Written By – PKC Desk, Edited By – Farith, Reviewed By – Sanjana
For those with substantial wealth, maximizing tax benefits under Indian tax laws can be complex. This is where tax planning for high net worth individuals comes into picture.
Explore with us all you need to know about optimizing your tax position as an HNI, from tax saving strategies to common mistakes to avoid.
Objectives of Tax Saving Plan for High Net Worth Individuals in India
HNIs often have complex financial portfolios, multiple income sources, and large asset bases. This makes effective tax planning extremely important.
The main objectives of a tax-saving plan for HNIs include:
- Minimize Tax Liabilities: The core objective of any tax-saving plan is to legally minimize tax liabilities.
- Optimize Investment Returns: To ensure that the investment portfolio is structured in a tax-efficient manner while maximizing returns.
- Structure Income for Lower Tax Rates: Structuring various income sources in a way that minimizes the overall tax rate.
- Planning for Wealth Transfer and Succession: Ensuring efficient transfer of wealth to future generations with minimal tax implications.
- Reduce Global Tax Exposure: Minimize tax liabilities on global income, especially for HNIs with international investments or overseas businesses.
- Ensure Compliance: Avoiding penalties and legal issues by staying compliant with Indian and international tax laws.
- Wealth Preservation: Protect accumulated wealth from excessive taxation to preserve it for long-term goals such as retirement, legacy planning, or philanthropy.
Top Strategies for Effective Tax Planning for High Net Worth Individuals
In order to attain the objectives stated above, here are key strategies for effective tax planning essential for HNIs:
New vs. Old Tax Regime:
HNIs should evaluate both the old and new tax regimes to determine which offers greater benefits based on their income sources and deductions available.
Those with significant investments and expenses that qualify for deductions (like insurance, housing loans) may benefit more from the old regime.
Others with simpler income structures might prefer the lower tax rates under the new regime.
Investments in Tax-efficient Avenues:
HNIs can maximize tax efficiency by investing in instruments like Equity-Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), Public Provident Fund (PPF), and National Pension Scheme (NPS).
However, these are available only under the old regime.
They not only offer tax deductions (under Section 80C) but also enable tax-free or tax-deferred growth, making them ideal for long-term financial planning.
Alternative Investments:
High-net-worth individuals can diversify their portfolio with alternative investments to maximize tax advantage.
- Venture Capital Funds: Investments in eligible startups can yield tax benefits under Section 54GB, allowing HNIs to defer capital gains taxes.
- Municipal Bonds: These provide tax-free interest income, supporting local projects while achieving tax efficiency.
Tax-Free Government Bonds:
HNIs can invest in tax-free government bonds issued by the government of India.
The interest income from these bonds (although low) is entirely tax-exempt (after a 5 year lock-in period), making them a safe and efficient way to generate returns while minimizing tax liability.
Capital Gains Tax Optimization:
HNIs should carefully manage short-term and long-term capital gains to minimize tax outflow.
Long-term capital gains (LTCG) on equities and real estate offer lower tax rates and can be further optimized using indexation benefits in certain cases.
Reinvestment under Sections 54, 54F, and 54EC (residential house or specified government bonds) can also help defer or reduce capital gains tax.
Tax Loss Harvesting:
Capital losses from underperforming assets can be strategically harvested to offset capital gains through tax loss harvesting.
This reduces the overall taxable gains and allows HNIs to lower their tax burden.
Losses can also be carried forward for up to eight years to offset future gains.
Exemptions and Deductions:
Depending on the tax regime they chose, HNIs should explore all available exemptions under various sections of the Income Tax Act.
These could include such as those for home loan interest and medical expenses.
Retirement Planning:
Planning for retirement through tax-efficient investments like the National Pension Scheme (NPS) and other retirement funds ensures both tax savings and financial security.
Contributions to NPS offer additional deductions under Section 80CCD(1B) beyond the standard 80C limit, and the proceeds at retirement can be withdrawn in a tax-efficient manner.
However, make sure you check the interest rates before investing and see if they align with your goals.
Succession and Estate Planning:
To avoid high tax liabilities on wealth transfers, HNIs should have a well-structured succession plan.
Tools like wills, family trusts, and family arrangements can help ensure efficient asset distribution while minimizing inheritance or gift tax liabilities.
Leveraging HUF Structure:
Forming an HUF allows HNIs to pool income and assets under a separate legal entity.
HUFs are taxed separately, enabling families to claim additional tax benefits, including exemptions and deductions (chapter VI A) that help reduce the overall family tax liability.
Income Splitting and Gifting:
Transferring income-generating assets or making tax-free gifts to family members in lower tax brackets can reduce the overall family tax burden.
Under Indian tax law, gifts to relatives are not subject to tax, providing an opportunity for tax-efficient wealth distribution.
Strategic Charitable Donations:
Donations to registered charities under Section 80G can significantly reduce taxable income while fulfilling philanthropic goals.
HNIs can also set up their own charitable foundations or trusts, allowing for long-term tax benefits and structured philanthropy.
The benefit you can claim varies, for some donations you can claim only 50% of benefit.
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs):
HNIs with foreign income or international investments can utilize India’s DTAAs with other countries to avoid paying taxes twice on the same income.
This ensures that income is taxed only in one jurisdiction, helping to lower global tax exposure and optimize foreign investment returns.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Tax Planning for HNIs in India
Tax planning is essential for High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNIs) in India, but several common mistakes can hinder effective strategies. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Focusing Solely on Tax Savings
Making investment decisions purely for tax benefits without considering overall financial goals or risk tolerance can be counterproductive.
HNIs should balance tax efficiency with the overall investment strategy, ensuring that investments align with long-term financial and personal goals.
2. Not Reporting All Income Sources
Failing to disclose all income sources, including foreign assets, can result in penalties and scrutiny from tax authorities.
It’s crucial to report every income stream accurately while filing the ITR form.
3. Neglecting Long-Term Tax Planning
Another mistake is focusing on short-term tax savings without a comprehensive, long-term strategy.
HNIs should adopt a long-term tax planning approach that aligns with their financial goals. Proper estate planning, succession, and retirement strategies are critical for sustained tax efficiency.
4. Ignoring Need of Professional Advice
Many HNIs attempt to navigate tax planning independently, neglecting the value of professional guidance.
Tax laws are complex and constantly changing; consulting with tax advisors from top firms like PKC Management Consulting can provide personalized strategies that meet financial goals.
5. Misunderstanding Capital Gains Tax Rules
Incorrectly calculating or mismanaging capital gains tax, especially when selling properties, equities, or other assets can be another error.
Understand the differences between short-term and long-term capital gains tax rates.
Use indexation benefits where applicable and reinvest capital gains into qualifying assets to reduce tax liability.
6. Poor Record Keeping
Inadequate documentation of income, investments, donations, and expenses, lead to potential tax penalties or missed deductions.
Maintain detailed financial records and documentation of all income sources, charitable donations, and deductible expenses.
This ensures compliance and allows for accurate tax returns.
Frequently Asked Questions
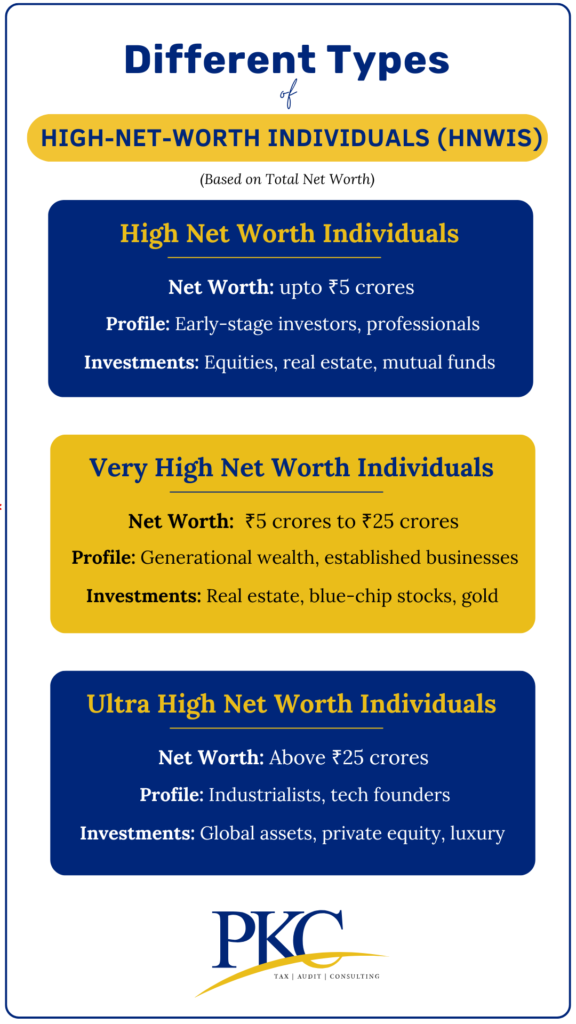
HNIs in India are typically defined as those with an annual income exceeding INR 50 lakhs or a net worth of over INR 5 crores. They often have significant investments and assets requiring specialized tax planning strategies.
HNIs face higher tax rates, including a base rate of 30%. Additionally, a 10% surcharge applies to incomes between INR 50 lakhs and INR 1 crore, while those earning above INR 1 crore incur a 15% surcharge on their tax liability.
HNIs can save on income tax by investing in tax-saving instruments such as Public Provident Fund (PPF), Equity-Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS), and tax-saving fixed deposits. They should also maximize deductions under Section 80C and other relevant sections of the Income Tax Act
Yes, seeking professional advice is crucial for HNIs due to the complexities of tax laws and regulations. Financial advisors can provide tailored strategies that align with individual financial goals, ensuring compliance while optimizing tax efficiency

 Expert verified
Expert verified 

