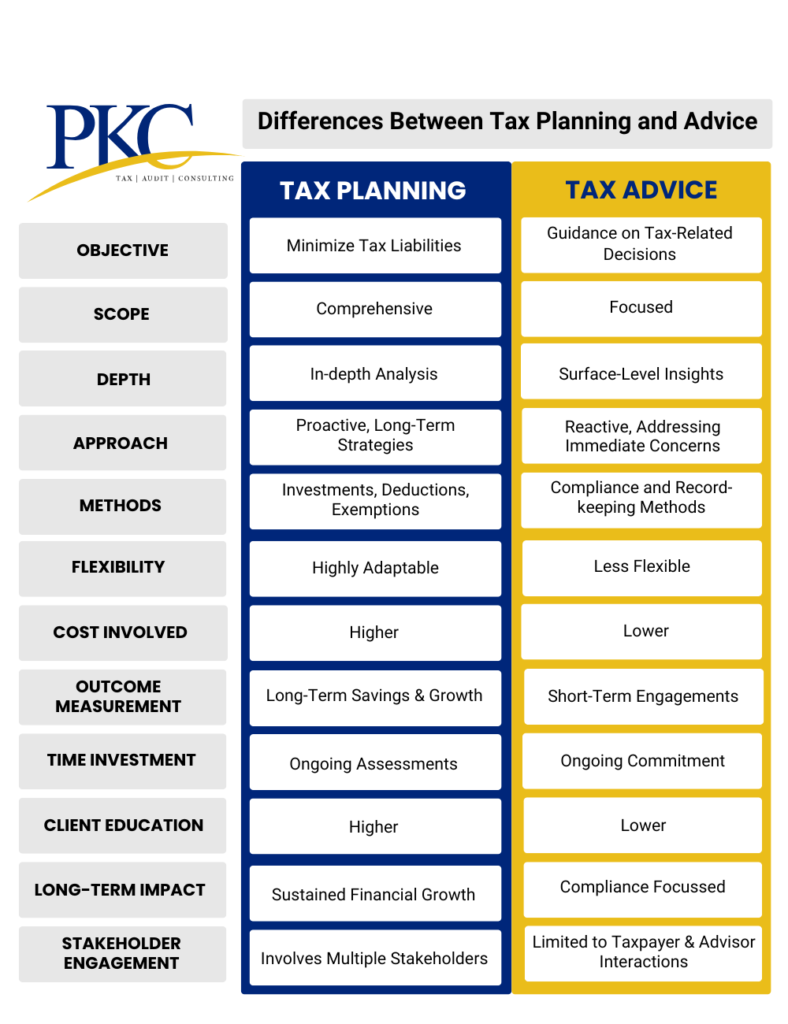
Objective Compared
The primary objective of tax planning is to minimize tax liabilities. This involves identifying deductions, exemptions, and investment opportunities that can reduce taxable income.
In contrast, tax advice focuses on providing guidance regarding specific tax-related queries. These can be related to ensuring compliance or helping clients navigate complex tax situations.
Scope Comparison
Tax planning has a much broader scope and can cover a broad range of financial activities, like investment strategies, retirement planning, and estate management, all aimed at optimizing tax outcomes.
It requires a comprehensive understanding of a client’s financial landscape.
Tax advice, however, has a more limited scope and generally focuses on immediate compliance issues.
They may be pertaining to issues like filing returns, claiming deductions, and addressing any notices or scrutiny from the tax authorities.
Depth Difference
Tax planning requires an in-depth analysis of an individual’s or a business’s finances, future goals, and potential tax liabilities over multiple years.
It is a holistic approach, where tax planners analyze various scenarios and projections to identify the most advantageous approaches for the taxpayer.
In contrast, tax advice tends to be more superficial, offering quick-fix solutions to immediate problems without delving deeply into long-term financial strategies.
Approach Analysis
Tax planning is proactive, forward-looking, and strategic. It involves planning investments, income sources, and expenditures in a way that aligns with both tax laws and the taxpayer’s financial objectives.
Tax advice, however, is reactive and problem-solving in nature. It focuses on resolving specific tax issues or complying with tax filing requirements based on the current financial situation.
Methods Used
In tax planning, methods include utilizing various deductions and exemptions available under Indian tax laws.
It uses a combination of financial forecasting, legal interpretation, and investment strategies, like utilizing Section 80C deductions, planning capital gains using sections 54F & 54, etc.
Tax advice, on the other hand, often involves providing legal interpretations of tax regulations, assisting with compliance documentation, and advising on procedural matters related to filing taxes or responding to audits.
Explore PKC’s Expert Tax Advisory Services
Flexibility of Each Approach
Tax planning is generally more flexible as it can adapt to changes in a client’s financial situation, changing tax laws, or market conditions.
It can be revised periodically as financial circumstances evolve, ensuring long-term tax efficiency.
Tax advice, in contrast, is generally less flexible because it addresses immediate, one-off issues that require resolution based on current tax laws and financial data.
Once the issue is resolved or a question answered, the engagement may conclude without further adjustments.
Costs Involved
The cost associated with tax planning can be higher due to its comprehensive nature and the ongoing relationship required between the planner and the client.
The taxpayer might have to take multiple consultations to develop a long-term tax-efficient strategy.
Tax advice, being more specific and short-term in nature, usually incurs a lower cost.
The cost is often of one-time consultations or specific services billed hourly or per engagement.
Outcome Measurement
The outcomes of tax planning are measured over a longer time horizon.
It is measured in terms of overall wealth accumulation, tax savings over multiple years, and alignment with financial goals.
On the other hand, the outcomes of tax advice are immediate and short-term, such as the successful filing of a tax return, a reduction in tax liabilities for the year, or resolving a tax-related issue.
Time Investment
Tax planning requires a significant investment of time, both initially and on an ongoing basis. It involves continuous monitoring of financial situations and tax law changes and regular consultations with professionals.
In comparison, tax advice usually involves shorter interactions focused on resolving specific queries or issues as they arise, leading to less overall time commitment from clients.
Client Education
Tax planning emphasizes educating clients about various strategies available for minimizing taxes and achieving their financial goals.
Planners work closely with clients and often educate clients about investment options, tax law changes, and financial management strategies.
Tax advice, in comparison, seldom provides some educational elements. It is more transactional and focuses on solving the immediate problem.
Long-Term Impact
Tax planning has a significant long-term impact as it shapes financial decisions over many years. Effective tax planning ensures sustained tax savings, risk mitigation, and wealth creation.
It contributes to achieving long-term financial goals with minimal tax leakage.
Tax advice, on the other hand, has a limited long-term impact as it deals primarily with immediate tax obligations and issues.
Its benefits are usually short-lived, providing relief for the current tax period.
Stakeholder Engagement
Tax planning often requires engagement with multiple stakeholders. It may involve family members or business partners who may be affected by financial decisions.
This collaborative approach ensures that all relevant parties are considered in important financial decisions.
Tax advice, being more limited in scope, generally involves fewer stakeholders. It’s usually limited to only the client unless the matter at hand has broader implications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Tax planning aims to minimize long-term tax liabilities through informed financial decisions. Tax advice focuses on providing guidance for specific tax-related queries and ensuring compliance.
Tax planning is proactive, anticipating future changes, while tax advice is reactive, addressing specific inquiries as they arise.
Choosing between tax planning and tax advisory services depends on your specific needs. If you seek to minimize long-term tax liabilities, tax planning is ideal. However, if you require ongoing guidance on tax compliance or tax related matters, then tax advisory services may be more beneficial.
Success in tax planning is measured by long-term savings, while tax advice focuses on immediate compliance outcomes.

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

